Hi3520D上手过程之U-boot学习
目录
一、烧写过程初探
1. 说明文件
2. 编译
3. 烧写
二、U-boot学习
1. u-boot流程
(1)u-boot起点
(2)u-boot引导过程
(3)u-boot终点
2. u-boot命令新增-update
一、烧写过程初探
当拿到SDK时,找到源码路径解压,一般如下所示:
运行sdk.unpack即可进行解压,若遇到不可运行的问题,可参考
https://blog.csdn.net/u013286409/article/details/45305911
1. 说明文件
参考Hi3520D_V100R001C01SPC040\release\01.software\board\documents_cn下的Hi3520D SDK 安装以及升级使用说明.txt了解源码的目录结构,除此之外,烧写u-boot和内核等程序的方法,以及DDR和Flash的初步划分,也在其中有详尽的说明
参考源码osdrv下的readme_cn.txt了解osdrv以及pub等目录结构,但是具体的编译方法建议不要直接参考readme_cn.txt中所述,直接参考osdrv/Makefile来得更加实际一些
2. 编译
交叉编译链位于Hi3520D_SDK_V1.0.4.0/osdrv/toolchain/arm-hisiv100nptl-linux下,./cross.install即可完成安装。
具体编译环节参照osdrv/Makefile可以减少很多坑,比如u-boot.bin编译出来后需要加上配置文件一同烧写成最终可以运行在开发板的镜像u-boot_hi3520d.bin
3. 烧写
Hi3520D SDK 安装以及升级使用说明.txt中说明了烧写方法,但有一种情况,就是第一次将u-boot烧写错误,板子成砖了,那就只能靠Hi3520D_SDK_V1.0.4.0\package\osdrv\tools\pc_tools\uboot_tools下的FastBoot3.1_BVT.exe来救了,使用方法可见Fastboot工具使用说明 Application Notes.pdf,在Hi3520D SDK 安装以及升级使用说明.txt的同级目录中,建议参照boot烧写的方式,简单可行(注:Fastboot工具对串口要求较为严苛,需要使用较好的U转串才可)。
二、U-boot学习
1. u-boot流程
(1)u-boot起点
u-boot源码根目录/arch/arm/cpu/hi3520d的u-boot.lds中标明了:
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm")
OUTPUT_ARCH(arm)
ENTRY(_start)
SECTIONS
{
. = 0x00000000;
. = ALIGN(4);
.text :
{
arch/arm/cpu/hi3520d/start.o (.text)
*(.text)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.rodata : { *(SORT_BY_ALIGNMENT(SORT_BY_NAME(.rodata*))) }
. = ALIGN(4);
.data : { *(.data) }
. = ALIGN(4);
.got : { *(.got) }
__u_boot_cmd_start = .;
.u_boot_cmd : { *(.u_boot_cmd) }
__u_boot_cmd_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
__bss_start = .;
.bss : { *(.bss) }
_end = .;
}其中
arch/arm/cpu/hi3520d/start.o (.text)标明了起始程序为start.S
ENTRY(_start)标明了start.S中的_start为程序的入口,可理解为start.S中的main函数
__u_boot_cmd_start = .;
.u_boot_cmd : { *(.u_boot_cmd) }
__u_boot_cmd_end = .;标明了u-boot命令存储的位置,以及起始和结束的标号
(2)u-boot引导过程
主要分为start.S中的过程和.C文件引导内核的过程
start.S中的过程为:
①检验REG_SC_GEN2系统寄存器(若为0x7a696a75则终止正常启动)===》②设置CPU模式SVC32===》③初始化I/D(指令/数据) cache===》④禁用MMU和cache===》⑤启用I cache===》⑥DDR软件training===》⑦重定向U-boot到RAM===》⑧初始化stack===》⑨初始化BSS===》⑩跳转到start_armboot运行(第二阶段)
.C文件引导内核的过程为:
①初始化全局结构体gb,bd
#define DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR register volatile gd_t *gd asm ("r8") /* Pointer is writable since we allocated a register for it */
gd = (gd_t*)(_armboot_start - CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_LEN - sizeof(gd_t));
/* compiler optimization barrier needed for GCC >= 3.4 */
__asm__ __volatile__("": : :"memory");
memset ((void*)gd, 0, sizeof (gd_t));
gd->bd = (bd_t*)((char*)gd - sizeof(bd_t));gd的定义为寄存器型变量,由r8寄存器进行存储指针地址,只要有这个宏的存在,就可以对gd进行赋值操作
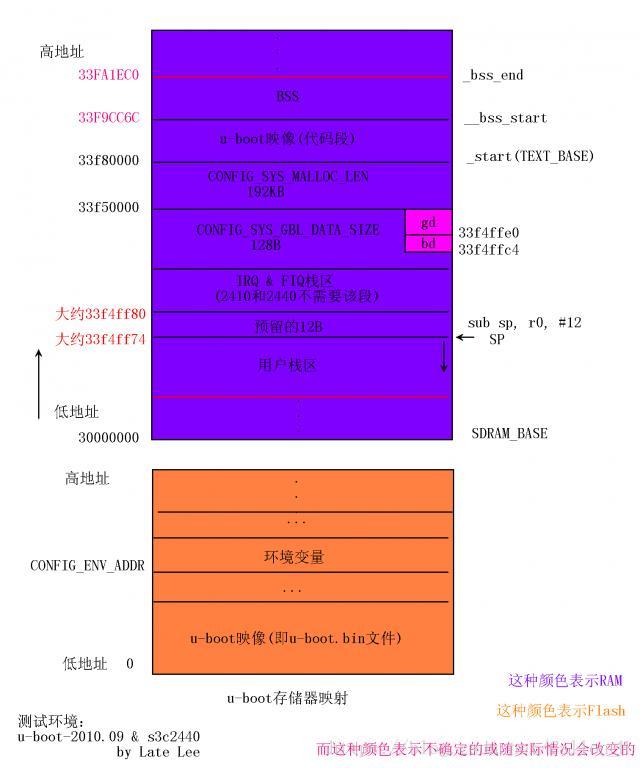
对于gd的地址,以及在u-boot中的内存分布。这里面有很经典的一张图
细化之后,还有static变量,全局变量,未初始化变量,局部变量的存储位置
②一系列初始化
for (init_fnc_ptr = init_sequence; *init_fnc_ptr; ++init_fnc_ptr) {
if ((*init_fnc_ptr)() != 0) {
hang ();
}
}init_fnc_t *init_sequence[] = {
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_CPU_INIT)
arch_cpu_init, /* basic arch cpu dependent setup */
#endif
timer_init, /* initialize timer before usb init */
board_init, /* basic board dependent setup */
#if defined(CONFIG_USE_IRQ)
interrupt_init, /* set up exceptions */
#endif
