支持向量机的代码实现
前言:
本篇文章主要实现了《机器学习实战》的支持向量机部分,我在代码中也尽量描述了对应公式的哪些变量。我建议搭配《统计学习方法》进行实战,下面这篇博文对于公式推导也是很不错的。
https://blog.csdn.net/u011067360/article/details/26503719
另外本篇依赖于jupyter notebook。故在代码后面会出现相应的结果。
正文:
SMO算法求支持向量机
SMO算法中的辅助函数
def loadDataSet(fileName):
"""读取数据"""
dataMat = [];labelMat = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr = line.strip().split('\t')
dataMat.append([float(lineArr[0]),float(lineArr[1])])
labelMat.append(float(lineArr[2]))
return dataMat,labelMatdef selectJrand(i,m):
"""
参数i:第一个alpha的下标,参数m:所有alpha的数目
在某个区间范围随机取一个整数
"""
j = i
while(j == i ):
j = int (random.uniform(0,m))
return jdef clipAlpha(aj,H,L):
"""用于在数值太大时进行调整"""
if aj > H:
aj = H
if L > aj:
aj = L
return ajdataArr,labelArr = loadDataSet("E:\\DataMining\\Project\\MLBook\\机器学习实战源代码\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch06\\testSet.txt")简化版SMO算法
def smoSimple(dataMatIn,classLabels,C,toler,maxIter):
"""参数dtatMatIn:数据集
参数classLabels:类别标签
参数C:常数C
参数toler:容错率
参数maxIter:退出前最大的循环次数"""
dataMatrix = mat(dataMatIn);labelMat =mat(classLabels).transpose()
b = 0;m,n = shape(dataMatrix)
alphas = mat(zeros((m,1)))
iter = 0 #储存在没有任何alpha改变的情况下遍历数据集的次数
while(iter < maxIter):
alphaPairsChanged = 0 #记录alpha是否已优化
for i in range(m):
#multiply() 数组元素对应相乘
#fXi 是预测值
fXi = float(multiply(alphas,labelMat).T *\
(dataMatrix * dataMatrix[i,:].T)) + b
Ei = fXi - float(labelMat[i])
#违反KKT条件最严重
# 以下几种情况出现将会出现不满足:(ui是预测值,ai是变量alpha)
#yiui<=1但是ai
#yiui>=1但是ai>0则是不满足的而原本ai=0
#yiui=1但是ai=0或者ai=C则表明不满足的,而原本应该是0
#所以要找出不满足KKT的这些ai,并更新这些ai
#在考虑这些点时有首先考虑0
if ((labelMat[i]*Ei < -toler) and (alphas[i] < C)) or \
((labelMat[i]*Ei > toler) and (alphas[i] > 0)):
#随机选择第二个alpha
j = selectJrand(i,m)
fXj = float(multiply(alphas,labelMat).T*\
(dataMatrix*dataMatrix[j,:].T)) + b
Ej = fXj - float(labelMat[j])
alphaIold = alphas[i].copy();alphaJold = alphas[j].copy()
#对类别同号异号分开求上下界
if (labelMat[i] != labelMat[j]):
L = max(0,alphas[j] - alphas[i])
H = min (C,C + alphas[j] - alphas[i])
else:
L = max(0,alphas[j] + alphas[i] - C)
H = min(C,alphas[j] + alphas[i])
if L==H:
print('L==H')
continue
#最优修改量eta
eta = 2.0 * dataMatrix[i,:]*dataMatrix[j,:].T -\
dataMatrix[i,:]*dataMatrix[i,:].T -\
dataMatrix[j,:]*dataMatrix[j,:].T
if eta >= 0:
print('eta>=0')
continue
#之所以是-= 是因为前面eta的求法对比书上公式是相反数的
alphas[j] -= labelMat[j] * (Ei-Ej)/eta
alphas[j] = clipAlpha(alphas[j],H,L) #调整alpha[j]
if (abs(alphas[j] - alphaJold) < 0.00001):
print('j not moving enough')
continue
#对i进行修改,修改量与j相同,方向相反
alphas[i] += labelMat[j]*labelMat[i]*(alphaJold - alphas[j])
#重新计算阈值b
b1 = b - Ei -labelMat[i]*(alphas[i]- alphaIold)* \
