《C Primer Plus》第六版 ----十六章编程练习答案参考
第十五章的练习我这里就直接跳过了,因为一般情况下不太用得上。
因此就直接开始第十六章的练习了!
目录
先看这里:
题目+源码+运行效果:
P16-1:
P16-2:
P16-3:
P16-4:
P16-5:
16-7:
先看这里:
博主的编译环境:
VS 2017 Community
运行环境:Windows 10
因为到了后期每个练习的代码量是越来越大的,
所以如果大家复制不了或者想轻松一下的,可以直接从下面的网址下载源码:
另外:如果网盘提示你下载客户端,可以单个地下载,这样不用下载客户端
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1YOAMrXZm5Jb3A-LgZBwLEA
提取码:uh57
题目+源码+运行效果:
P16-1:
开发一个包含你需要的预处理器定义的头文件。
//useful functions are included here
//Func.h
#ifndef FUNC_H
#define FUNC_H#include
#include
#include#define QUIT 5
#define SPACE ' '
#define SIZE 100#endif
P16-2:
两数的调和平均数这样计算:先得到两数的倒数,然后计算两个倒数的平均值,最后取计算结果的倒数。
使用 #define 指令定义一个宏 "函数" ,执行该运算。编写一个简单的程序测试该宏。
#include
#define harmonic(numa, numb) (1 /((1 / (numa) + 1 / (numb)) / 2))
int main(void)
{
double numa = 3, numb = 3;printf("the harmonic mean of 3 and 3 is %.2f.", (double) harmonic(numa, numb));
return 0;
}
P16-3:
极坐标使用向量的模和向量相对 X 轴逆时针旋转的角度来描述该向量。直角坐标用向量的
X 轴和 Y 轴来描述该向量。编写一个程序,读取向量的模和角度(单位:度)
然后显示 X 轴和 Y 轴的坐标。相关方程:X = r * cos A Y = r * sin A
需要一个函数来完成转换,该函数接受一个包含极坐标的结构,
并返回一个包含直角坐标的结构(或指向该结构的指针)
/*
16-3
一弧度 = PI / 180
*/#include
#include//provide sin(), cos() #define RAD(X) ((X) * (3.1415926 / 180))
#define EATLINE while(getchar() != '\n') continuetypedef struct Polar_coor_sys
{
double r;
double angle;
}POLAR;typedef struct Rectan_coor
{
double x;
double y;
}RECTAN;void InitStruct(POLAR * polar, RECTAN * rectan);
void Get_P_coor(POLAR * polar);
//return the coor
RECTAN Change(POLAR * polar);int main(void)
{
POLAR polar;
RECTAN rectan;InitStruct(&polar, &rectan);
Get_P_coor(&polar);rectan = Change(&polar);
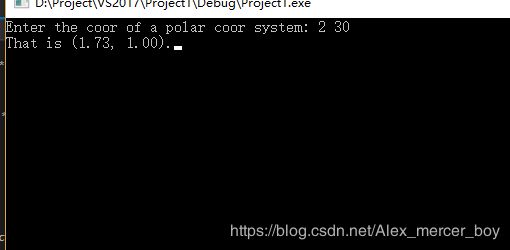
printf("That is (%.2f, %.2f).", rectan.x, rectan.y);
return 0;
}void InitStruct(POLAR * polar, RECTAN * rectan)
{
polar->r = 0;
polar->angle = 0;rectan->x = 0;
rectan->x = 0;
}void Get_P_coor(POLAR * polar)
{
double r = 0, ang = 0;printf("Enter the coor of a polar coor system: ");
while (scanf_s("%lf %lf", &r, &ang) != 2 || r <= 0 || ang == 0)
{
printf("Input error! Try again:");
EATLINE; //宏
continue;
}polar->r = r;
polar->angle = ang;
}//return the answer
RECTAN Change(POLAR * polar)
{
double rad = RAD(polar->angle);
RECTAN rectan;//work out the coor
rectan.x = polar->r * cos(rad);
rectan.y = polar->r * sin(rad);return rectan;
}
P16-4:
题目太长了.......
