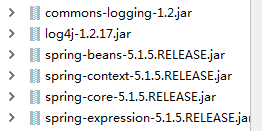
- Long类型前后端数据不一致
igotyback
前端
响应给前端的数据浏览器控制台中response中看到的Long类型的数据是正常的到前端数据不一致前后端数据类型不匹配是一个常见问题,尤其是当后端使用Java的Long类型(64位)与前端JavaScript的Number类型(最大安全整数为2^53-1,即16位)进行数据交互时,很容易出现精度丢失的问题。这是因为JavaScript中的Number类型无法安全地表示超过16位的整数。为了解决这个问
- LocalDateTime 转 String
igotyback
java开发语言
importjava.time.LocalDateTime;importjava.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;publicclassMain{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//获取当前时间LocalDateTimenow=LocalDateTime.now();//定义日期格式化器DateTimeFormatterformat
- Linux下QT开发的动态库界面弹出操作(SDL2)
13jjyao
QT类qt开发语言sdl2linux
需求:操作系统为linux,开发框架为qt,做成需带界面的qt动态库,调用方为java等非qt程序难点:调用方为java等非qt程序,也就是说调用方肯定不带QApplication::exec(),缺少了这个,QTimer等事件和QT创建的窗口将不能弹出(包括opencv也是不能弹出);这与qt调用本身qt库是有本质的区别的思路:1.调用方缺QApplication::exec(),那么我们在接口
- DIV+CSS+JavaScript技术制作网页(旅游主题网页设计与制作)云南大理
STU学生网页设计
网页设计期末网页作业html静态网页html5期末大作业网页设计web大作业
️精彩专栏推荐作者主页:【进入主页—获取更多源码】web前端期末大作业:【HTML5网页期末作业(1000套)】程序员有趣的告白方式:【HTML七夕情人节表白网页制作(110套)】文章目录二、网站介绍三、网站效果▶️1.视频演示2.图片演示四、网站代码HTML结构代码CSS样式代码五、更多源码二、网站介绍网站布局方面:计划采用目前主流的、能兼容各大主流浏览器、显示效果稳定的浮动网页布局结构。网站程
- 【华为OD机试真题2023B卷 JAVA&JS】We Are A Team
若博豆
java算法华为javascript
华为OD2023(B卷)机试题库全覆盖,刷题指南点这里WeAreATeam时间限制:1秒|内存限制:32768K|语言限制:不限题目描述:总共有n个人在机房,每个人有一个标号(1<=标号<=n),他们分成了多个团队,需要你根据收到的m条消息判定指定的两个人是否在一个团队中,具体的:1、消息构成为:abc,整数a、b分别代
- 关于城市旅游的HTML网页设计——(旅游风景云南 5页)HTML+CSS+JavaScript
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业javascripthtmlcss旅游风景
⛵源码获取文末联系✈Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业|游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作|HTML期末大学生网页设计作业,Web大学生网页HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScrip
- HTML网页设计制作大作业(div+css) 云南我的家乡旅游景点 带文字滚动
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业web设计网页规划与设计htmlcssjavascriptdreamweaver前端
Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作HTML期末大学生网页设计作业HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScript:做与用户的交互行为文章目录前端学习路线
- node.js学习
小猿L
node.jsnode.js学习vim
node.js学习实操及笔记温故node.js,node.js学习实操过程及笔记~node.js学习视频node.js官网node.js中文网实操笔记githubcsdn笔记为什么学node.js可以让别人访问我们编写的网页为后续的框架学习打下基础,三大框架vuereactangular离不开node.jsnode.js是什么官网:node.js是一个开源的、跨平台的运行JavaScript的运行
- SpringBlade dict-biz/list 接口 SQL 注入漏洞