dataMatrix[i,:]*dataMatrix[i,:].T - \
labelMat[j]*(alphas[j]-alphaJold)*dataMatrix[i,:]*dataMatrix[j,:].T
b2 = b - Ej -labelMat[i]*(alphas[i]- alphaIold)* \
dataMatrix[i,:]*dataMatrix[j,:].T - \
labelMat[j]*(alphas[j]-alphaJold)*dataMatrix[j,:]*dataMatrix[j,:].T
if (0 < alphas[i]) and (C > alphas[i]):
b = b1
elif (0 < alphas[j]) and (C > alphas[j]):
b = b2
else:
b = (b1 + b2 ) / 2.0
alphaPairsChanged += 1
print('iter:{0} i:{1} paris change {2}'.format(iter,i,alphaPairsChanged))
if (alphaPairsChanged == 0):
iter += 1
else:
iter = 0
print('iteration numebr :{}'.format(iter))
return b,alphas
from numpy import *
b,alphas = smoSimple(dataArr,labelArr,0.6,0.001,40)L==H
L==H
iter:0 i:8 paris change 2
j not moving enough
j not moving enough
iteration numebr :39
j not moving enough
j not moving enough
iteration numebr :40
bmatrix([[-3.85138014]])
alphas[alphas>0]matrix([[0.11792374, 0.243914 , 0.00461456, 0.35722318]])
了解哪些数据点是支持向量
for i in range(100):
if alphas[i] > 0.0:
print(dataArr[i],labelArr[i]) # 输出对应下标的样本点[4.658191, 3.507396] -1.0
[3.457096, -0.082216] -1.0
[5.286862, -2.358286] 1.0
[6.080573, 0.418886] 1.0
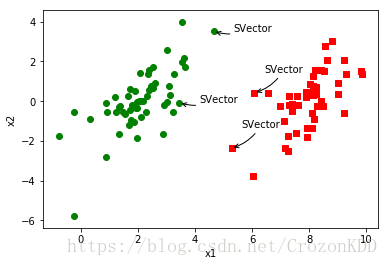
作图标记出来
def plotTool():
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dataMat,labelMat = loadDataSet("E:\\DataMining\\Project\\MLBook\\机器学习实战源代码\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch06\\testSet.txt")
dataArr = array(dataMat)
n = shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1 = [];ycord1 = []
xcord2 = [];ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if int (labelMat[i]) ==1:
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,0]);ycord1.append(dataArr[i,1])
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,0]);ycord2.append(dataArr[i,1])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1,ycord1,c='red',marker='s')
ax.scatter(xcord2,ycord2,c='green')
plt.xlabel('x1');plt.ylabel('x2')
#标记出支持向量
ax.annotate("SVector",xy=(4.658191, 3.507396),xycoords='data',xytext=(20,0),textcoords='offset points',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->',connectionstyle='arc3,rad=-0.2'))
ax.annotate("SVector",xy=(3.457096, -0.082216),xycoords='data',xytext=(20,0),textcoords='offset points',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->',connectionstyle='arc3,rad=-0.2'))
ax.annotate("SVector",xy=(5.286862, -2.358286),xycoords='data',xytext=(10,20),textcoords='offset points',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->',connectionstyle='arc3,rad=-0.2'))
