Spark性能优化:数据倾斜调优
1、如何判断数据切斜的发生源头?
根据stage划分原理和sparkUI
2、数据倾斜解决方案
解决方案一:使用Hive ETL预处理数据
解决方案二:过滤少数导致倾斜的key
解决方案三:提高shuffle操作的并行度
解决方案四:两阶段聚合(局部聚合+全局聚合)
方案适用场景:对RDD执行reduceByKey等聚合类shuffle算子或者在Spark SQL中使用group by语句进行分组聚合时,比较适用这种方案。
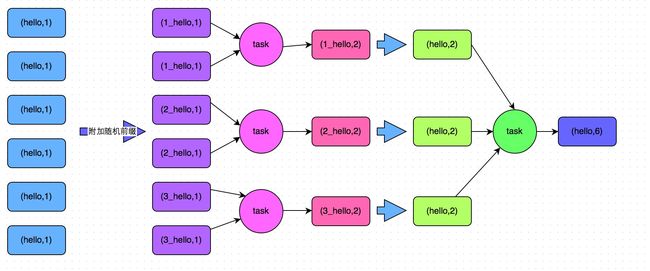
方案实现思路:这个方案的核心实现思路就是进行两阶段聚合。第一次是局部聚合,先给每个key都打上一个随机数,比如10以内的随机数,此时原先一样的key就变成不一样的了,比如(hello, 1) (hello, 1) (hello, 1) (hello, 1),就会变成(1_hello, 1) (1_hello, 1) (2_hello, 1) (2_hello, 1)。接着对打上随机数后的数据,执行reduceByKey等聚合操作,进行局部聚合,那么局部聚合结果,就会变成了(1_hello, 2) (2_hello, 2)。然后将各个key的前缀给去掉,就会变成(hello,2)(hello,2),再次进行全局聚合操作,就可以得到最终结果了,比如(hello, 4)。
// 第一步,给RDD中的每个key都打上一个随机前缀。
JavaPairRDD randomPrefixRdd = rdd.mapToPair(
new PairFunction, String, Long>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Tuple2 call(Tuple2 tuple)
throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
int prefix = random.nextInt(10);
return new Tuple2(prefix + "_" + tuple._1, tuple._2);
}
});
// 第二步,对打上随机前缀的key进行局部聚合。
JavaPairRDD localAggrRdd = randomPrefixRdd.reduceByKey(
new Function2() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Long call(Long v1, Long v2) throws Exception {
return v1 + v2;
}
});
// 第三步,去除RDD中每个key的随机前缀。
JavaPairRDD removedRandomPrefixRdd = localAggrRdd.mapToPair(
new PairFunction, Long, Long>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Tuple2 call(Tuple2 tuple)
throws Exception {
long originalKey = Long.valueOf(tuple._1.split("_")[1]);
return new Tuple2(originalKey, tuple._2);
}
});
// 第四步,对去除了随机前缀的RDD进行全局聚合。
JavaPairRDD globalAggrRdd = removedRandomPrefixRdd.reduceByKey(
new Function2() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Long call(Long v1, Long v2) throws Exception {
return v1 + v2;
}
}); scala版本: val list=Array("you jump","jump jump","jump jump","jump jump","jump jump","jump jump","jump jump","jump jump")
val listRDD=sc.parallelize(list, 1);
listRDD.flatMap { line => line.split("\t") }
.map { word => (word,1) }
.map(word =>{
val prefix= (new util.Random).nextInt(4)
(prefix+"_"+word._1,word._2)
})
.reduceByKey(_+_)
.map(word =>{
val key=word._1.split("_")(1)
(key,word._2)
})
.reduceByKey(_+_)
.foreach(result => println(result._1 + " : "+result._2))解决方案五:将reduce join转为map join
使用broadcast。
方案适用场景:在对RDD使用join类操作,或者是在Spark SQL中使用join语句时,而且join操作中的一个RDD或表的数据量比较小(比如几百M或者一两G),比较适用此方案。
方案实现思路:不使用join算子进行连接操作,而使用Broadcast变量与map类算子实现join操作,进而完全规避掉shuffle类的操作,彻底避免数据倾斜的发生和出现。将较小RDD中的数据直接通过collect算子拉取到Driver端的内存中来,然后对其创建一个Broadcast变量;接着对另外一个RDD执行map类算子,在算子函数内,从Broadcast变量中获取较小RDD的全量数据,与当前RDD的每一条数据按照连接key进行比对,如果连接key相同的话,那么就将两个RDD的数据用你需要的方式连接起来。
解决方案六:采样倾斜key并分拆join操作
方案适用场景:两个RDD/Hive表进行join的时候,如果数据量都比较大,无法采用“解决方案五”,那么此时可以看一下两个RDD/Hive表中的key分布情况。如果出现数据倾斜,是因为其中某一个RDD/Hive表中的少数几个key的数据量过大,而另一个RDD/Hive表中的所有key都分布比较均匀,那么采用这个解决方案是比较合适的。
方案实现思路:
- 对包含少数几个数据量过大的key的那个RDD,通过sample算子采样出一份样本来,然后统计一下每个key的数量,计算出来数据量最大的是哪几个key。
- 然后将这几个key对应的数据从原来的RDD中拆分出来,形成一个单独的RDD,并给每个key都打上n以内的随机数作为前缀,而不会导致倾斜的大部分key形成另外一个RDD。
- 接着将需要join的另一个RDD,也过滤出来那几个倾斜key对应的数据并形成一个单独的RDD,将每条数据膨胀成n条数据,这n条数据都按顺序附加一个0~n的前缀,不会导致倾斜的大部分key也形成另外一个RDD。
- 再将附加了随机前缀的独立RDD与另一个膨胀n倍的独立RDD进行join,此时就可以将原先相同的key打散成n份,分散到多个task中去进行join了。
- 而另外两个普通的RDD就照常join即可。
- 最后将两次join的结果使用union算子合并起来即可,就是最终的join结果。