// timer_init, /* initialize timer */
#ifdef CONFIG_FSL_ESDHC
get_clocks,
#endif
env_init, /* initialize environment */
init_baudrate, /* initialze baudrate settings */
serial_init, /* serial communications setup */
console_init_f, /* stage 1 init of console */
display_banner, /* say that we are here */
#if defined(CONFIG_DISPLAY_CPUINFO)
print_cpuinfo, /* display cpu info (and speed) */
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_DISPLAY_BOARDINFO)
checkboard, /* display board info */
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_HARD_I2C) || defined(CONFIG_SOFT_I2C)
init_func_i2c,
#endif
dram_init, /* configure available RAM banks */
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_PCI) || defined (CONFIG_PCI)
arm_pci_init,
#endif
/* display_dram_config */
NULL,
};其中较为重要的是board_init,board_init的重要在于初始化了
gd->bd->bi_arch_number = MACH_TYPE_HI3520D;
gd->bd->bi_boot_params = CFG_BOOT_PARAMS;这两个变量将在内核阶段再次使用
③存储部分的初始化
④环境变量的初始化env_relocate
需要注意的是,如之前提到的图,环境变量区位于flash上,这也是为什么环境变量的初始化要放到存储部分初始化之后
void env_relocate (void)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_RELOC_FIXUP_WORKS
DEBUGF ("%s[%d] offset = 0x%lx\n", __FUNCTION__,__LINE__,
gd->reloc_off);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_AMIGAONEG3SE
enable_nvram();
#endif
#ifdef ENV_IS_EMBEDDED
/*
* The environment buffer is embedded with the text segment,
* just relocate the environment pointer
*/
#ifndef CONFIG_RELOC_FIXUP_WORKS
env_ptr = (env_t *)((ulong)env_ptr + gd->reloc_off);
#endif
DEBUGF ("%s[%d] embedded ENV at %p\n", __FUNCTION__,__LINE__,env_ptr);
#else
/*
* We must allocate a buffer for the environment
*/
env_ptr = (env_t *)malloc (CONFIG_ENV_SIZE);
DEBUGF ("%s[%d] malloced ENV at %p\n", __FUNCTION__,__LINE__,env_ptr);
#endif
if (gd->env_valid == 0) {
#if defined(CONFIG_GTH) || defined(CONFIG_ENV_IS_NOWHERE) /* Environment not changable */
puts ("Using default environment\n\n");
#else
puts ("*** Warning - bad CRC, using default environment\n\n");
show_boot_progress (-60);
#endif
set_default_env();
}
else {
env_relocate_spec ();
}
gd->env_addr = (ulong)&(env_ptr->data);
#ifdef CONFIG_AMIGAONEG3SE
disable_nvram();
#endif
}该函数主要功能为,检验flash中的环境变量是否有效,若无效,则使用默认的环境变量default_environment,
uchar default_environment[] = {
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTARGS
"bootargs=" CONFIG_BOOTARGS "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND
"bootcmd=" CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_RAMBOOTCOMMAND
"ramboot=" CONFIG_RAMBOOTCOMMAND "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NFSBOOTCOMMAND
"nfsboot=" CONFIG_NFSBOOTCOMMAND "\0"
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_BOOTDELAY) && (CONFIG_BOOTDELAY >= 0)
"bootdelay=" MK_STR(CONFIG_BOOTDELAY) "\0"
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_BAUDRATE) && (CONFIG_BAUDRATE >= 0)
"baudrate=" MK_STR(CONFIG_BAUDRATE) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LOADS_ECHO
"loads_echo=" MK_STR(CONFIG_LOADS_ECHO) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MDIO_INTF
"mdio_intf=" CONFIG_MDIO_INTF "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ETHADDR
"ethaddr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_ETHADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ETH1ADDR