ax.annotate("SVector",xy=(6.080573, 0.418886),xycoords='data',xytext=(10,20),textcoords='offset points',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->',connectionstyle='arc3,rad=-0.2'))
plt.show()plotTool()计算w值
def calWs(alphas,dataArr,classLabels):
X = mat(dataArr);labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose()
m,n = shape(X)
w = zeros((n,1))
for i in range(m):
w += multiply(alphas[i]*labelMat[i],X[i,:].T)
return ww = calWs(alphas,dataArr,labelArr)完整版Platt SMO的支持函数
PS:在calcEk()注释掉了后面引入核函数需要修改的部分
class optStruct:
def __init__(self,dataMatIn,classLabels,C,toler):
'''建立一个数据结构来保存所有重要的值'''
self.X = dataMatIn
self.labelMat = classLabels
self.C = C
self.tol = toler
self.m = shape(dataMatIn)[0] #行
self.alphas = mat(zeros((self.m,1)))
self.b = 0
self.eCache = mat(zeros((self.m,2))) #第一列给出的是eCache是否有效的标志位,第二列是实际的E值
def calcEk(oS,k):
'''
参数oS:optStruct的对象
参数k:下标
计算E值并返回'''
#以下部分为未引入核函数后的fXk,Ek计算
fXk = float(multiply(oS.alphas,oS.labelMat).T*\
(oS.X*oS.X[k,:].T)) + oS.b
#以下部分为引入核函数后的fXk,Ek计算
#fXk = float(multiply(oS.alphas,oS.labelMat).T*oS.K[:,k]+oS.b)
Ek = fXk - float(oS.labelMat[k])
return Ek
def selectJ(i,oS,Ei):
'''启发式方法选择内循环的alpha'''
maxK = -1;maxDeltaE = 0;Ej = 0
oS.eCache[i] = [1,Ei]
#nonzero():
#返回一个长度为a.ndim(数组a的轴数)的元祖,元祖的每个元素都是一个整数数组,其值为非零元素的下标在对应轴上的值
#>>> b2 = np.array([[True, False, True], [True, False, False]])
#>>> np.nonzero(b2)
#(array([0, 0, 1], dtype=int64), array([0, 2, 0], dtype=int64))
#它的第0个元素是数组a中值不为0的元素的第0轴的下标,第1个元素则是第1轴的下标,因此从下面的结果可知b2[0,0]、b[0,2]和b2[1,0]的值不为0:
#matrix.A 表示将矩阵转为array数组
validEcacheList = nonzero(oS.eCache[:,0].A)[0]
if (len(validEcacheList)) > 1:
#对E中非0的值的下标进行循环
for k in validEcacheList:
if k == i:
continue
Ek = calcEk(oS,k)
deltaE = abs(Ei - Ek)
if (deltaE > maxDeltaE):
maxK = k;maxDeltaE = deltaE;Ej = Ek
return maxK,Ej
else:
j = selectJrand(i,oS.m)
Ej = calcEk(oS,j)
return j,Ej
def updateEk(oS,k):
'''计算误差值并存入缓存中'''
Ek = calcEk(oS,k)
oS.eCache[k] = [1,Ek]完整Platt SMO 算法中的优化例程
PS:下面代码内部增添了在引入核函数后的内容,会注释掉,要用时再删除注释即可 File "", line 1
PS:下面代码内部增添了在引入核函数后的内容,会注释掉,要用时再删除注释即可
^
SyntaxError: invalid character in identifier
def innerL(i,oS):
Ei = calcEk(oS,i)
if ((oS.labelMat[i]*Ei < -oS.tol) and (oS.alphas[i] < oS.C)) or\
((oS.labelMat[i]*Ei > oS.tol) and (oS.alphas[i] > 0)):
j,Ej = selectJ(i,oS,Ei)
alphaIold = oS.alphas[i].copy();alphaJold = oS.alphas[j].copy()
if (oS.labelMat[i] != oS.labelMat[j]):
L = max(0,oS.alphas[j]-oS.alphas[i])
H = min(oS.C,oS.C + oS.alphas[j] - oS.alphas[i])
else:
L = max(0,oS.alphas[j] + oS.alphas[i] - oS.C)
H = min(oS.C,oS.alphas[j] + oS.alphas[i])
if L == H:
print('L==H');return 0
