Spring 几个注解 context:annotation-config
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/j080624/article/details/60883328
现在常用框架中SpringMVC.xml配置是:
<mvc:annotation-driven/>和<context:component-scan>- 1
那么
首先看一下三个注解各自定义:
①
1.如果你想使用@Autowired注解,那么就必须事先在 Spring 容器中声明 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor Bean。
2.如果想使用@Resource 、@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy等注解就必须声明CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
3.如果想使用@PersistenceContext注解,就必须声明PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的Bean。
4.如果想使用 @Required的注解,就必须声明RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的Bean。
使用
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、
RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor以及
PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
即
之所以这样说是因为
对于没有在spring容器中注册的bean,它并不能执行任何操作,也就是说如果你并没有spring容器中注册过bean(spring配置文件中配置bean就是注册(也就是说spring中不存在你想使用的bean)),那么上述的那些注解并不会在你未注册过的bean中起作用。
这里可能会有疑问,比如明明注册了AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessorbean,那么岂不是可以随意使用@Autowired注解?
这里需要注意的是,@Autowired注解在你使用的时候自动注入的前提是,spring容器中已经有了该bean!
那么你可以随意在某个controller或者service使用该注解。并非该注解可以无中生有立即造一个bean给你使用!!
②
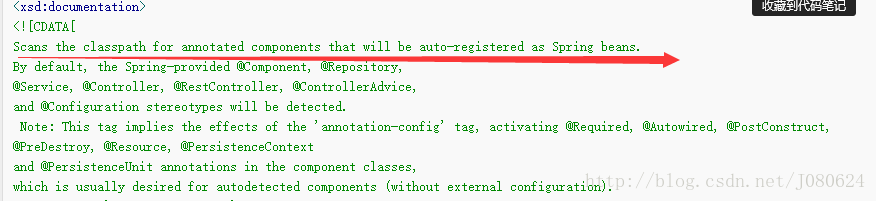
<context:component-scan>做了<context:annotation-config>要做的事情,还额外支持@Component,@Repository,@Service,
@Controller @RestController, @ControllerAdvice, and @Configuration 注解。
并且<context:component-scan>扫描base-package并且在application context中注册扫描到的使用注解注入的beans.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
这里着重注意第二段话,@controller @service @component..的bean!!!
也就是说,你不用xml中显示配置,需要的时候尽管用@Resource或者@Autowired来自动注入!!!
所以配置
该标签的XSD说明见下图:
③
至于该项看前缀就应该知道是springmvc所需要的注解。
我们找到对应的实现类是:
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser
源码示例如下:
/**
* A {@link BeanDefinitionParser} that provides the configuration for the
* {@code This class registers the following {@link HandlerMapping}s:
*
* - {@link RequestMappingHandlerMapping}
* ordered at 0 for mapping requests to annotated controller methods.
*
- {@link BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping}
* ordered at 2 to map URL paths to controller bean names.
*
*
* Note: Additional HandlerMappings may be registered
* as a result of using the {@code } or the
* {@code } MVC namespace elements.
*
* This class registers the following {@link HandlerAdapter}s:
*
* - {@link RequestMappingHandlerAdapter}
* for processing requests with annotated controller methods.
*
- {@link HttpRequestHandlerAdapter}
* for processing requests with {@link HttpRequestHandler}s.
*
- {@link SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter}
* for processing requests with interface-based {@link Controller}s.
*
*
* This class registers the following {@link HandlerExceptionResolver}s:
*
* - {@link ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver} for handling exceptions
* through @{@link ExceptionHandler} methods.
*
- {@link ResponseStatusExceptionResolver} for exceptions annotated
* with @{@link ResponseStatus}.
*
- {@link DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver} for resolving known Spring
* exception types
*
*
* This class registers an {@link org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher}
* and a {@link org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper} to be used by:
*
* - the {@link RequestMappingHandlerMapping},
*
- the {@link HandlerMapping} for ViewControllers
*
- and the {@link HandlerMapping} for serving resources
*
* Note that those beans can be configured by using the {@code path-matching} MVC namespace element.
*
* Both the {@link RequestMappingHandlerAdapter} and the
* {@link ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver} are configured with instances of
* the following by default:
*
* - A {@link ContentNegotiationManager}
*
- A {@link DefaultFormattingConversionService}
*
- A {@link org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean}
* if a JSR-303 implementation is available on the classpath
*
- A range of {@link HttpMessageConverter}s depending on what 3rd party
* libraries are available on the classpath.
*
*
* @author Keith Donald
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Brian Clozel
* @author Agim Emruli
* @since 3.0
*/
class AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
public static final String HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME = RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class.getName();
public static final String HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME = RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.class.getName();
public static final String CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME = "mvcContentNegotiationManager";
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
通过阅读类注释文档,我们发现这个类主要是用来向工厂中注册了
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
- RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
- HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
- SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
- ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
- DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
上面几个Bean实例。这几个类都是用来做什么的呢?
前两个是HandlerMapping接口的实现类,用来处理请求映射的。
-
- 其中第一个是处理@RequestMapping注解的。
-
- 第二个会将controller类的名字映射为请求url。
中间三个是用来处理请求的。具体点说就是确定调用哪个controller的哪个方法来处理当前请求。
-
- 第一个处理@Controller注解的处理器,支持自定义方法参数和返回值(很酷)。
-
- 第二个是处理继承HttpRequestHandler的处理器。
-
- 第三个处理继承自Controller接口的处理器。
后面三个是用来处理异常的解析器。
另外还将提供以下支持:
① 支持使用ConversionService实例对表单参数进行类型转换;
② 支持使用@NumberFormatannotation、@DateTimeFormat注解完成数据类型的格式化;
③ 支持使用@Valid注解对Java bean实例进行JSR 303验证;
④ 支持使用@RequestBody和@ResponseBody注解