CenterNet代码解析
这篇文章主要就是介绍一些用到的重要的函数,只介绍detection部分。
0.网站
https://github.com/xingyizhou/CenterNet
install:
https://github.com/xingyizhou/CenterNet/blob/master/readme/INSTALL.md
dataset:
https://github.com/xingyizhou/CenterNet/blob/master/readme/DATA.md
1.ctdet_decode:作用是将heat_map解码成b-box
将输出转化成det的函数是lib\models\decode.py中的ctdet_decode。
1.1 首先经过_nms:
def _nms(heat, kernel=3):
pad = (kernel - 1) // 2
hmax = nn.functional.max_pool2d(
heat, (kernel, kernel), stride=1, padding=pad)
keep = (hmax == heat).float()
return heat * keephmax用来寻找8-近邻极大值点,keep为h极大值点的位置,返回heat*keep,筛选出极大值点,为原值,其余为0。
2.1 之后经过_topk:
def _topk(scores, K=40):
batch, cat, height, width = scores.size()
topk_scores, topk_inds = torch.topk(scores.view(batch, cat, -1), K)
topk_inds = topk_inds % (height * width)
topk_ys = (topk_inds / width).int().float()
topk_xs = (topk_inds % width).int().float()
topk_score, topk_ind = torch.topk(topk_scores.view(batch, -1), K)
topk_clses = (topk_ind / K).int()
topk_inds = _gather_feat(
topk_inds.view(batch, -1, 1), topk_ind).view(batch, K)
topk_ys = _gather_feat(topk_ys.view(batch, -1, 1), topk_ind).view(batch, K)
topk_xs = _gather_feat(topk_xs.view(batch, -1, 1), topk_ind).view(batch, K)
return topk_score, topk_inds, topk_clses, topk_ys, topk_xstopk_scores: batch * cat * K, batch代表batchsize,cat代表类别数,K代表K个最大值。
topk_inds:batch * cat * K, index取值:[0, W x H - 1]
topk_scores和topk_inds分别为每个batch每张heatmap(每个类别)中前K个最大的score和id。
之后对topk_inds使用取余和除法得到横纵坐标top_ys、top_xs。
然后在每个batch中取所有heatmap的前K个最大score以及id,不考虑类别的影响。
topk_score:batch * K
topk_ind:batch * K index取值:[0, cat x K - 1]
之后对topk_inds(view后)和topk_ind调用了_gather_feat函数,在utils文件中:
2.2 _gather_feat
def _gather_feat(feat, ind, mask=None):
dim = feat.size(2)
ind = ind.unsqueeze(2).expand(ind.size(0), ind.size(1), dim)
feat = feat.gather(1, ind)
if mask is not None:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(2).expand_as(feat)
feat = feat[mask]
feat = feat.view(-1, dim)
return feat输入:
feat(topk_inds): batch * (cat x K) * 1 (假设输入的是topk_inds和topk_ind)
ind(topk_ind):batch * K
首先将ind扩展一个指标,变为 batch * K * 1
之后使用gather,将ind对应的值取出来。
返回的是index:
feat: batch * K * 1 取值:[0, cat x K - 1]
更一般的情况如下:
feat : A * B * C
ind:A * D
首先将ind扩展一个指标,并且expand为dim的大小,变为 A * D * C,其中对于任意的i, j, 数组ind[i, j, :]中所有的元素均相同,等于原来A * D shape的ind[i, j]。
之后使用gather,将ind对应的值取出来。
得到的feat: A * D * C
2.3 返回值
最后返回有四个:topk_score, topk_inds, topk_clses, topk_ys, topk_xs
topk_score:batch * K。每张图片中最大的K个值
topk_inds:batch * K 。没张图片中最大的K个值对应的index,这个index在[0, W x H - 1]之间。
后两个类似。
3.3 _tranpose_and_gather_feat,将_topk得到的index用于取值。
_tranpose_and_gather_feat的输入有reg,也有wh,前者应该是回归offset的,后者应该是得到bbox的W和H的。
scores, inds, clses, ys, xs = _topk(heat, K=K)
if reg is not None:
reg = _tranpose_and_gather_feat(reg, inds)wh = _tranpose_and_gather_feat(wh, inds)以下是_tranpose_and_gather_feat的定义:
def _tranpose_and_gather_feat(feat, ind):
feat = feat.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
feat = feat.view(feat.size(0), -1, feat.size(3))
feat = _gather_feat(feat, ind)
return feat输入:
feat:batch * C(channel) * W * H
ind:batch * K
首先将feat中各channel的元素放到最后一个index中,并且使用contiguous将内存变为连续的,用于后面的view。
之后将feat变为batch * (W x H) * C的形状,使用_gather_feat根据ind取出feat中对应的元素
返回:
feat:batch * K * C
feat[i, j, k]为第i个batch,第k个channel的第j个最大值。
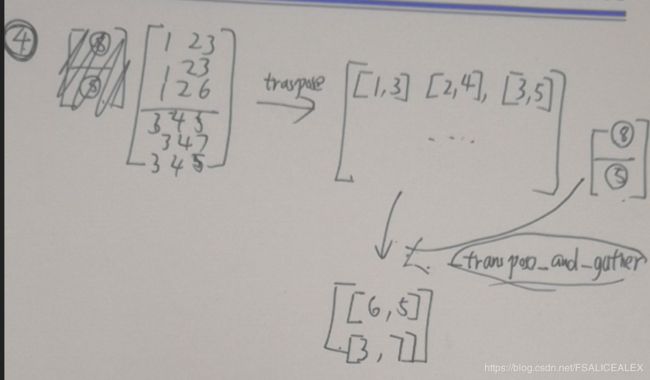
总体来说有点复杂,直接把它的逻辑用图来描述出来
