Linux下的avr系列的编译烧录调试方法 — 大工CSDN – EE01工作室【附件】
-avr系列的编译烧录调试方法
Galaxy2416
联系方式:[email protected]
附件内容: 程序源码,Makefile模板,相关文档。
http://download.csdn.net/detail/galaxy_blue/4277134附件网址~
系列说明:LINUX下程序开发具有一定的成熟性,包括大部分的MCU,FPGA,DSP甚至PCB制图等都是可行的。本系列将针对AVR系列的MCU,而后的系列将会对Linux下的其他方面内容进行探讨。
本文环境如下:
OS系统:ubuntu 12.04(原为10.04最近升级了)
编译器 :avr-gcc
烧录软件 :avrdude
调试软件:avarice ,GDB和ddd (可视界面)
开发板:
1. xplain(xmega128a1)无法调试,只能烧录,因为官方没有公开其调试的协议。
2. Mega16开发板。
仿真器or烧录器:dragon和usbasp(使用较多)
程序编写:Vim(升级版的记事本,很好用,很推荐)
关于使用前的准备和说明
至于为什么要使用linux下开发avr,原因主要是因为比较有趣。其次便是win下的环境用起来其实并不是很方便。IAR是付费软件(但是的确好用),Avr-studio虽然是免费版,不过优缺点是太过庞大,并且是以vc2010为基础开发,这个也就算不上真正的免费了。至于win-avr其实蛮不错的。win下也可以搭建如下环境。
准备:
软件安装,软件安装建议使用ubuntu的软件中心,比较方便。需要avr-gcc,avrdude,avarice,gdb,ddd即可了。文本编辑什么都行。可以集成在codeblocks和eclipse里面。Codeblocks如此做用起来感觉不错,eclipse需要配置,但原理都是一样的。
对于命令行可以如下安装
sudo apt-get install gcc-avrbinuilts-avr avr-libc
sudo apt-get installvim
sudo apt-get installavrdude强烈建议顺便安上手册
sudo apt-get installavrdude-doc
sudo apt-get installavarice
sudo apt-get installgdb
sudo apt-get installddd
然后就都安装完毕了。下一步就可以开始了。
开始之前需要先写一个.c的程序
代码会在文章最后和附件里提出。这是一个很简单让一个led亮的程序。
之后介绍一个makefile的东西,此物是简化操作流程的一个东西。让敲好多行命令才能完成的只需简单的一句话就行了。附件里会包含一个makefile的模板,是winavr下模板改的可用版。具体的内容是如何实现的,可以翻阅官方makefile手册和百度,谷歌。
简单介绍Makefile里面的几个命令,有过经验可以无视
AVRDUDE_PROGRAMMER = usbasp
#dragon_jtag
AVRDUDE_PORT = usb # programmer connected to serial device
AVRDUDE_WRITE_FLASH = -Uflash:w:$(TARGET).hex
AVRDUDE_FLAGS = -p $(MCU) -P$(AVRDUDE_PORT) -c $(AVRDUDE_PROGRAMMER)
AVRDUDE_FLAGS += $(AVRDUDE_NO_VERIFY)
AVRDUDE_FLAGS += $(AVRDUDE_VERBOSE)
AVRDUDE_FLAGS += $(AVRDUDE_ERASE_COUNTER)
上面这些都是定义变量,makefile里的
program: $(TARGET).hex $(TARGET).eep