#下一行为未引入核函数后的:
eta = 2.0 * oS.X[i,:]*oS.X[j,:].T - oS.X[i,:]*oS.X[i,:].T - oS.X[j,:]*oS.X[j,:].T
#下一行为引入核函数后的:
#eta = 2.0 * oS.K[i,j] - oS.K[i,i] - oS.K[j,j]
if eta >= 0:
print('eta>=0');return 0
oS.alphas[j] -= oS.labelMat[j]*(Ei - Ej)/eta
oS.alphas[j] = clipAlpha(oS.alphas[j],H,L)
updateEk(oS,j) #更新误差进缓存
if (abs(oS.alphas[j] - alphaJold) < 0.00001):
print('j not moving enough');return 0
oS.alphas[i] += oS.labelMat[j]*oS.labelMat[i]*(alphaJold - oS.alphas[j])
updateEk(oS,i)
#更新阈值b
#以下b1,b2是未引入核函数之后的:
b1 = oS.b - Ei -oS.labelMat[i]*(oS.alphas[i]-alphaIold)*\
oS.X[i,:]*oS.X[i,:].T - oS.labelMat[j]*\
(oS.alphas[j] - alphaJold)*oS.X[i,:]*oS.X[j,:].T
b2 = oS.b - Ej -oS.labelMat[i]*(oS.alphas[i]-alphaIold)*\
oS.X[i,:]*oS.X[j,:].T - oS.labelMat[j]*\
(oS.alphas[j] - alphaJold)*oS.X[j,:]*oS.X[j,:].T
#以下b1,b2是引入核函数之后的:
#b1 = oS.b - Ei - oS.labelMat[i]*(oS.alphas[i]-alphaIold)*oS.K[i,i] -\
# oS.labelMat[j]*(oS.alphas[j]-alphaJold)*oS.K[i,j]
#b2 = oS.b - Ej - oS.labelMat[i]*(oS.alphas[i]-alphaIold)*oS.K[i,j] -\
# oS.labelMat[j]*(oS.alphas[j]-alphaJold)*oS.K[j,j]
if (0 < oS.alphas[i]) and (oS.C > oS.alphas[i]):
oS.b = b1
elif (0 < oS.alphas[j]) and (oS.C > oS.alphas[j]):
oS.b = b2
else:
oS.b = (b1 + b2)/2.0
return 1
else : return 0完整版Platt SMO的外循环代码
def smoP(dataMatIn,classLabels,C,toler,maxIter,kTup=('lin',0)):
oS = optStruct(mat(dataMatIn),mat(classLabels).transpose(),C,toler,kTup)
iter = 0
entireSet = True;alphaPairsChanged = 0
while(iter < maxIter) and ((alphaPairsChanged > 0) or (entireSet)):
alphaPairsChanged = 0
if entireSet:
#遍历所有的值
for i in range(oS.m):
alphaPairsChanged += innerL(i,oS)
print('fullSet,iter:{0} i:{1},pairs changed {2}'.format(iter,i,alphaPairsChanged))
iter += 1
else:
nonBoundIs = nonzero((oS.alphas.A > 0)*(oS.alphas.A < C))[0]
#遍历非边界值
for i in nonBoundIs:
alphaPairsChanged += innerL(i,oS)
print('non-bound,iter:{0} i:{1},pairs changed {2}'.format(iter,i,alphaPairsChanged))
iter += 1
if entireSet:
entireSet = False
elif (alphaPairsChanged == 0):
entireSet = True
print("iteration number:{}".format(iter))
return oS.b,oS.alphas进行测试
b,alphas = smoP(dataArr,labelArr,0.6,0.001,40)fullSet,iter:0 i:0,pairs changed 1
fullSet,iter:3 i:96,pairs changed 0
fullSet,iter:3 i:97,pairs changed 0
fullSet,iter:3 i:98,pairs changed 0
fullSet,iter:3 i:99,pairs changed 0
iteration number:4
了解哪些数据点是支持向量,可以看到与简易版SMO是不一样的
for i in range(100):
if alphas[i] > 0.0:
print(dataArr[i],labelArr[i]) # 输出对应下标的样本点[3.634009, 1.730537] -1.0
[3.125951, 0.293251] -1.0
[4.658191, 3.507396] -1.0
[3.223038, -0.552392] -1.0
[3.457096, -0.082216] -1.0