// 首先从包含了少数几个导致数据倾斜key的rdd1中,采样10%的样本数据。
JavaPairRDD sampledRDD = rdd1.sample(false, 0.1);
// 对样本数据RDD统计出每个key的出现次数,并按出现次数降序排序。
// 对降序排序后的数据,取出top 1或者top 100的数据,也就是key最多的前n个数据。
// 具体取出多少个数据量最多的key,由大家自己决定,我们这里就取1个作为示范。
JavaPairRDD mappedSampledRDD = sampledRDD.mapToPair(
new PairFunction, Long, Long>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Tuple2 call(Tuple2 tuple)
throws Exception {
return new Tuple2(tuple._1, 1L);
}
});
JavaPairRDD countedSampledRDD = mappedSampledRDD.reduceByKey(
new Function2() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Long call(Long v1, Long v2) throws Exception {
return v1 + v2;
}
});
JavaPairRDD reversedSampledRDD = countedSampledRDD.mapToPair(
new PairFunction, Long, Long>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Tuple2 call(Tuple2 tuple)
throws Exception {
return new Tuple2(tuple._2, tuple._1);
}
});
final Long skewedUserid = reversedSampledRDD.sortByKey(false).take(1).get(0)._2;
// 从rdd1中分拆出导致数据倾斜的key,形成独立的RDD。
JavaPairRDD skewedRDD = rdd1.filter(
new Function, Boolean>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Boolean call(Tuple2 tuple) throws Exception {
return tuple._1.equals(skewedUserid);
}
});
// 从rdd1中分拆出不导致数据倾斜的普通key,形成独立的RDD。
JavaPairRDD commonRDD = rdd1.filter(
new Function, Boolean>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Boolean call(Tuple2 tuple) throws Exception {
return !tuple._1.equals(skewedUserid);
}
});
// rdd2,就是那个所有key的分布相对较为均匀的rdd。
// 这里将rdd2中,前面获取到的key对应的数据,过滤出来,分拆成单独的rdd,并对rdd中的数据使用flatMap算子都扩容100倍。
// 对扩容的每条数据,都打上0~100的前缀。
JavaPairRDD skewedRdd2 = rdd2.filter(
new Function, Boolean>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Boolean call(Tuple2 tuple) throws Exception {
return tuple._1.equals(skewedUserid);
}
}).flatMapToPair(new PairFlatMapFunction, String, Row>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Iterable> call(
Tuple2 tuple) throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
List> list = new ArrayList>();
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list.add(new Tuple2(i + "_" + tuple._1, tuple._2));
}
return list;
}
});
// 将rdd1中分拆出来的导致倾斜的key的独立rdd,每条数据都打上100以内的随机前缀。
// 然后将这个rdd1中分拆出来的独立rdd,与上面rdd2中分拆出来的独立rdd,进行join。
JavaPairRDD> joinedRDD1 = skewedRDD.mapToPair(
new PairFunction, String, String>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Tuple2 call(Tuple2 tuple)
throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
int prefix = random.nextInt(100);
return new Tuple2(prefix + "_" + tuple._1, tuple._2);
}
})
.join(skewedUserid2infoRDD)
.mapToPair(new PairFunction>, Long, Tuple2>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Tuple2> call(
Tuple2> tuple)
throws Exception {
long key = Long.valueOf(tuple._1.split("_")[1]);
return new Tuple2>(key, tuple._2);
}
});
// 将rdd1中分拆出来的包含普通key的独立rdd,直接与rdd2进行join。
JavaPairRDD> joinedRDD2 = commonRDD.join(rdd2);
// 将倾斜key join后的结果与普通key join后的结果,uinon起来。
// 就是最终的join结果。
JavaPairRDD> joinedRDD = joinedRDD1.union(joinedRDD2); 解决方案七:使用随机前缀和扩容RDD进行join
方案实现思路:
- 该方案的实现思路基本和“解决方案六”类似,首先查看RDD/Hive表中的数据分布情况,找到那个造成数据倾斜的RDD/Hive表,比如有多个key都对应了超过1万条数据。
- 然后将该RDD的每条数据都打上一个n以内的随机前缀。
- 同时对另外一个正常的RDD进行扩容,将每条数据都扩容成n条数据,扩容出来的每条数据都依次打上一个0~n的前缀。
- 最后将两个处理后的RDD进行join即可。