$(AVRDUDE)$(AVRDUDE_FLAGS) $(AVRDUDE_WRITE_FLASH) $(AVRDUDE_WRITE_EEPROM)
当我们输入make program时就会执行上面这句之前的都不用关心了。翻译过来就变成了(如果叫main.hex)
avrdude -P usb -p m16 -c usbasp -U flash:w:main.hex就是说用usb下的usbasp烧录m16的flash,内容为main.hex
如果用dragon的话一般用jtag就是-c dragon_jtag。具体可以查看avrdude手册。
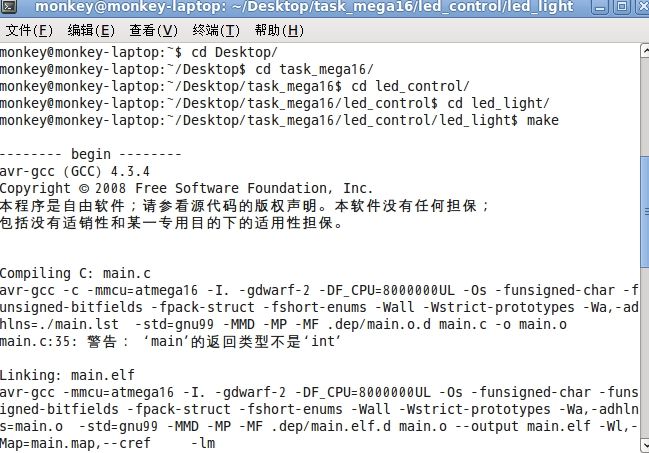
了解之后先打开终端,找到.c文件目录下。Makefile文件放在同一目录下
根据需要更改其内容
输入make
便会输出一些信息,最后会有提示编译成功
之后就可以烧录了
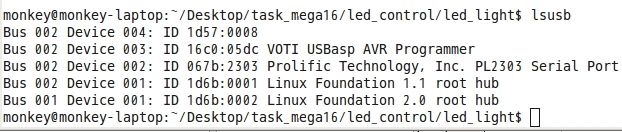
烧录之前看一下烧录器是否在
输入lsusb
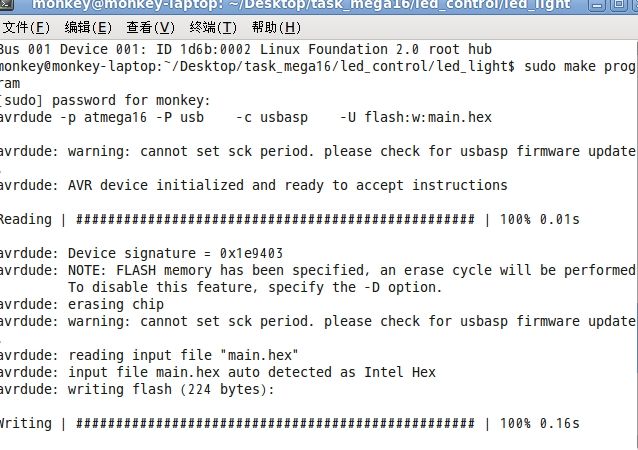
显然,usbasp存在。那么输入sudo make program
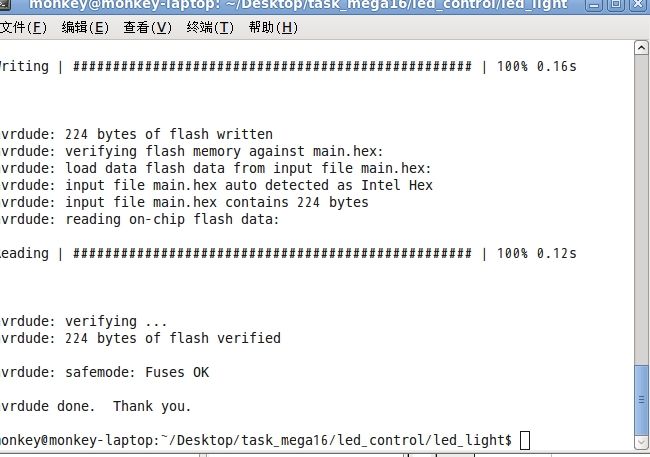
会在很快的时间内烧录成功,比win快的多。最后提示你烧录成功
至于debug,usbasp没有这个功能。需要用dragon的jtag。
住:Debug其实不是很推荐使用,虽然比较高效,建议利用串口的信息输入输出(以后会介绍),这是因为在进入系统的嵌入后,常规的debug经常会无法使用。
实际的命令会是
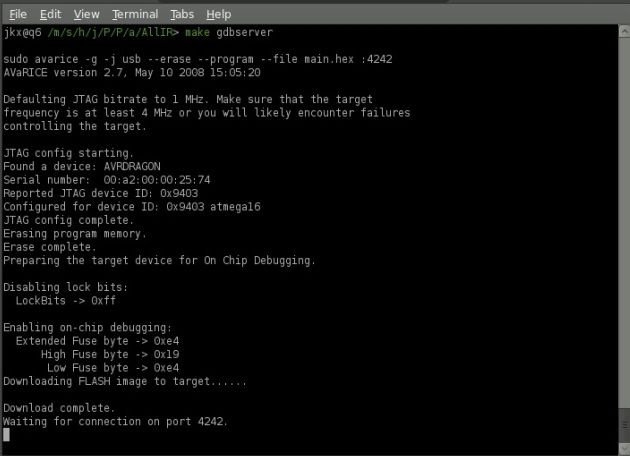
avarice -g -j usb --erase --program --filemain.hex :4242不过如果makefile里已经写好的话直接输入sudo make debug就可以了
下面为命令的结果
现在属于等待GDB,可视化的话就是DDD的状态中了
比如在gdb.conf中添加
file main.elf
target remotelocalhost:4242
启动DDD
ddd–-debugger “avr-gdb -x gdb.conf”
也可以手起动,然后配置,ui界面比较友好。
还有一句话。makefile里面已经把上步骤都做好了~当然会根据需求要求更改的。尤其是debug的时候。
总结:本文所说有些简略了,Linux开发的困难主要在于搭建环境,因此需要多看一下相关的官方手册。
测试代码:
main.c
// avr-gcc application builder : 2011-11-1
// Target : M16
// Crystal: 12.000Mhz
#include
#include
#define SET(a,b) a|(1< Makefile:
# Hey Emacs, this is a -*- makefile -*-
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# WinAVR Makefile Template written by Eric B. Weddington, Jörg Wunsch, et al.
# Linux GCC using is changed by Galaxy2416
# Released to the Public Domain
#
# Additional material for this makefile was written by:
# Peter Fleury
# Tim Henigan
# Colin O'Flynn
# Reiner Patommel
# Markus Pfaff
# Sander Pool
# Frederik Rouleau
# Carlos Lamas
#
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# On command line:
#
# make all = Make software.
#
# make clean = Clean out built project files.
#
# make coff = Convert ELF to AVR COFF.
#
# make extcoff = Convert ELF to AVR Extended COFF.
#
# make program = Download the hex file to the device, using avrdude.
# Please customize the avrdude settings below first!
#
# make debug = Start either simulavr or avarice as specified for debugging,
# with avr-gdb or avr-insight as the front end for debugging.
#
# make filename.s = Just compile filename.c into the assembler code only.
#
# make filename.i = Create a preprocessed source file for use in submitting
# bug reports to the GCC project.
#
# To rebuild project do "make clean" then "make all".
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# MCU name
MCU = atmega16
#atxmega128a1
# Processor frequency.
# This will define a symbol, F_CPU, in all source code files equal to the
# processor frequency. You can then use this symbol in your source code to
# calculate timings. Do NOT tack on a 'UL' at the end, this will be done
# automatically to create a 32-bit value in your source code.
# Typical values are:
# F_CPU = 1000000
# F_CPU = 1843200
# F_CPU = 2000000
# F_CPU = 3686400
# F_CPU = 4000000
# F_CPU = 7372800
# F_CPU = 8000000
# F_CPU = 11059200
# F_CPU = 14745600
# F_CPU = 16000000
# F_CPU = 18432000
# F_CPU = 20000000
F_CPU = 8000000
# Output format. (can be srec, ihex, binary)
FORMAT = ihex
# Target file name (without extension).
TARGET = main
# Object files directory
# To put object files in current directory, use a dot (.), do NOT make
# this an empty or blank macro!
OBJDIR = .