[5.286862, -2.358286] 1.0
[6.080573, 0.418886] 1.0
计算w值
ws = calWs(alphas,dataArr,labelArr)
wsarray([[ 0.74764704],
[-0.17895243]])
以第一个数据点为例进行分类:大于0为正类,否则负类
dataMat = mat(dataArr)
dataMat[0]*mat(ws)+bmatrix([[-0.98996178]])
在复杂数据上应用核函数
核函数转换函数
def kernelTrans(X,A,kTup):
'''
返回一个指定类型的核函数
参数kTup:是一个包含核函数信息的元组,第一个参数是描述核函数类型的字符串,其它2个参数是可能需要的可选参数
'''
m,n = shape(X)
K = mat(zeros((m,1)))
if kTup[0] == 'lin':
K = X * A.T
elif kTup[0] =='rbf':
for j in range(m):
deltaRow = X[j,:] - A
K[j] = deltaRow*deltaRow.T
K = exp(K/(-1*kTup[1]**2))
else:
raise NameError('Houston We Have a Problem - - That Kernel is not recognized')
return K
class optStruct:
def __init__(self,dataMatIn,classLabels,C,toler,kTup):
self.X = dataMatIn
self.labelMat = classLabels
self.C = C
self.tol = toler
self.m = shape(dataMatIn)[0] #行
self.alphas = mat(zeros((self.m,1)))
self.b = 0
self.eCache = mat(zeros((self.m,2)))
self.K = mat(zeros((self.m,self.m)))
#修改optStruct类,增加核函数
for i in range(self.m):
self.K[:,i] = kernelTrans(self.X,self.X[i,:],kTup)
利用核函数进行分类的径向基测试函数
def testRbf(k1=1.3):
#训练部分
dataArr,labelArr = loadDataSet('E:\\DataMining\\Project\\MLBook\\机器学习实战源代码\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch06\\testSetRBF.txt')
b,alphas = smoP(dataArr,labelArr,200,0.0001,10000,('rbf',k1))
dataMat = mat(dataArr);labelMat = mat(labelArr).transpose()
svInd=nonzero(alphas.A>0)[0]
sVs = dataMat[svInd]
labelSV = labelMat[svInd]
print("there are {} Support Vectors".format(shape(sVs)[0]))
m,n = shape(dataMat)
errorCount = 0
for i in range(m):
kernelEval = kernelTrans(sVs,dataMat[i,:],('rbf',k1))
predict = kernelEval.T*multiply(labelSV,alphas[svInd]) + b
if sign(predict) != sign(labelArr[i]):
errorCount += 1
print('the training error rate is:{}'.format(float(errorCount)/m))
#测试部分
dataArr,labelArr = loadDataSet('E:\\DataMining\\Project\\MLBook\\机器学习实战源代码\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch06\\testSetRBF2.txt')
errorCount = 0
dataMat = mat(dataArr);labelMat = mat(labelArr).transpose()
m,n = shape(dataMat)
for i in range(m):
kernelEval = kernelTrans(sVs,dataMat[i,:],('rbf',k1))
predict = kernelEval.T*multiply(labelSV,alphas[svInd]) + b
if sign(predict) != sign(labelArr[i]):
errorCount += 1
print('the test error rate is:{}'.format(float(errorCount)/m))在测试前要将前面innerL()和calcEk()的注释掉未引入核函数的代码
testRbf()fullSet,iter:0 i:0,pairs changed 1
fullSet,iter:5 i:97,pairs changed 0
fullSet,iter:5 i:98,pairs changed 0
fullSet,iter:5 i:99,pairs changed 0
iteration number:6
there are 27 Support Vectors
the training error rate is:0.01
the test error rate is:0.02