"eth1addr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_ETH1ADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ETH2ADDR
"eth2addr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_ETH2ADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ETH3ADDR
"eth3addr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_ETH3ADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ETH4ADDR
"eth4addr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_ETH4ADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ETH5ADDR
"eth5addr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_ETH5ADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IPADDR
"ipaddr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_IPADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SERVERIP
"serverip=" MK_STR(CONFIG_SERVERIP) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_AUTOLOAD
"autoload=" CONFIG_SYS_AUTOLOAD "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PREBOOT
"preboot=" CONFIG_PREBOOT "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ROOTPATH
"rootpath=" MK_STR(CONFIG_ROOTPATH) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GATEWAYIP
"gatewayip=" MK_STR(CONFIG_GATEWAYIP) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETMASK
"netmask=" MK_STR(CONFIG_NETMASK) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_HOSTNAME
"hostname=" MK_STR(CONFIG_HOSTNAME) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTFILE
"bootfile=" MK_STR(CONFIG_BOOTFILE) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LOADADDR
"loadaddr=" MK_STR(CONFIG_LOADADDR) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CLOCKS_IN_MHZ
"clocks_in_mhz=1\0"
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_PCI_BOOTDELAY) && (CONFIG_PCI_BOOTDELAY > 0)
"pcidelay=" MK_STR(CONFIG_PCI_BOOTDELAY) "\0"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_EXTRA_ENV_SETTINGS
CONFIG_EXTRA_ENV_SETTINGS
#endif
"\0"
};若有效则加载flash中的环境变量
memcpy (env_ptr, (void*)flash_addr, CONFIG_ENV_SIZE);最后使用gd->env_addr来保存地址
⑤其他初始化(包含串口控制台,网络等)
⑥等待串口命令main_loop(默认启动内核)
默认启动内核一项,主要是环境变量中的bootcmd
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT
if (bootlimit && (bootcount > bootlimit)) {
printf ("Warning: Bootlimit (%u) exceeded. Using altbootcmd.\n",
(unsigned)bootlimit);
s = getenv ("altbootcmd");
}
else
#endif /* CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT */
s = getenv ("bootcmd");
debug ("### main_loop: bootcmd=\"%s\"\n", s ? s : "");
if (bootdelay >= 0 && s && !abortboot (bootdelay)) {
# ifdef CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED
int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking */
# endif
# ifndef CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSER
run_command (s, 0);
# else
parse_string_outer(s, FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON |
FLAG_EXIT_FROM_LOOP);
# endif
# ifdef CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED
disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
# endif
} 若无这一项,则不存在自动启动内核部分,而是不断地解析命令而已
for (;;) {
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOT_RETRY_TIME
if (rc >= 0) {
/* Saw enough of a valid command to
* restart the timeout.