文章永久免费只为良心
oracle数据库
SpringBladedict-biz/list接口SQL注入漏洞POC:构造请求包查看返回包你的网址/api/blade-system/dict-biz/list?updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,md5(1),0x7e),1)=1漏洞概述在SpringBlade框架中,如果dict-biz/list接口的后台处理逻辑没有正确地对用户输入进行过滤或参数化查询(PreparedSta
- Java 重写(Override)与重载(Overload)
叨唧唧的
Java重写(Override)与重载(Overload)重写(Override)重写是子类对父类的允许访问的方法的实现过程进行重新编写,返回值和形参都不能改变。即外壳不变,核心重写!重写的好处在于子类可以根据需要,定义特定于自己的行为。也就是说子类能够根据需要实现父类的方法。重写方法不能抛出新的检查异常或者比被重写方法申明更加宽泛的异常。例如:父类的一个方法申明了一个检查异常IOExceptio
- 简单了解 JVM
记得开心一点啊
jvm
目录♫什么是JVM♫JVM的运行流程♫JVM运行时数据区♪虚拟机栈♪本地方法栈♪堆♪程序计数器♪方法区/元数据区♫类加载的过程♫双亲委派模型♫垃圾回收机制♫什么是JVMJVM是JavaVirtualMachine的简称,意为Java虚拟机。虚拟机是指通过软件模拟的具有完整硬件功能的、运行在一个完全隔离的环境中的完整计算机系统(如:JVM、VMwave、VirtualBox)。JVM和其他两个虚拟机
- 1分钟解决 -bash: mvn: command not found,在Centos 7中安装Maven
Energet!c
开发语言
1分钟解决-bash:mvn:commandnotfound,在Centos7中安装Maven检查Java环境1下载Maven2解压Maven3配置环境变量4验证安装5常见问题与注意事项6总结检查Java环境Maven依赖Java环境,请确保系统已经安装了Java并配置了环境变量。可以通过以下命令检查:java-version如果未安装,请先安装Java。1下载Maven从官网下载:前往Apach
- Java企业面试题3
马龙强_
java
1.break和continue的作用(智*图)break:用于完全退出一个循环(如for,while)或一个switch语句。当在循环体内遇到break语句时,程序会立即跳出当前循环体,继续执行循环之后的代码。continue:用于跳过当前循环体中剩余的部分,并开始下一次循环。如果是在for循环中使用continue,则会直接进行条件判断以决定是否执行下一轮循环。2.if分支语句和switch分
- JVM、JRE和 JDK:理解Java开发的三大核心组件
Y雨何时停T
Javajava
Java是一门跨平台的编程语言,它的成功离不开背后强大的运行环境与开发工具的支持。在Java的生态中,JVM(Java虚拟机)、JRE(Java运行时环境)和JDK(Java开发工具包)是三个至关重要的核心组件。本文将探讨JVM、JDK和JRE的区别,帮助你更好地理解Java的运行机制。1.JVM:Java虚拟机(JavaVirtualMachine)什么是JVM?JVM,即Java虚拟机,是Ja
- Java面试题精选:消息队列(二)
芒果不是芒
Java面试题精选javakafka
一、Kafka的特性1.消息持久化:消息存储在磁盘,所以消息不会丢失2.高吞吐量:可以轻松实现单机百万级别的并发3.扩展性:扩展性强,还是动态扩展4.多客户端支持:支持多种语言(Java、C、C++、GO、)5.KafkaStreams(一个天生的流处理):在双十一或者销售大屏就会用到这种流处理。使用KafkaStreams可以快速的把销售额统计出来6.安全机制:Kafka进行生产或者消费的时候会
- 白骑士的Java教学基础篇 2.5 控制流语句
白骑士所长
Java教学java开发语言
欢迎继续学习Java编程的基础篇!在前面的章节中,我们了解了Java的变量、数据类型和运算符。接下来,我们将探讨Java中的控制流语句。控制流语句用于控制程序的执行顺序,使我们能够根据特定条件执行不同的代码块,或重复执行某段代码。这是编写复杂程序的基础。通过学习这一节内容,你将掌握如何使用条件语句和循环语句来编写更加灵活和高效的代码。条件语句条件语句用于根据条件的真假来执行不同的代码块。if语句‘
- python语法——三目运算符
HappyRocking
pythonpython三目运算符
在java中,有三目运算符,如:intc=(a>b)?a:b表示c取两者中的较大值。但是在python,不能直接这样使用,估计是因为冒号在python有分行的关键作用。那么在python中,如何实现类似功能呢?可以使用ifelse语句,也是一行可以完成,格式为:aifbelsec表示如果b为True,则表达式等于a,否则等于c。如:c=(aif(a>b)elseb)同样是完成了取最大值的功能。
- spring如何整合druid连接池?
