深入学习SpringAOP源码(三)——揭开JDK动态代理和CGLIB代理的神秘面纱
前言
版本:【Spring 5.1.4】、【SpringAOP 5.1.4】
经过前两个章节的介绍,已经了解了Spring是如何注册解析AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,然后AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator又是如何解析通知、创建代理,创建代理的目的又是什么呢?那么接下来本片文章将从深入解析源码的方式并借以《深入学习SpringAOP源码(一)》里Demo为例,来揭开JDK动态代理和CGLIB代理。
深入学习SpringAOP源码(一)——注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
深入学习SpringAOP源码(二)—— 深入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
正文
1. CGLIB动态代理
1.1 引入简单的CGLIB例子
在讲解CGLIB动态代理之前,先看一下最简单的CGLIB动态代理的例子。
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class EnhancerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(EnhancerDemo.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptorImpl());
EnhancerDemo demo = (EnhancerDemo) enhancer.create();
demo.test();
System.out.println(demo);
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("EnhancerDemo test()");
}
private static class MethodInterceptorImpl implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.err.println("Before invoke " + method);
Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
System.err.println("After invoke" + method);
return result;
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
EnhancerDemo test()
After invokepublic void com.bruis.learnaop.testcglibaop.EnhancerDemo.test()
Before invoke public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()
Before invoke public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
After invokepublic native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
After invokepublic java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()
com.bruis.learnaop.testcglibaop.EnhancerDemo$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$413eae0d@53e25b76
可以看到运行结果,除了demo.test()方法之外,System.our.println(demo)也被代理了,首先调用了toString()方法,然后又调用了hashCode,生成的对象为EnhancerDemo的实例,这个类是运行时由CGLIB产生的,Enhancer最关键的步骤就是setCallback()方法来设置拦截器,来拦截代理类的方法。Demo中用到的Enhancer是CGLIB的字节码增强器,用于为无接口的类创建代理proxy,方便对代理类进行拓展,Demo中的代理类就是EnhancerDemo。它的功能与java自带的Proxy类挺相似的,它会根据某个给定的类创建子类,并且非final的方法都带有回调方法。
创建代理对象的几个步骤:
- 生成代理类的二进制字节码文件
- 加载二进制字节码,生成Class对象(例如使用Class.forName()方法)
- 通过反射机制获取实例构造,并创建代理类对象
具体可以查看Enhancer create()源码方法。
1.2 深入代理逻辑源码
回到SpringAOP源码。在《深入学习SpringAOP源码(二)》中,介绍到DefaultAopProxyFactory源码部分
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (!config.isOptimize() && !config.isProxyTargetClass() && !this.hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
} else {
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
} else {
return (AopProxy)(!targetClass.isInterface() && !Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) ? new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config) : new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config));
}
}
}
}
从createAopProxy()源码中可以看到,创建SpringAOP有两种方式,一、JDK动态代理;二、CGLIB动态代理;点进ObjenesisCglibAopProxy源码,发现它继承了CglibAopFactory
class ObjenesisCglibAopProxy extends CglibAopProxy {
protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) {
// 通过增强器获取代理类的class对象
Class proxyClass = enhancer.createClass();
Object proxyInstance = null;
if (objenesis.isWorthTrying()) {
try {
// 创建代理类实例对象
proxyInstance = objenesis.newInstance(proxyClass, enhancer.getUseCache());
} catch (Throwable var7) {
logger.debug("Unable to instantiate proxy using Objenesis, falling back to regular proxy construction", var7);
}
}
if (proxyInstance == null) {
try {
Constructor ctor = this.constructorArgs != null ? proxyClass.getDeclaredConstructor(this.constructorArgTypes) : proxyClass.getDeclaredConstructor();
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
proxyInstance = this.constructorArgs != null ? ctor.newInstance(this.constructorArgs) : ctor.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable var6) {
throw new AopConfigException("Unable to instantiate proxy using Objenesis, and regular proxy instantiation via default constructor fails as well", var6);
}
}
// 为代理类实例创建回调方法(拦截器链)
((Factory)proxyInstance).setCallbacks(callbacks);
return proxyInstance;
}
}
createProxyClassAndInstance方法和前面总结的CGLIB创建代理的步骤一样。
继续查看CglibAopProxy是如何准备Enhancer增强器以及创建拦截器链的。
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
// 获取目标代理类
Class rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class proxySuperClass = rootClass;
int x;
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
Class[] var5 = additionalInterfaces;
int var6 = additionalInterfaces.length;
for(x = 0; x < var6; ++x) {
Class additionalInterface = var5[x];
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// 验证class
this.validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// 获取增强器
Enhancer enhancer = this.createEnhancer();
// 为Enhancer设置类加载器
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && ((SmartClassLoader)classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
// 设置代理类,这一步很关键哦。
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
// 设置strategy策略器
enhancer.setStrategy(new CglibAopProxy.ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = this.getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class[] types = new Class[callbacks.length];