#include
#include//clock()
#include//sleep() #define ONE_SECOND 1555
int main(void)
{
clock_t time_begin = 0;
clock_t time_end = 0;
double sum = 0;time_begin = clock();
Sleep(ONE_SECOND);
time_end = clock();
//work out the answer.
sum = (double)(time_end - time_begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("sleeping for %.2f seconds costs %.2f seconds.", (ONE_SECOND / (double)1000), sum);return 0;
}
P16-5:
title: 编写一个函数接受这些参数:内含 int 类型元素的数组名,数组的大小和一个代表选取次数的值。
该函数从数组中随机选择指定数量的元素,并打印它们。每个元素只能使用一次(模拟抽奖数字或
挑选陪审团成员)。另外,如果你的实现有 time() 或类似的函数,可以再srand() 中
使用这个函数的输出来初始化随机数生成器 rand()。编写一个简单的程序测试该函数。
//title: 编写一个函数接受这些参数:内含 int 类型元素的数组名,数组的大小和一个代表选取次数的值。
// 该函数从数组中随机选择指定数量的元素,并打印它们。每个元素只能使用一次(模拟抽奖数字或
// 挑选陪审团成员)。另外,如果你的实现有 time() 或类似的函数,可以再srand() 中
// 使用这个函数的输出来初始化随机数生成器 rand()。编写一个简单的程序测试该函数。
// A lottery game.#include
#include//provide time()
#include//provide srand(), rand() //There are 100 winners in max.
#define WINNER_NUM_MAX 100//Init array
void InitArray(int * arr, int min, int element_num, int mode);//Get the number of winners-----0~100
int GetNum(void);//Print out lucky numbers.
void Print_Winners(int lucky_num[], int element_num, int amount);int main(void)
{
int winners_num = 0; //Get the max amount of winnners
int Lucky_num[WINNER_NUM_MAX];srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //Set random number seed
InitArray(Lucky_num, 0, WINNER_NUM_MAX, 1);winners_num = GetNum();
Print_Winners(Lucky_num, WINNER_NUM_MAX, winners_num);return 0;
}//Init array-----0~element_num
void InitArray(int * arr, int min, int element_num, int mode)
{
switch (mode)
{
case 0: //set all number 0
for (int i = min; i < element_num; i++)
{
*arr++ = 0;
}
break;
case 1:
for (int i = min + 1; i <= element_num; i++)
{
*arr++ = i;
}
break;
}}
//Get the number of winners-----0~100
int GetNum(void)
{
int num = 0;printf("Give a number-----0~100 to get the program ready: ");
while (scanf_s("%d", &num) != 1 || num < 1 || num > 100)
{
printf("Your input is invalid. Give the correct one: ");
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return num;
}//Print out lucky numbers.
void Print_Winners(int lucky_num[], int element_num, int amount)
{
int haveWon[WINNER_NUM_MAX];
InitArray(haveWon, 0, WINNER_NUM_MAX, 0);
int num = 0;printf("The winners: \n\n");
for (int i = 0; i < amount; i++)
{
num = rand() % element_num + 1;
if (haveWon[num - 1] == 0)
{
printf("%d\t", num);
haveWon[num - 1] = 1;
}
else
{
i--;
continue;
}if ((i + 1) % 6 == 0)
{
putchar('\n');
}
}
}
16-7:
由于题目太长了,就不打了。
/*
16-7.c
title: The title is too long that I just don't want to make a copy.
*/#include
#include//provide srand(), rand()
#include//provide 变参函数 void show_array(const double ar[], int n);
double * new_d_array(int n, ...); //首个变参函数int main(void)
{
double * p1;
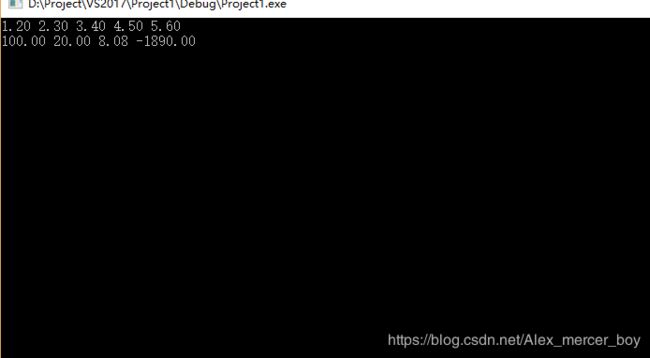
double * p2;p1 = new_d_array(5, 1.2, 2.3, 3.4, 4.5, 5.6); //变参函数 + 动态内存分配 = A wonder.
p2 = new_d_array(4, 100.0, 20.00, 8.08, -1890.0);show_array(p1, 5);
show_array(p2, 4);
free(p1);
free(p2);return 0;
}
double * new_d_array(int n, ...)
{
double * pointer;
va_list ap;pointer = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double) * n);
va_start(ap, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //访问每个元素
{
pointer[i] = va_arg(ap, double);
}
va_end(ap);return pointer;
}void show_array(const double ar[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%.2f ", ar[i]);if (i % 6 == 0 && i != 0)
{
putchar('\n');
}
}
putchar('\n');
}