*/
reset_cmd_timeout();
}
#endif
len = readline (CONFIG_SYS_PROMPT);
flag = 0; /* assume no special flags for now */
if (len > 0)
strcpy (lastcommand, console_buffer);
else if (len == 0)
flag |= CMD_FLAG_REPEAT;
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOT_RETRY_TIME
else if (len == -2) {
/* -2 means timed out, retry autoboot
*/
puts ("\nTimed out waiting for command\n");
# ifdef CONFIG_RESET_TO_RETRY
/* Reinit board to run initialization code again */
do_reset (NULL, 0, 0, NULL);
# else
return; /* retry autoboot */
# endif
}
#endif
if (len == -1)
puts ("\n");
else
rc = run_command (lastcommand, flag);
/* invalid command or not repeatable, forget it */
lastcommand[0] = 0;
} (3)u-boot终点
前面其实已经谈到了u-boot的终点即bootcmd中的命令,通过查找定义
#define CONFIG_BOOTCOMMAND "sf probe 0;sf read 0x82000000 0x100000 0x400000;bootm 0x82000000"结合之前Hi3520D SDK 安装以及升级使用说明.txt中烧写命令的介绍,最终确定是依赖于bootm命令启动内核(前面的命令是spi flash的操作,即将flash偏移0x100000的0x400000长度的内核,读取到内存的0x82000000地址处)。这里也简单介绍一下u-boot命令的组成,在u-boot根目录/common目录下存在许多cmd开头的c文件,其中这些就是u-boot中的命令组成,其中bootm命令对应的就是cmd_bootm.c。除此之外,每一个命令C文件中都包含至少一个U_BOOT_CMD结构,如下
U_BOOT_CMD(
bootm, CONFIG_SYS_MAXARGS, 1, do_bootm,
"boot application image from memory",
"[addr [arg ...]]\n - boot application image stored in memory\n"
"\tpassing arguments 'arg ...'; when booting a Linux kernel,\n"
"\t'arg' can be the address of an initrd image\n"
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_LIBFDT)
"\tWhen booting a Linux kernel which requires a flat device-tree\n"
"\ta third argument is required which is the address of the\n"
"\tdevice-tree blob. To boot that kernel without an initrd image,\n"
"\tuse a '-' for the second argument. If you do not pass a third\n"
"\ta bd_info struct will be passed instead\n"
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_FIT)
"\t\nFor the new multi component uImage format (FIT) addresses\n"
"\tmust be extened to include component or configuration unit name:\n"
"\taddr: - direct component image specification\n"
"\taddr# - configuration specification\n"
"\tUse iminfo command to get the list of existing component\n"
"\timages and configurations.\n"
#endif
"\nSub-commands to do part of the bootm sequence. The sub-commands "
"must be\n"
"issued in the order below (it's ok to not issue all sub-commands):\n"
"\tstart [addr [arg ...]]\n"
"\tloados - load OS image\n"
#if defined(CONFIG_PPC) || defined(CONFIG_M68K) || defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
"\tramdisk - relocate initrd, set env initrd_start/initrd_end\n"
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_LIBFDT)
"\tfdt - relocate flat device tree\n"
#endif
"\tcmdline - OS specific command line processing/setup\n"
"\tbdt - OS specific bd_t processing\n"
"\tprep - OS specific prep before relocation or go\n"
"\tgo - start OS"
); struct cmd_tbl_s {
char *name; /* Command Name */
int maxargs; /* maximum number of arguments */
int repeatable; /* autorepeat allowed? */
/* Implementation function */
int (*cmd)(struct cmd_tbl_s *, int, int, char *[]);
char *usage; /* Usage message (short) */
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP
char *help; /* Help message (long) */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE
/* do auto completion on the arguments */
int (*complete)(int argc, char *argv[], char last_char, int maxv, char *cmdv[]);