for(x = 0; x < types.length; ++x) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// 设置回调过滤器
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new CglibAopProxy.ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// 创建代理类实例,调用子类的createProxyClassAndInstance()方法
return this.createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | CodeGenerationException var9) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() + ": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class", var9);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", var10);
}
}
// 获取回调方法
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class rootClass) throws Exception {
// 获取expose-proxy属性设置
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
// 将aop拦截器封装在DynamicAdvisedInterceptor中
Callback aopInterceptor = new CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
Object targetInterceptor;
if (exposeProxy) {
targetInterceptor = isStatic ? new CglibAopProxy.StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new CglibAopProxy.DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource());
} else {
targetInterceptor = isStatic ? new CglibAopProxy.StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new CglibAopProxy.DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Callback targetDispatcher = isStatic ? new CglibAopProxy.StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new CglibAopProxy.SerializableNoOp();
// 添加主要的拦截器链
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[]{aopInterceptor, (Callback)targetInterceptor, new CglibAopProxy.SerializableNoOp(), (Callback)targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher, new CglibAopProxy.EqualsInterceptor(this.advised), new CglibAopProxy.HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)};
Callback[] callbacks;
if (isStatic && isFrozen) {
Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();
Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];
this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap(methods.length);
for(int x = 0; x < methods.length; ++x) {
List拦截器链在CGLIB中扮演者重要角色,从上面源码中看出拦截器被封装为了DynamicAdvisedInterceptor,那么其核心逻辑就应该在DynamicAdvisedInterceptor中,那看看DynamicAdvisedInterceptor都做了哪些事情。
1.3 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor都做了些啥工作?
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
// 获取要拦截的通知源
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
Object var16;
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class targetClass = target != null ? target.getClass() : null;
// 获取拦截器链,这里的拦截器链是啥?从哪获取拦截器链?
List1.4 啥是拦截器链?拦截器链从哪获取?
啥是拦截器链?从哪获取拦截器链?下面继续深入DefaultAdvisorChainFactory方法的getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice()方法
public class DefaultAdvisorChainFactory implements AdvisorChainFactory, Serializable {
public List在DefaultAdvisorChainFactory的getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice方法中,主要工作是:
- 先获取通知适配器注册器
- 将注册器包装为可用的拦截器
在这过程中,DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry扮演者非常关键的角色。
public class DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry implements AdvisorAdapterRegistry, Serializable {
private final List adapters = new ArrayList(3);
// 在构造方法里注册前置通知、后置通知和异常通知的适配器,
public DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry() {
this.registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter());
this.registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter());
this.registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter());
}
// wrap方法在AbstractAutoProxyCreator的buildAdvisors方法中已经讲解到了,用于构建Advisor数组,这里就不再讲解
public Advisor wrap(Object adviceObject) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
if (adviceObject instanceof Advisor) {
return (Advisor)adviceObject;
} else if (!(adviceObject instanceof Advice)) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(adviceObject);
} else {
Advice advice = (Advice)adviceObject;
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice);
} else {
Iterator var3 = this.adapters.iterator();
AdvisorAdapter adapter;
do {
if (!var3.hasNext()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advice);
}
adapter = (AdvisorAdapter)var3.next();
} while(!adapter.supportsAdvice(advice));
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice);
}
}
}
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List interceptors = new ArrayList(3);
// 获取通知
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
// 判断通知是否是MethodInterceptor类型
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor)advice);
}
Iterator var4 = this.adapters.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
// 将通知强转为AdvisorAdapter类型
AdvisorAdapter adapter = (AdvisorAdapter)var4.next();
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
} else {
return (MethodInterceptor[])interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[0]);
}
}
public void registerAdvisorAdapter(AdvisorAdapter adapter) {
this.adapters.add(adapter);
}
}
DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry类主要负责:
- 在构造方法里注册前置通知、后置通知和异常通知的适配器
- 包装Advisor
- 将Advisor包装为拦截器
既然获取到了拦截器链,那么每个拦截器链都做了些啥呢?回到DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的intercept()方法
1.5 调用拦截器链的proceed方法
视线回到DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的intercept方法,在
List chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
执行完成之后,chain中存放好了拦截器链,分别是
- ExposeInvocationInterceptor
- AspectJAfterAdvice
- AspectJAroundAdvice
- MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
List chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
// 如果拦截器链为空,则直接进入拦截器链
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
} else {
// 调用拦截器链的proceed方法
retVal = (new CglibAopProxy.CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy)).proceed();
}
retVal = CglibAopProxy.processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
var16 = retVal;
后置通知实现逻辑:
public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
Object var2;
try {
var2 = mi.proceed();
} finally {
this.invokeAdviceMethod(this.getJoinPointMatch(), (Object)null, (Throwable)null);
}
return var2;
}
}
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
protected final Object proxy;
@Nullable
protected final Object target;
protected final Method method;
protected Object[] arguments = new Object[0];
@Nullable
private final Class targetClass;
@Nullable
private Map userAttributes;
protected final List interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
private int currentInterceptorIndex = -1;
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return this.invokeJoinpoint();
} else {
// 获取拦截器链的元素
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class targetClass = this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass();
return dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments) ? dm.interceptor.invoke(this) : this.proceed();
} else {
return ((MethodInterceptor)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
}
}
这里总结下proceed的逻辑:
- 根据索引值获取拦截器链中的拦截器
- 要么调用拦截器的invoke方法,要么就调用proceed进行下一轮的递归
- proceed方法在这里起到了递归的作用
环绕通知实现逻辑:
public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
} else {
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation)mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = this.lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
JoinPointMatch jpm = this.getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
return this.invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, (Object)null, (Throwable)null);
}
}
protected ProceedingJoinPoint lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(ProxyMethodInvocation rmi) {
return new MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint(rmi);
}
}
public abstract class AbstractAspectJAdvice implements Advice, AspectJPrecedenceInformation, Serializable {
protected Object invokeAdviceMethod(JoinPoint jp, @Nullable JoinPointMatch jpMatch, @Nullable Object returnValue, @Nullable Throwable t) throws Throwable {
return this.invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(this.argBinding(jp, jpMatch, returnValue, t));
}
protected Object invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object[] actualArgs = args;
if (this.aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterCount() == 0) {
actualArgs = null;
}
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.aspectJAdviceMethod);
return this.aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke(this.aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectInstance(), actualArgs);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException var4) {
throw new AopInvocationException("Mismatch on arguments to advice method [" + this.aspectJAdviceMethod + "]; pointcut expression [" + this.pointcut.getPointcutExpression() + "]", var4);
} catch (InvocationTargetException var5) {
throw var5.getTargetException();
}
}
}
总结下:
- AspectJAroundAdvice的invoke方法作用为获取代理方法以及正在处理的切点对象
- 将代理方法、切点信息传入AbstractAspectJAdvice的invokeAdviceMethod里进行进一步的参数绑定
- invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs方法调用aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke方法,调用AspectJTest类中aroundTest方法
前置通知实现逻辑:
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable {
private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return mi.proceed();
}
}
public class AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice, Serializable {
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, @Nullable Object target) throws Throwable {
this.invokeAdviceMethod(this.getJoinPointMatch(), (Object)null, (Throwable)null);
}
}
可以注意到:
- 代理类的before方法是由AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice类before方法执行的
- 在before方法执行完后,调用了MethodInvocation的proceed方法,最终是回到了AspectJAfterAdvice的invoke方法
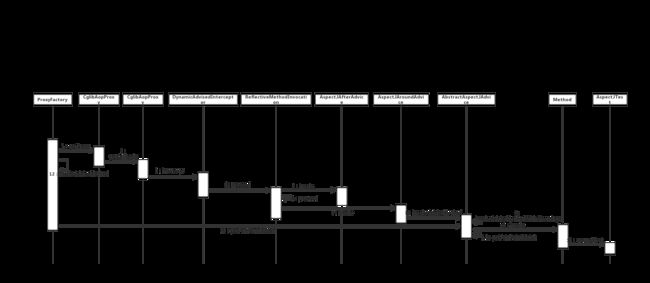
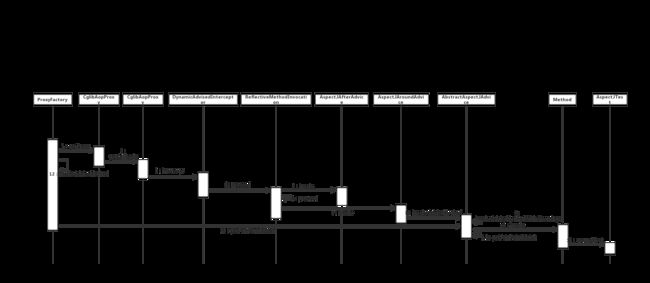
这整个过程随着AspectJAfterAdvice执行完,整个Demo代码也都走完了。虽然结合着文章开头的时序图,辅以源码来学习整个SpringAOP的运作过程,但也并不能把整个过程描述的非常清楚,下面以本人非常喜欢的一种方式把整个过程展开来。


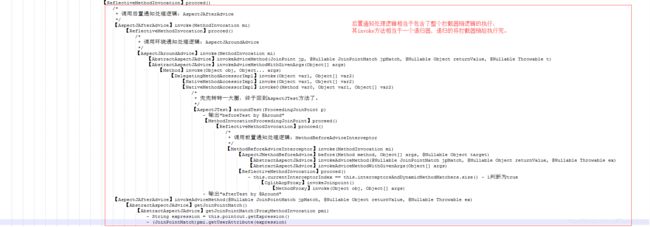
以上面这种文本方式,结合着时序图,能够进一步加深对CGLIB源码逻辑的理解。
2. JDK动态代理
未完待续…