惜.己
springspringjunit数据库javaidea后端xml
目录spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目2.新建mavenModule3.导入相关依赖4.配置log4j2.xml5.配置druid.xml1)xml中如何引入properties2)下面是配置文件6.准备jdbc.propertiesJDBC配置项解释7.配置druid8.测试spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目打开IDE(比如IntelliJIDEA,Ecl
- ArrayList 源码解析
程序猿进阶
Java基础ArrayListListjava面试性能优化架构设计idea
ArrayList是Java集合框架中的一个动态数组实现,提供了可变大小的数组功能。它继承自AbstractList并实现了List接口,是顺序容器,即元素存放的数据与放进去的顺序相同,允许放入null元素,底层通过数组实现。除该类未实现同步外,其余跟Vector大致相同。每个ArrayList都有一个容量capacity,表示底层数组的实际大小,容器内存储元素的个数不能多于当前容量。当向容器中添
- Java爬虫框架(一)--架构设计
狼图腾-狼之传说
java框架java任务html解析器存储电子商务
一、架构图那里搜网络爬虫框架主要针对电子商务网站进行数据爬取,分析,存储,索引。爬虫:爬虫负责爬取,解析,处理电子商务网站的网页的内容数据库:存储商品信息索引:商品的全文搜索索引Task队列:需要爬取的网页列表Visited表:已经爬取过的网页列表爬虫监控平台:web平台可以启动,停止爬虫,管理爬虫,task队列,visited表。二、爬虫1.流程1)Scheduler启动爬虫器,TaskMast
- Java:爬虫框架
dingcho
Javajava爬虫
一、ApacheNutch2【参考地址】Nutch是一个开源Java实现的搜索引擎。它提供了我们运行自己的搜索引擎所需的全部工具。包括全文搜索和Web爬虫。Nutch致力于让每个人能很容易,同时花费很少就可以配置世界一流的Web搜索引擎.为了完成这一宏伟的目标,Nutch必须能够做到:每个月取几十亿网页为这些网页维护一个索引对索引文件进行每秒上千次的搜索提供高质量的搜索结果简单来说Nutch支持分
- python怎么将png转为tif_png转tif
weixin_39977276
发国外的文章要求图片是tif,cmyk色彩空间的。大小尺寸还有要求。比如网上大神多,找到了一段代码,感谢!https://www.jianshu.com/p/ec2af4311f56https://github.com/KevinZc007/image2Tifimportjava.awt.image.BufferedImage;importjava.io.File;importjava.io.Fi
- SpringCloudAlibaba—Sentinel(限流)
菜鸟爪哇
前言:自己在学习过程的记录,借鉴别人文章,记录自己实现的步骤。借鉴文章:https://blog.csdn.net/u014494148/article/details/105484410Sentinel介绍Sentinel诞生于阿里巴巴,其主要目标是流量控制和服务熔断。Sentinel是通过限制并发线程的数量(即信号隔离)来减少不稳定资源的影响,而不是使用线程池,省去了线程切换的性能开销。当资源
- springboot+vue项目实战一-创建SpringBoot简单项目
苹果酱0567
面试题汇总与解析springboot后端java中间件开发语言
这段时间抽空给女朋友搭建一个个人博客,想着记录一下建站的过程,就当做笔记吧。虽然复制zjblog只要一个小时就可以搞定一个网站,或者用cms系统,三四个小时就可以做出一个前后台都有的网站,而且想做成啥样也都行。但是就是要从新做,自己做的意义不一样,更何况,俺就是专门干这个的,嘿嘿嘿要做一个网站,而且从零开始,首先呢就是技术选型了,经过一番思量决定选择-SpringBoot做后端,前端使用Vue做一
- JavaScript 中,深拷贝(Deep Copy)和浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)
跳房子的前端
前端面试javascript开发语言ecmascript
在JavaScript中,深拷贝(DeepCopy)和浅拷贝(ShallowCopy)是用于复制对象或数组的两种不同方法。了解它们的区别和应用场景对于避免潜在的bugs和高效地处理数据非常重要。以下是对深拷贝和浅拷贝的详细解释,包括它们的概念、用途、优缺点以及实现方式。1.浅拷贝(ShallowCopy)概念定义:浅拷贝是指创建一个新的对象或数组,其中包含了原对象或数组的基本数据类型的值和对引用数
- JAVA·一个简单的登录窗口
MortalTom
java开发语言学习