#endif
};
#define Struct_Section __attribute__ ((unused,section (".u_boot_cmd")))
typedef struct cmd_tbl_s cmd_tbl_t;
#define U_BOOT_CMD(name,maxargs,rep,cmd,usage,help) \
cmd_tbl_t __u_boot_cmd_##name Struct_Section = {#name, maxargs, rep, cmd, usage, help}每用U_BOOT_CMD定义一个,就相当于定义了一个__u_boot_cmd_xxx结构,存放于.u_boot_cmd段中(在链接器脚本中有说明),每个命令的查找过程在run_command函数中实现
①find_cmd(比对是否有与输入字符串name相同的cmd_tbl_t结构)
②校验maxargs(输入参数不得大于这个值,命令不带参数也是有一个argc的)
③调用相应的cmd函数进行执行
也就是说,bootm命令最终将调用do_bootm函数来完成启动内核的操作:
①bootm_start(在指定的内存地址中寻找可用的内核镜像,并剥离出镜像的os类型,赋值images.ep等)
②bootm_load_os(将镜像的数据从images.os.image_start复制到images.os.load 打印:Loading Kernel Image)
③boot_fn(由boot_os[images.os.os]进行赋值,根据操作系统的类型获取引导操作系统的函数,即do_bootm_linux)
④theKernel = (void (*)(int, int, uint))images->ep
这本只是一个赋值,但是需要说明images->ep,即在bootm_start中赋值的真相:
在u-boot根目录/tools下的mkimage.c文件中main函数
case 'e':
if (--argc <= 0)
usage ();
params.ep = strtoul (*++argv, &ptr, 16);
if (*ptr) {
fprintf (stderr,
"%s: invalid entry point %s\n",
params.cmdname, *argv);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
params.eflag = 1;
goto NXTARG;当使用mkimage这个命令的-e选项后,将指定images->ep的位置,而mkimage的调用处需要追到内核编译部分了
linux源码根目录/arch/arm/boot的Makefile说明了这个问题
# Note: the following conditions must always be true:
# ZRELADDR == virt_to_phys(PAGE_OFFSET + TEXT_OFFSET)
# PARAMS_PHYS must be within 4MB of ZRELADDR
# INITRD_PHYS must be in RAM
ZRELADDR := $(zreladdr-y)
PARAMS_PHYS := $(params_phys-y)
INITRD_PHYS := $(initrd_phys-y)
quiet_cmd_uimage = UIMAGE $@
cmd_uimage = $(CONFIG_SHELL) $(MKIMAGE) -A arm -O linux -T kernel \
-C none -a $(LOADADDR) -e $(STARTADDR) \
-n 'Linux-$(KERNELRELEASE)' -d $< $@
ifeq ($(CONFIG_ZBOOT_ROM),y)
$(obj)/uImage: LOADADDR=$(CONFIG_ZBOOT_ROM_TEXT)
else
$(obj)/uImage: LOADADDR=$(ZRELADDR)
endif
$(obj)/uImage: STARTADDR=$(LOADADDR)由于CONFIG_ZBOOT_ROM这个宏在linux源码根目录下的.config(即linux源码根目录/arch/arm/configs下的hi3520d_full_defconfig)中是未定义的,因此-e选项就确定了值为ZRELADDR,即zreladdr-y,在linux源码根目录/arch/arm/mach-3520d的Makefile.boot中最终确认
zreladdr-y := 0x80008000
params_phys-y := 0x00000100
initrd_phys-y := 0x00800000若不想这么复杂,可在编译内核后,存在于linux源码根目录/arch/arm/boot下的.uImage.cmd中进行查看
cmd_arch/arm/boot/uImage := /bin/sh /home/callon-huang/Documents/Hi3520D_SDK_V1.0.4.0/osdrv/kernel/linux-3.0.y/scripts/mkuboot.sh -A arm -O linux -T kernel -C none -a 0x80008000 -e 0x80008000 -n 'Linux-3.0.8' -d arch/arm/boot/zImage arch/arm/boot/uImage由于这个images->ep是从mkimage命令生成的uImage中确定下来的,因此来寻找到正确的镜像后,自然也可以确定整个内核镜像的入口了
⑤设置bd->bi_boot_params给内核传参
#if defined (CONFIG_SETUP_MEMORY_TAGS) || \
defined (CONFIG_CMDLINE_TAG) || \
defined (CONFIG_INITRD_TAG) || \
defined (CONFIG_SERIAL_TAG) || \
defined (CONFIG_REVISION_TAG)
setup_start_tag (bd);
#ifdef CONFIG_SERIAL_TAG
setup_serial_tag (bd);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_REVISION_TAG
setup_revision_tag (bd);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SETUP_MEMORY_TAGS
setup_memory_tags (bd);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CMDLINE_TAG
setup_commandline_tag (bd, commandline);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_INITRD_TAG
if (images->rd_start && images->rd_end)
setup_initrd_tag (bd, images->rd_start, images->rd_end);
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_ETHMDIO_INF)