假设输入是:![\begin{bmatrix} [1 & 2 & 3\\ 1 & 2 & 3\\ 1 & 2 & 6]\\ [3 & 4 & 5\\ 3 & 4 & 7\\ 3 & 4 & 5]\\ \end{bmatrix}](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/398f0fb087cc4dcba02bb0f45c24da77.gif) ,shape为batch * C * W * H(batch size直接设为1,忽略),对应于图中就是1 * 2 * 3 * 3,假设K=2。则经过以下两步之后
,shape为batch * C * W * H(batch size直接设为1,忽略),对应于图中就是1 * 2 * 3 * 3,假设K=2。则经过以下两步之后
scores, inds, clses, ys, xs = _topk(heat, K=K)
if reg is not None:
reg = _tranpose_and_gather_feat(reg, inds)最终得到的是:![]() ,shape为batch * K * C。[3, 7]中的7是所有channel中最大的元素,6则是第二大的元素,将所有channel对应对应位置的元素取出来就得到了最终的结果。
,shape为batch * K * C。[3, 7]中的7是所有channel中最大的元素,6则是第二大的元素,将所有channel对应对应位置的元素取出来就得到了最终的结果。
其中__gather_feat起到的作用是消除各个channel区别的作用,最终得到的inds是对于所有channel而言的。
而_tranpose_and_gather_feat的作用则是解码获得的inds,取得最终的结果。
_topk输入的feat就是定位的heat_map,在这上面获得inds后,这个inds就可以应用到offset_heat_map、size_heat_map上面。
下面用图示详细解释这两行代码的过程:
ctdet_decode的代码解释如下:
def ctdet_decode(heat, wh, reg=None, cat_spec_wh=False, K=100):
batch, cat, height, width = heat.size()
# heat = torch.sigmoid(heat)
# perform nms on heatmaps
heat = _nms(heat)
scores, inds, clses, ys, xs = _topk(heat, K=K)
# xs、ys是inds转化成在heat_map上面的行、列
if reg is not None:
reg = _tranpose_and_gather_feat(reg, inds)
reg = reg.view(batch, K, 2)
xs = xs.view(batch, K, 1) + reg[:, :, 0:1]
ys = ys.view(batch, K, 1) + reg[:, :, 1:2]
else:
xs = xs.view(batch, K, 1) + 0.5
ys = ys.view(batch, K, 1) + 0.5
# xs、ys都加上一个偏移
wh = _tranpose_and_gather_feat(wh, inds)
# 取wh中对应与inds的元素,就像上面的例子中一样。
if cat_spec_wh:
wh = wh.view(batch, K, cat, 2)
clses_ind = clses.view(batch, K, 1, 1).expand(batch, K, 1, 2).long()
wh = wh.gather(2, clses_ind).view(batch, K, 2)
else:
wh = wh.view(batch, K, 2)
clses = clses.view(batch, K, 1).float()
scores = scores.view(batch, K, 1)
bboxes = torch.cat([xs - wh[..., 0:1] / 2,
ys - wh[..., 1:2] / 2,
xs + wh[..., 0:1] / 2,
ys + wh[..., 1:2] / 2], dim=2)
# bbox就这样获得了。
detections = torch.cat([bboxes, scores, clses], dim=2)
return detections2.后处理
上面根据heatmap得到了dets,但是还需要进一步处理:
1. demo中的line 30:ret = detector.run(img),detector为ctdet
2. base_detector中的line 82:run函数:
images -> output、dets
dets-> dets = self.post_process(dets, meta, scale) -> detections.append(dets)
detections -> results = self.merge_outputs(detections) ->results
3.上面的两个过程:post_process和merge_outputs在ctdet中进行了定义
4.post_process:
dets = dets.detach().cpu().numpy()
dets = dets.reshape(1, -1, dets.shape[2])
dets = ctdet_post_process(
dets.copy(), [meta['c']], [meta['s']],
meta['out_height'], meta['out_width'], self.opt.num_classes)
for j in range(1, self.num_classes + 1):
dets[0][j] = np.array(dets[0][j], dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 5)
dets[0][j][:, :4] /= scale
return dets[0]做的应该就是尺度变换之类的吧。
5.merge_outputs:
def merge_outputs(self, detections):
results = {}
for j in range(1, self.num_classes + 1):
results[j] = np.concatenate(
[detection[j] for detection in detections], axis=0).astype(np.float32)
if len(self.scales) > 1 or self.opt.nms:
soft_nms(results[j], Nt=0.5, method=2)
scores = np.hstack(
[results[j][:, 4] for j in range(1, self.num_classes + 1)])
if len(scores) > self.max_per_image:
kth = len(scores) - self.max_per_image
thresh = np.partition(scores, kth)[kth]
for j in range(1, self.num_classes + 1):
keep_inds = (results[j][:, 4] >= thresh)
results[j] = results[j][keep_inds]
return results
大致上是先做soft_nms,之后scores进行一个筛选,将那些大于最多检测框(100)剔除掉。