文章目录概要整体架构流程技术名词解释技术细节资源概要JavaSwing是Java基础类库的一部分,主要用于开发图形用户界面(GUI)程序整体架构流程新建项目,导入sql.jar包(链接放在了文末),编译项目并运行技术名词解释一、特点丰富的组件提供了多种可视化组件,如按钮(JButton)、文本框(JTextField)、标签(JLabel)、下拉列表(JComboBox)等,可以满足不同的界面设计
- Spring MVC 全面指南:从入门到精通的详细解析
一杯梅子酱
技术栈学习springmvcjava
引言:SpringMVC,作为Spring框架的一个重要模块,为构建Web应用提供了强大的功能和灵活性。无论是初学者还是有一定经验的开发者,掌握SpringMVC都将显著提升你的Web开发技能。本文旨在为初学者提供一个全面且易于理解的学习路径,通过详细的知识点分析和实际案例,帮助你快速上手SpringMVC,让学习过程既深刻又高效。一、SpringMVC简介1.1什么是SpringMVC?Spri
- Spring Boot中实现跨域请求
BABA8891
springboot后端java
在SpringBoot中实现跨域请求(CORS,Cross-OriginResourceSharing)可以通过多种方式,以下是几种常见的方法:1.使用@CrossOrigin注解在SpringBoot中,你可以在控制器或者具体的请求处理方法上使用@CrossOrigin注解来允许跨域请求。在控制器上应用:importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.
- WebMagic:强大的Java爬虫框架解析与实战
Aaron_945
Javajava爬虫开发语言
文章目录引言官网链接WebMagic原理概述基础使用1.添加依赖2.编写PageProcessor高级使用1.自定义Pipeline2.分布式抓取优点结论引言在大数据时代,网络爬虫作为数据收集的重要工具,扮演着不可或缺的角色。Java作为一门广泛使用的编程语言,在爬虫开发领域也有其独特的优势。WebMagic是一个开源的Java爬虫框架,它提供了简单灵活的API,支持多线程、分布式抓取,以及丰富的
- 博客网站制作教程
2401_85194651
javamaven
首先就是技术框架:后端:Java+SpringBoot数据库:MySQL前端:Vue.js数据库连接:JPA(JavaPersistenceAPI)1.项目结构blog-app/├──backend/│├──src/main/java/com/example/blogapp/││├──BlogApplication.java││├──config/│││└──DatabaseConfig.java
- springmvc 下 freemarker页面枚举的遍历输出
杨白白
enumfreemarker
spring mvc freemarker 中遍历枚举
1枚举类型有一个本地方法叫values(),这个方法可以直接返回枚举数组。所以可以利用这个遍历。
enum
public enum BooleanEnum {
TRUE(Boolean.TRUE, "是"), FALSE(Boolean.FALSE, "否");
- 实习简要总结
byalias
工作
来白虹不知不觉中已经一个多月了,因为项目还在需求分析及项目架构阶段,自己在这段
时间都是在学习相关技术知识,现在对这段时间的工作及学习情况做一个总结:
(1)工作技能方面
大体分为两个阶段,Java Web 基础阶段和Java EE阶段
1)Java Web阶段
在这个阶段,自己主要着重学习了 JSP, Servlet, JDBC, MySQL,这些知识的核心点都过
了一遍,也
- Quartz——DateIntervalTrigger触发器
eksliang
quartz
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2208559 一.概述
simpleTrigger 内部实现机制是通过计算间隔时间来计算下次的执行时间,这就导致他有不适合调度的定时任务。例如我们想每天的 1:00AM 执行任务,如果使用 SimpleTrigger,间隔时间就是一天。注意这里就会有一个问题,即当有 misfired 的任务并且恢复执行时,该执行时间
- Unix快捷键
18289753290
unixUnix;快捷键;
复制,删除,粘贴:
dd:删除光标所在的行 &nbs
- 获取Android设备屏幕的相关参数
酷的飞上天空
android
包含屏幕的分辨率 以及 屏幕宽度的最大dp 高度最大dp
TextView text = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
DisplayMetrics dm = new DisplayMetrics();
text.append("getResources().ge
- 要做物联网?先保护好你的数据
蓝儿唯美
数据
根据Beecham Research的说法,那些在行业中希望利用物联网的关键领域需要提供更好的安全性。
在Beecham的物联网安全威胁图谱上,展示了那些可能产生内外部攻击并且需要通过快速发展的物联网行业加以解决的关键领域。