setup_eth_mdiointf_tag(bd, getenv("mdio_intf"));
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_ETHADDR_TAG)
setup_ethaddr_tag(bd, getenv("ethaddr"));
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_NANDID_TAG)
setup_nandid_tag(bd);
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_SPIID_TAG)
setup_spiid_tag(bd);
#endif
setup_end_tag (bd);
#endif#if defined(CONFIG_SETUP_MEMORY_TAGS) || \
defined(CONFIG_CMDLINE_TAG) || \
defined(CONFIG_INITRD_TAG) || \
defined(CONFIG_SERIAL_TAG) || \
defined(CONFIG_REVISION_TAG) || \
defined(CONFIG_ETHADDR_TAG)
static void setup_start_tag (bd_t *bd)
{
params = (struct tag *) bd->bi_boot_params;
params->hdr.tag = ATAG_CORE;
params->hdr.size = tag_size (tag_core);
params->u.core.flags = 0;
params->u.core.pagesize = 0;
params->u.core.rootdev = 0;
params = tag_next (params);
}
static void setup_end_tag (bd_t *bd)
{
params->hdr.tag = ATAG_NONE;
params->hdr.size = 0;
}从setup_start_tag到setup_end_tag,中间都是在进行一系列的对bd->bi_boot_params的赋值操作,而该区域也是在board_init中指明了为内存中的CFG_BOOT_PARAMS地址处,随后打印Starting kernel ...
⑥启动内核
theKernel (0, machid, bd->bi_boot_params);这里便是u-boot的终点,即内核的起点,分析内核时也将根据该地址来找寻内核的起点,一步步往下分析,在此同时附上打印和u-boot中函数调用的对应关系:
2. u-boot命令新增-update
u-boot命令的解析方式了解后,添加就很简单了,在u-boot根目录/common下操作即可
①修改Makefile,添加如下行
COBJS-y += cmd_update.o②添加cmd_update.c,添加代码如下
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_DATAFLASH
#include
#endif
#include
#include
#include
#include
#ifndef CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_SPEED
# define CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_SPEED 1000000
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_MODE
# define CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_MODE SPI_MODE_3
#endif
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_MEM_WRITE_ADDR "82000000"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_MEM_WRITE_VALUE "ff"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_SIZE "100000"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_UIMAGE_SIZE "400000"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_ROOTFS_SIZE "b00000"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP_LOAD_ADDR "0x82000000"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_FILE_NAME "u-boot_hi3520d.bin"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_UIMAGE_FILE_NAME "uImage_hi3520d_full"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_ROOTFS_FILE_NAME "rootfs.jffs2"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_ERASE_ADDR "0"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_UIMAGE_ERASE_ADDR "100000"
#define CONFIG_UPDATE_ROOTFS_ERASE_ADDR "500000"
static struct spi_flash *flash;
static int do_spi_flash_probe(unsigned int cs)
{
struct spi_flash *new;
new = spi_flash_probe(0, cs, CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_SPEED, CONFIG_SF_DEFAULT_MODE);
if (!new)
{
printf("Failed to initialize SPI flash at %u:%u\n", 0, 0);
return 1;
}
if (flash)
spi_flash_free(flash);
flash = new;
printf("%u KiB %s at %u:%u is now current device\n",
flash->size >> 10, flash->name, 0, cs);
return 0;
}
static int do_mem_write_byte(const char *addr, const char *val, const char *size)
{
ulong address, writeval, count;
/* Address is specified since argc > 1
*/
address = simple_strtoul(addr, NULL, 16);
/* Get the value to write.