# List C source files here. (C dependencies are automatically generated.)
SRC = $(TARGET).c
# List C++ source files here. (C dependencies are automatically generated.)
CPPSRC =
# List Assembler source files here.
# Make them always end in a capital .S. Files ending in a lowercase .s
# will not be considered source files but generated files (assembler
# output from the compiler), and will be deleted upon "make clean"!
# Even though the DOS/Win* filesystem matches both .s and .S the same,
# it will preserve the spelling of the filenames, and gcc itself does
# care about how the name is spelled on its command-line.
ASRC =
# Optimization level, can be [0, 1, 2, 3, s].
# 0 = turn off optimization. s = optimize for size.
# (Note: 3 is not always the best optimization level. See avr-libc FAQ.)
OPT = s
# Debugging format.
# Native formats for AVR-GCC's -g are dwarf-2 [default] or stabs.
# AVR Studio 4.10 requires dwarf-2.
# AVR [Extended] COFF format requires stabs, plus an avr-objcopy run.
DEBUG = dwarf-2
# List any extra directories to look for include files here.
# Each directory must be seperated by a space.
# Use forward slashes for directory separators.
# For a directory that has spaces, enclose it in quotes.
EXTRAINCDIRS =
# Compiler flag to set the C Standard level.
# c89 = "ANSI" C
# gnu89 = c89 plus GCC extensions
# c99 = ISO C99 standard (not yet fully implemented)
# gnu99 = c99 plus GCC extensions
CSTANDARD = -std=gnu99
# Place -D or -U options here for C sources
CDEFS = -DF_CPU=$(F_CPU)UL
# Place -D or -U options here for ASM sources
ADEFS = -DF_CPU=$(F_CPU)
# Place -D or -U options here for C++ sources
CPPDEFS = -DF_CPU=$(F_CPU)UL
#CPPDEFS += -D__STDC_LIMIT_MACROS
#CPPDEFS += -D__STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS
#---------------- Compiler Options C ----------------
# -g*: generate debugging information
# -O*: optimization level
# -f...: tuning, see GCC manual and avr-libc documentation
# -Wall...: warning level
# -Wa,...: tell GCC to pass this to the assembler.
# -adhlns...: create assembler listing
CFLAGS = -g$(DEBUG)
CFLAGS += $(CDEFS)
CFLAGS += -O$(OPT)
CFLAGS += -funsigned-char
CFLAGS += -funsigned-bitfields
CFLAGS += -fpack-struct
CFLAGS += -fshort-enums
CFLAGS += -Wall
CFLAGS += -Wstrict-prototypes
#CFLAGS += -mshort-calls
#CFLAGS += -fno-unit-at-a-time
#CFLAGS += -Wundef
#CFLAGS += -Wunreachable-code
#CFLAGS += -Wsign-compare
CFLAGS += -Wa,-adhlns=$(<:%.c=$(OBJDIR)/%.lst)
CFLAGS += $(patsubst %,-I%,$(EXTRAINCDIRS))
CFLAGS += $(CSTANDARD)
#---------------- Compiler Options C++ ----------------
# -g*: generate debugging information
# -O*: optimization level
# -f...: tuning, see GCC manual and avr-libc documentation
# -Wall...: warning level
# -Wa,...: tell GCC to pass this to the assembler.
# -adhlns...: create assembler listing
CPPFLAGS = -g$(DEBUG)
CPPFLAGS += $(CPPDEFS)
CPPFLAGS += -O$(OPT)
CPPFLAGS += -funsigned-char
CPPFLAGS += -funsigned-bitfields
CPPFLAGS += -fpack-struct
CPPFLAGS += -fshort-enums
CPPFLAGS += -fno-exceptions
CPPFLAGS += -Wall
CPPFLAGS += -Wundef
#CPPFLAGS += -mshort-calls
#CPPFLAGS += -fno-unit-at-a-time
#CPPFLAGS += -Wstrict-prototypes
#CPPFLAGS += -Wunreachable-code
#CPPFLAGS += -Wsign-compare
CPPFLAGS += -Wa,-adhlns=$(<:%.cpp=$(OBJDIR)/%.lst)
CPPFLAGS += $(patsubst %,-I%,$(EXTRAINCDIRS))
#CPPFLAGS += $(CSTANDARD)
#---------------- Assembler Options ----------------
# -Wa,...: tell GCC to pass this to the assembler.
# -adhlns: create listing
# -gstabs: have the assembler create line number information; note that
# for use in COFF files, additional information about filenames
# and function names needs to be present in the assembler source
# files -- see avr-libc docs [FIXME: not yet described there]
# -listing-cont-lines: Sets the maximum number of continuation lines of hex
# dump that will be displayed for a given single line of source input.
ASFLAGS = $(ADEFS) -Wa,-adhlns=$(<:%.S=$(OBJDIR)/%.lst),-gstabs,--listing-cont-lines=100