Beecham Research的技术主管Jon Howes说:“之所以我们目前还没有看到与物联网相关的严重安全事件,是因为目前还没有在大型客户和企业应用中进行部署,也就
- Java取模(求余)运算
随便小屋
java
整数之间的取模求余运算很好求,但几乎没有遇到过对负数进行取模求余,直接看下面代码:
/**
*
* @author Logic
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO A
- SQL注入介绍
aijuans
sql注入
二、SQL注入范例
这里我们根据用户登录页面
<form action="" > 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="passwor
- 优雅代码风格
aoyouzi
代码
总结了几点关于优雅代码风格的描述:
代码简单:不隐藏设计者的意图,抽象干净利落,控制语句直截了当。
接口清晰:类型接口表现力直白,字面表达含义,API 相互呼应以增强可测试性。
依赖项少:依赖关系越少越好,依赖少证明内聚程度高,低耦合利于自动测试,便于重构。
没有重复:重复代码意味着某些概念或想法没有在代码中良好的体现,及时重构消除重复。
战术分层:代码分层清晰,隔离明确,
- 布尔数组
百合不是茶
java布尔数组
androi中提到了布尔数组;
布尔数组默认的是false, 并且只会打印false或者是true
布尔数组的例子; 根据字符数组创建布尔数组
char[] c = {'p','u','b','l','i','c'};
//根据字符数组的长度创建布尔数组的个数
boolean[] b = new bool
- web.xml之welcome-file-list、error-page
bijian1013
javaweb.xmlservleterror-page
welcome-file-list
1.定义:
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>login.jsp</welcome>
</welcome-file-list>
2.作用:用来指定WEB应用首页名称。
error-page1.定义:
<error-page&g
- richfaces 4 fileUpload组件删除上传的文件
sunjing
clearRichfaces 4fileupload
页面代码
<h:form id="fileForm"> <rich:
- 技术文章备忘
bit1129
技术文章
Zookeeper
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/bab171ffaef8941ea76e05b8.html
http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=8thAIwFTnPh2KL2b0p1V7XSgmF9ZEFgw4V_MkIpA9j8BX2rDQMPgK5l3wcs9oBTxeekOnm5P3BK8c6K2DWynq9nfUCkRlTt9uV
- org.hibernate.hql.ast.QuerySyntaxException: unexpected token: on near line 1解决方案
白糖_
Hibernate
文章摘自:http://blog.csdn.net/yangwawa19870921/article/details/7553181
在编写HQL时,可能会出现这种代码:
select a.name,b.age from TableA a left join TableB b on a.id=b.id
如果这是HQL,那么这段代码就是错误的,因为HQL不支持
- sqlserver按照字段内容进行排序
bozch
按照内容排序
在做项目的时候,遇到了这样的一个需求:
从数据库中取出的数据集,首先要将某个数据或者多个数据按照地段内容放到前面显示,例如:从学生表中取出姓李的放到数据集的前面;
select * fro
- 编程珠玑-第一章-位图排序
bylijinnan
java编程珠玑
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.util.Random;
public class BitMapSearch {
- Java关于==和equals
chenbowen00
java
关于==和equals概念其实很简单,一个是比较内存地址是否相同,一个比较的是值内容是否相同。虽然理解上不难,但是有时存在一些理解误区,如下情况:
1、
String a = "aaa";
a=="aaa";
==> true
2、
new String("aaa")==new String("aaa
- [IT与资本]软件行业需对外界投资热情保持警惕
comsci
it
我还是那个看法,软件行业需要增强内生动力,尽量依靠自有资金和营业收入来进行经营,避免在资本市场上经受各种不同类型的风险,为企业自主研发核心技术和产品提供稳定,温和的外部环境...