*/
writeval = simple_strtoul(val, NULL, 16);
count = simple_strtoul(size, NULL, 16);
while (count-- > 0) {
*((u_char *)address) = (u_char)writeval;
address += 1;
}
return 0;
}
static int do_spi_flash_erase(const char *addr, const char *len)
{
unsigned long offset;
unsigned long length;
char *endp;
int ret;
struct mtd_info_ex *spiflash_info = get_spiflash_info();
unsigned long erase_start, erase_len, erase_step;
int percent_complete = -1;
offset = simple_strtoul(addr, &endp, 16);
length = simple_strtoul(len, &endp, 16);
if (offset + length > spiflash_info->chipsize * spiflash_info->numchips) {
printf("ERROR: erase area is out of range!\n\n");
return 1;
}
if (offset & (spiflash_info->erasesize-1)) {
printf("ERROR: erase start address is not block aligned!\n\n");
return 1;
}
if (length & (spiflash_info->erasesize-1)) {
printf("ERROR: erase length is not block aligned!\n\n");
return 1;
}
erase_start = offset;
erase_len = length;
erase_step = spiflash_info->erasesize;
while (length > 0) {
if (length < erase_step)
erase_step = length;
ret = spi_flash_erase(flash, offset, erase_step);
if (ret) {
printf("SPI flash erase failed\n");
return 1;
}
length -= erase_step;
offset += erase_step;
do {
unsigned long long n = (unsigned long long)
(offset - erase_start) * 100;
int percent;
do_div(n, erase_len);
percent = (int)n;
/* output progress message only at whole percent
* steps to reduce the number of messages printed
* on (slow) serial consoles
*/
if (percent != percent_complete) {
percent_complete = percent;
printf("\rErasing at 0x%lx -- %3d%% complete.",
offset, percent);
}
} while (0);
}
puts("\n");
return 0;
}
static int do_spi_flash_write(const char *from, const char *to, const char *len)
{
unsigned long addr;
unsigned long offset;
unsigned long length;
void *buf;
char *endp;
int ret;
struct mtd_info_ex *spiflash_info = get_spiflash_info();
addr = simple_strtoul(from, &endp, 16);
offset = simple_strtoul(to, &endp, 16);
length = simple_strtoul(len, &endp, 16);
if (offset + length >
spiflash_info->chipsize * spiflash_info->numchips) {
printf(
"ERROR: read/write area is out of range!\n\n");
return -1;
}
buf = map_physmem(addr, length, MAP_WRBACK);
if (!buf) {
puts("Failed to map physical memory\n");
return 1;
}
do{
unsigned long write_start, write_len, write_step;
int percent_complete = -1;
char *pbuf = buf;
write_start = offset;
write_len = length;
write_step = spiflash_info->erasesize;
while (length > 0) {
if (length < write_step)
write_step = length;
ret = spi_flash_write(flash, offset, write_step, pbuf);
if (ret)
break;
offset += write_step;
pbuf += write_step;
length -= write_step;
do {
unsigned long long n = (unsigned long long)
(offset - write_start) * 100;
int percent;
do_div(n, write_len);
percent = (int)n;
/* output progress message only at whole percent
* steps to reduce the number of messages
* printed on (slow) serial consoles
*/
if (percent != percent_complete) {
percent_complete = percent;
printf("\rWriting at 0x%lx -- %3d%% "
"complete.", offset, percent);
}
} while (0);
}
}while(0);
puts("\n");
unmap_physmem(buf, length);
if (ret) {
printf("SPI flash write failed\n");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
static void netboot_update_env (void)
{
char tmp[22];
if (NetOurGatewayIP) {
ip_to_string (NetOurGatewayIP, tmp);
setenv ("gatewayip", tmp);
}
if (NetOurSubnetMask) {
ip_to_string (NetOurSubnetMask, tmp);
setenv ("netmask", tmp);
}
if (NetOurHostName[0])
setenv ("hostname", NetOurHostName);
if (NetOurRootPath[0])
setenv ("rootpath", NetOurRootPath);
if (NetOurIP) {
ip_to_string (NetOurIP, tmp);
setenv ("ipaddr", tmp);
}
if (NetServerIP) {
ip_to_string (NetServerIP, tmp);
setenv ("serverip", tmp);
}
if (NetOurDNSIP) {
ip_to_string (NetOurDNSIP, tmp);
setenv ("dnsip", tmp);
}