#---------------- Library Options ----------------
# Minimalistic printf version
PRINTF_LIB_MIN = -Wl,-u,vfprintf -lprintf_min
# Floating point printf version (requires MATH_LIB = -lm below)
PRINTF_LIB_FLOAT = -Wl,-u,vfprintf -lprintf_flt
# If this is left blank, then it will use the Standard printf version.
PRINTF_LIB =
#PRINTF_LIB = $(PRINTF_LIB_MIN)
#PRINTF_LIB = $(PRINTF_LIB_FLOAT)
# Minimalistic scanf version
SCANF_LIB_MIN = -Wl,-u,vfscanf -lscanf_min
# Floating point + %[ scanf version (requires MATH_LIB = -lm below)
SCANF_LIB_FLOAT = -Wl,-u,vfscanf -lscanf_flt
# If this is left blank, then it will use the Standard scanf version.
SCANF_LIB =
#SCANF_LIB = $(SCANF_LIB_MIN)
#SCANF_LIB = $(SCANF_LIB_FLOAT)
MATH_LIB = -lm
# List any extra directories to look for libraries here.
# Each directory must be seperated by a space.
# Use forward slashes for directory separators.
# For a directory that has spaces, enclose it in quotes.
EXTRALIBDIRS =
#---------------- External Memory Options ----------------
# 64 KB of external RAM, starting after internal RAM (ATmega128!),
# used for variables (.data/.bss) and heap (malloc()).
#EXTMEMOPTS = -Wl,-Tdata=0x801100,--defsym=__heap_end=0x80ffff
# 64 KB of external RAM, starting after internal RAM (ATmega128!),
# only used for heap (malloc()).
#EXTMEMOPTS = -Wl,--section-start,.data=0x801100,--defsym=__heap_end=0x80ffff
EXTMEMOPTS =
#---------------- Linker Options ----------------
# -Wl,...: tell GCC to pass this to linker.
# -Map: create map file
# --cref: add cross reference to map file
LDFLAGS = -Wl,-Map=$(TARGET).map,--cref
LDFLAGS += $(EXTMEMOPTS)
LDFLAGS += $(patsubst %,-L%,$(EXTRALIBDIRS))
LDFLAGS += $(PRINTF_LIB) $(SCANF_LIB) $(MATH_LIB)
#LDFLAGS += -T linker_script.x
#---------------- Programming Options (avrdude) ----------------
# Programming hardware
# Type: avrdude -c ?
# to get a full listing.
#
AVRDUDE_PROGRAMMER = usbasp
#dragon_jtag
# com1 = serial port. Use lpt1 to connect to parallel port.
AVRDUDE_PORT = usb # programmer connected to serial device
AVRDUDE_WRITE_FLASH = -U flash:w:$(TARGET).hex
#AVRDUDE_WRITE_EEPROM = -U eeprom:w:$(TARGET).eep
# Uncomment the following if you want avrdude's erase cycle counter.
# Note that this counter needs to be initialized first using -Yn,
# see avrdude manual.
#AVRDUDE_ERASE_COUNTER = -y
# Uncomment the following if you do /not/ wish a verification to be
# performed after programming the device.
#AVRDUDE_NO_VERIFY = -V
# Increase verbosity level. Please use this when submitting bug
# reports about avrdude. See
# to submit bug reports.
#AVRDUDE_VERBOSE = -v -v
AVRDUDE_FLAGS = -p $(MCU) -P $(AVRDUDE_PORT) -c $(AVRDUDE_PROGRAMMER)
#AVRDUDE_FLAGS = -p m16 -P $(AVRDUDE_PORT) -c $(AVRDUDE_PROGRAMMER)
AVRDUDE_FLAGS += $(AVRDUDE_NO_VERIFY)
AVRDUDE_FLAGS += $(AVRDUDE_VERBOSE)
AVRDUDE_FLAGS += $(AVRDUDE_ERASE_COUNTER)
#---------------- Debugging Options ----------------
# For simulavr only - target MCU frequency.
DEBUG_MFREQ = $(F_CPU)
