spring-cloud 分布式日志采集
由于微服务架构中每个服务可能分散在不同的服务器上,因此需要一套分布式日志的解决方案。spring-cloud提供了一个
用来trace服务的组件sleuth。它可以通过日志获得服务的依赖关系。基于sleuth,可以通过现有的日志工具实现分布式日志的采集。
这里使用的是ELK,也就是elasticsearch、logstash、kibana。
一、sleuth
第一步:sleuth管理端
sleuth一般单独放在一个工程中。需要添加如下依赖
io.zipkin.java
zipkin-autoconfigure-ui
runtime
io.zipkin.java
zipkin-server
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:1111/eureka/
package com.wlf.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import zipkin.server.EnableZipkinServer;
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableZipkinServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
第二步:被管理的微服务端
在我们的其他微服务端需要简单的配置,纳入到zipkin的管理之中
引入依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin
spring:
sleuth:
sampler:
percentage: 1
zipkin:
base-url: http://localhost:9411如果始终抓取日志的话对性能会有影响,因此可以自己配置。一般在开发环境,该值设置为1,生产环境视情况而定。
spring.zipkin.base-url:为第一步配置的zipkin管理端微服务的地址
现在分别启动服务注册中心,网关,需要的微服务,以及sleuth。
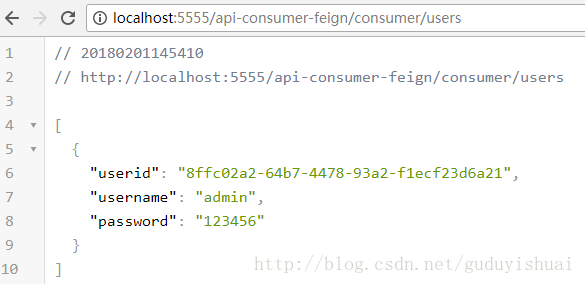
随便调用一个微服务
然后我们可以看到相关的跟踪日志
同样我们也可以看到微服务之间的依赖关系,这里是通过网关调用了myservice-consumer-feign微服务,然后通过
myservice-consumer-feign微服务调用了myservice-provider微服务
二、搭建ELK
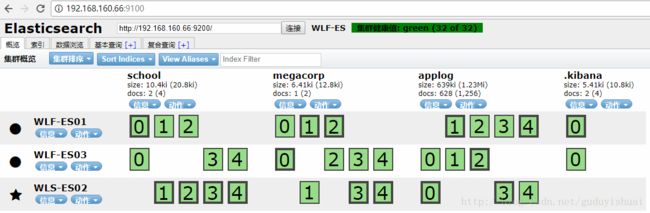
1、elasticsearch的安装与配置,由于之前的文章已经介绍了elasticsearch的单点,集群的安装,head插件的安装。这里
不再总结。
elasticsearch单点搭建
elasticsearch head插件安装
elasticsearch集群搭建
2、kibana的安装,没什么好说的,解压,运行就可以了
3、logstash的安装,解压即可
在config下新建配置文件
output {
input {
tcp {
port => 4560
codec => json_lines
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.160.66:9200","192.168.160.88:9200","192.168.160.166:9200"]
index => "applog"
}
}
为日志存储的elasticsearch索引。
启动需要调用bin下的logstash命令,通过-f指定配置文件
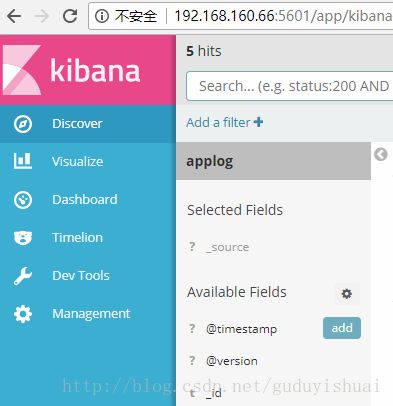
4、使用kibana
启动elasticsearch、head、kibana、logstash
创建索引applog
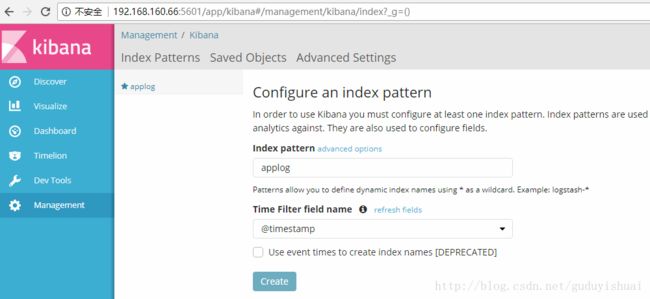
将applog配置到kibana中,在index pattern中输入我们的applog索引
最后点击create即可
点击菜单中的discover即可查看日志
三、logback配置
spring-cloud、logstash都是支持logback的,因此需要为微服务配置好相应的logback-spring.xml
这里值得注意的是,在spring-boot中,logback-spring.xml的加载在application.yml之前。而我们需要在
logback-spring.xml中使用spring.application.name。因此,我们需要把spring.application.name配置提到bootstrap.yml中。
加载顺序为bootstrap.yml,logback-spring.xml,application.yml
相比普通的logback-spring.xml,我们主要配置这几样东西spring.application.name,logstash的appender
这里提供一个logback-spring.xml的例子
true
${CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN}
utf8
192.168.160.66:4560
UTC
{
"severity":"%level",
"service": "${springAppName:-}",
"trace": "%X{X-B3-TraceId:-}",
"span": "%X{X-B3-SpanId:-}",
"exportable": "%X{X-Span-Export:-}",
"pid": "${PID:-}",
"thread": "%thread",
"class": "%logger{40}",
"rest": "%message"
}
main.log
main.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
30
%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{35} - %msg %n
DEBUG
三、查询日志
启动服务注册中心,网关,需要的微服务,以及sleuth
启动elasticsearch,head,kibana,logstash
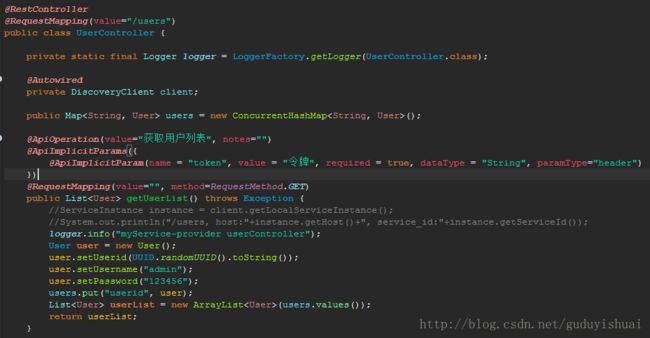
这里会输出一行日志,内容为myService-provider userController
通过网关调用
eclipse控制台输出日志
![]()
在kibana中搜索日志
我们看到日志信息在rest字段中。另外,通过trace和span还可以跟踪到整个微服务的调用过程
到此为止,整个日志采集就搭建完成了。系统上线后只需要在elasticsearch中就能搜索到各个服务器上,各个微服务的日志内容了