#if defined(CONFIG_BOOTP_DNS2)
if (NetOurDNS2IP) {
ip_to_string (NetOurDNS2IP, tmp);
setenv ("dnsip2", tmp);
}
#endif
if (NetOurNISDomain[0])
setenv ("domain", NetOurNISDomain);
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_SNTP) \
&& defined(CONFIG_BOOTP_TIMEOFFSET)
if (NetTimeOffset) {
sprintf (tmp, "%d", NetTimeOffset);
setenv ("timeoffset", tmp);
}
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_SNTP) \
&& defined(CONFIG_BOOTP_NTPSERVER)
if (NetNtpServerIP) {
ip_to_string (NetNtpServerIP, tmp);
setenv ("ntpserverip", tmp);
}
#endif
}
static int
netboot_common (const char *start_addr, const char *file_name)
{
extern ulong upload_addr;
extern ulong upload_size;
char *s;
char *end;
int rcode = 0;
int size;
ulong addr;
load_addr = simple_strtoul(start_addr, NULL, 16);
copy_filename (BootFile, file_name, sizeof(BootFile));
upload_size = 0;
show_boot_progress (80);
if ((size = NetLoop(TFTP)) < 0) {
show_boot_progress (-81);
return 1;
}
show_boot_progress (81);
/* NetLoop ok, update environment */
netboot_update_env();
/* done if no file was loaded (no errors though) */
if (size == 0) {
show_boot_progress (-82);
return 0;
}
/* flush cache */
flush_cache(load_addr, size);
show_boot_progress (84);
return 0;
}
static int do_update(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc > 2 ||
(strcmp(argv[1], "1") != 0
&& strcmp(argv[1], "2") != 0
&& strcmp(argv[1], "3") != 0))
{
goto usage;
}
printf("start update...\n");
do{
char *update_size = NULL;
char *update_name = NULL;
char *update_addr = NULL;
int cmd = simple_strtoul(argv[1], NULL, 16);
switch(cmd)
{
case 1:
update_size = CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_SIZE;
update_name = CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_FILE_NAME;
update_addr = CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_ERASE_ADDR;
printf("select uboot\n");
break;
case 2:
update_size = CONFIG_UPDATE_UIMAGE_SIZE;
update_name = CONFIG_UPDATE_UIMAGE_FILE_NAME;
update_addr = CONFIG_UPDATE_UIMAGE_ERASE_ADDR;
printf("select uImage\n");
break;
case 3:
update_size = CONFIG_UPDATE_ROOTFS_SIZE;
update_name = CONFIG_UPDATE_ROOTFS_FILE_NAME;
update_addr = CONFIG_UPDATE_ROOTFS_ERASE_ADDR;
printf("select rootfs\n");
break;
default:
update_size = CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_SIZE;
update_name = CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_FILE_NAME;
update_addr = CONFIG_UPDATE_UBOOT_ERASE_ADDR;
printf("select uboot\n");
break;
}
if (0 != do_spi_flash_probe(0))
{
printf("do_spi_flash_probe is err!\n");
return 1;
}
if (0 != do_mem_write_byte(CONFIG_UPDATE_MEM_WRITE_ADDR, CONFIG_UPDATE_MEM_WRITE_VALUE, update_size))
{
printf("do_mem_write_byte is err!\n");
return 1;
}
if (0 != netboot_common (CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP_LOAD_ADDR, update_name))
{
printf("netboot_common is err!\n");
return 1;
}
if (0 != do_spi_flash_probe(0))
{
printf("do_spi_flash_probe is err!\n");
return 1;
}
if (0 != do_spi_flash_erase(update_addr, update_size))
{
printf("do_spi_flash_erase is err!\n");
return 1;
}
if (0 != do_spi_flash_write(CONFIG_UPDATE_MEM_WRITE_ADDR, update_addr, update_size))
{
printf("do_spi_flash_write is err!\n");
return 1;
}
}while(0);
printf("update successfully!\n");
return 0;
usage:
cmd_usage(cmdtp);
return 1;
}
U_BOOT_CMD(
update, 2, 1, do_update,
"Usage - update with one param to select file.",
"update 1 - select u-boot_hi3520d.bin\n"
"update 2 - select uImage_hi3520d_full\n"
"update 3 - select rootfs.jffs2\n"
"update command will find the image automatically!\n"
"make sure the network(tftp server) first!\n"
); 所有实现原理基本是参照u-boot、kernel、根文件系统的烧写流程来的,子函数的实现方式基本为其他的cmd函数中的方式,如sf probe 0这个命令,找到cmd_sf.c便可把它的实现找出来,移植到自己代码中便可。实现了update命令,便可不通过繁杂的操作,直接可以实现一个命令完成tftp->erase->write整套流程,还是很方便的,感兴趣的朋友可以尝试下。