如果我们在自己尚未掌握核心技术之前,企图依靠上市来筹集资金,然后使劲往某个领域砸钱,然
- oracle 数据块结构
daizj
oracle块数据块块结构行目录
oracle 数据块是数据库存储的最小单位,一般为操作系统块的N倍。其结构为:
块头--〉空行--〉数据,其实际为纵行结构。
块的标准大小由初始化参数DB_BLOCK_SIZE指定。具有标准大小的块称为标准块(Standard Block)。块的大小和标准块的大小不同的块叫非标准块(Nonstandard Block)。同一数据库中,Oracle9i及以上版本支持同一数据库中同时使用标
- github上一些觉得对自己工作有用的项目收集
dengkane
github
github上一些觉得对自己工作有用的项目收集
技能类
markdown语法中文说明
回到顶部
全文检索
elasticsearch
bigdesk elasticsearch管理插件
回到顶部
nosql
mapdb 支持亿级别map, list, 支持事务. 可考虑做为缓存使用
C
- 初二上学期难记单词二
dcj3sjt126com
englishword
dangerous 危险的
panda 熊猫
lion 狮子
elephant 象
monkey 猴子
tiger 老虎
deer 鹿
snake 蛇
rabbit 兔子
duck 鸭
horse 马
forest 森林
fall 跌倒;落下
climb 爬;攀登
finish 完成;结束
cinema 电影院;电影
seafood 海鲜;海产食品
bank 银行
- 8、mysql外键(FOREIGN KEY)的简单使用
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
一、基本概念
1、MySQL中“键”和“索引”的定义相同,所以外键和主键一样也是索引的一种。不同的是MySQL会自动为所有表的主键进行索引,但是外键字段必须由用户进行明确的索引。用于外键关系的字段必须在所有的参照表中进行明确地索引,InnoDB不能自动地创建索引。
2、外键可以是一对一的,一个表的记录只能与另一个表的一条记录连接,或者是一对多的,一个表的记录与另一个表的多条记录连接。
3、如
- java循环标签 Foreach
shuizhaosi888
标签java循环foreach
1. 简单的for循环
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1, y = i + 10; i < 5 && y < 12; i++, y = i * 2) {
System.err.println("i=" + i + " y="
- Spring Security(05)——异常信息本地化
234390216
exceptionSpring Security异常信息本地化
异常信息本地化
Spring Security支持将展现给终端用户看的异常信息本地化,这些信息包括认证失败、访问被拒绝等。而对于展现给开发者看的异常信息和日志信息(如配置错误)则是不能够进行本地化的,它们是以英文硬编码在Spring Security的代码中的。在Spring-Security-core-x
- DUBBO架构服务端告警Failed to send message Response
javamingtingzhao
架构DUBBO
废话不多说,警告日志如下,不知道有哪位遇到过,此异常在服务端抛出(服务器启动第一次运行会有这个警告),后续运行没问题,找了好久真心不知道哪里错了。
WARN 2015-07-18 22:31:15,272 com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher.ChannelEventRunnable.run(84)
- JS中Date对象中几个用法
leeqq
JavaScriptDate最后一天
近来工作中遇到这样的两个需求
1. 给个Date对象,找出该时间所在月的第一天和最后一天
2. 给个Date对象,找出该时间所在周的第一天和最后一天
需求1中的找月第一天很简单,我记得api中有setDate方法可以使用
使用setDate方法前,先看看getDate
var date = new Date();
console.log(date);
// Sat J
- MFC中使用ado技术操作数据库
你不认识的休道人
sqlmfc
1.在stdafx.h中导入ado动态链接库
#import"C:\Program Files\Common Files\System\ado\msado15.dll" no_namespace rename("EOF","end")2.在CTestApp文件的InitInstance()函数中domodal之前写::CoIniti
- Android Studio加速
rensanning
android studio
Android Studio慢、吃内存!启动时后会立即通过Gradle来sync & build工程。
(1)设置Android Studio
a) 禁用插件
File -> Settings... Plugins 去掉一些没有用的插件。
比如:Git Integration、GitHub、Google Cloud Testing、Google Cloud
- 各数据库的批量Update操作
tomcat_oracle
javaoraclesqlmysqlsqlite
MyBatis的update元素的用法与insert元素基本相同,因此本篇不打算重复了。本篇仅记录批量update操作的
sql语句,懂得SQL语句,那么MyBatis部分的操作就简单了。 注意:下列批量更新语句都是作为一个事务整体执行,要不全部成功,要不全部回滚。
MSSQL的SQL语句
WITH R AS(
SELECT 'John' as name, 18 as
- html禁止清除input文本输入缓存
xp9802
input
多数浏览器默认会缓存input的值,只有使用ctl+F5强制刷新的才可以清除缓存记录。如果不想让浏览器缓存input的值,有2种方法:
方法一: 在不想使用缓存的input中添加 autocomplete="off"; eg: <input type="text" autocomplete="off" name