# Set the DEBUG_UI to either gdb or insight.
# DEBUG_UI = gdb
DEBUG_UI = gdb
# Set the debugging back-end to either avarice, simulavr.
DEBUG_BACKEND = avarice
#DEBUG_BACKEND = simulavr
# GDB Init Filename.
GDBINIT_FILE = __avr_gdbinit
# When using avarice settings for the JTAG
JTAG_DEV = usb
# Debugging port used to communicate between GDB / avarice / simulavr.
DEBUG_PORT = 4242
# Debugging host used to communicate between GDB / avarice / simulavr, normally
# just set to localhost unless doing some sort of crazy debugging when
# avarice is running on a different computer.
DEBUG_HOST = localhost
#============================================================================
# Define programs and commands.
SHELL = sh
CC = avr-gcc
OBJCOPY = avr-objcopy
OBJDUMP = avr-objdump
SIZE = avr-size
AR = avr-ar rcs
NM = avr-nm
AVRDUDE = avrdude
REMOVE = rm -f
REMOVEDIR = rm -rf
COPY = cp
WINSHELL =
# Define Messages
# English
MSG_ERRORS_NONE = Errors: none
MSG_BEGIN = -------- begin --------
MSG_END = -------- end --------
MSG_SIZE_BEFORE = Size before:
MSG_SIZE_AFTER = Size after:
MSG_COFF = Converting to AVR COFF:
MSG_EXTENDED_COFF = Converting to AVR Extended COFF:
MSG_FLASH = Creating load file for Flash:
MSG_EEPROM = Creating load file for EEPROM:
MSG_EXTENDED_LISTING = Creating Extended Listing:
MSG_SYMBOL_TABLE = Creating Symbol Table:
MSG_LINKING = Linking:
MSG_COMPILING = Compiling C:
MSG_COMPILING_CPP = Compiling C++:
MSG_ASSEMBLING = Assembling:
MSG_CLEANING = Cleaning project:
MSG_CREATING_LIBRARY = Creating library:
# Define all object files.
OBJ = $(SRC:%.c=$(OBJDIR)/%.o) $(CPPSRC:%.cpp=$(OBJDIR)/%.o) $(ASRC:%.S=$(OBJDIR)/%.o)
# Define all listing files.
LST = $(SRC:%.c=$(OBJDIR)/%.lst) $(CPPSRC:%.cpp=$(OBJDIR)/%.lst) $(ASRC:%.S=$(OBJDIR)/%.lst)
# Compiler flags to generate dependency files.
GENDEPFLAGS = -MMD -MP -MF .dep/$(@F).d
# Combine all necessary flags and optional flags.
# Add target processor to flags.
ALL_CFLAGS = -mmcu=$(MCU) -I. $(CFLAGS) $(GENDEPFLAGS)
ALL_CPPFLAGS = -mmcu=$(MCU) -I. -x c++ $(CPPFLAGS) $(GENDEPFLAGS)
ALL_ASFLAGS = -mmcu=$(MCU) -I. -x assembler-with-cpp $(ASFLAGS)
# Default target.
all: begin gccversion sizebefore build sizeafter end
# Change the build target to build a HEX file or a library.
build: elf hex eep lss sym
#build: lib
elf: $(TARGET).elf
hex: $(TARGET).hex
eep: $(TARGET).eep
lss: $(TARGET).lss
sym: $(TARGET).sym
LIBNAME=lib$(TARGET).a
lib: $(LIBNAME)
# Eye candy.
# AVR Studio 3.x does not check make's exit code but relies on
# the following magic strings to be generated by the compile job.
begin:
@echo
@echo $(MSG_BEGIN)
end:
@echo $(MSG_END)
@echo
# Display size of file.
HEXSIZE = $(SIZE) --target=$(FORMAT) $(TARGET).hex
ELFSIZE = $(SIZE) --mcu=$(MCU) --format=avr $(TARGET).elf
sizebefore:
@if test -f $(TARGET).elf; then echo; echo $(MSG_SIZE_BEFORE); $(ELFSIZE); \
2>/dev/null; echo; fi
sizeafter:
@if test -f $(TARGET).elf; then echo; echo $(MSG_SIZE_AFTER); $(ELFSIZE); \
2>/dev/null; echo; fi
# Display compiler version information.
gccversion :
@$(CC) --version
# Program the device.
program: $(TARGET).hex $(TARGET).eep
$(AVRDUDE) $(AVRDUDE_FLAGS) $(AVRDUDE_WRITE_FLASH) $(AVRDUDE_WRITE_EEPROM)
# Generate avr-gdb config/init file which does the following:
# define the reset signal, load the target file, connect to target, and set
# a breakpoint at main().
gdb-config:
@$(REMOVE) $(GDBINIT_FILE)
@echo define reset >> $(GDBINIT_FILE)
@echo SIGNAL SIGHUP >> $(GDBINIT_FILE)
@echo end >> $(GDBINIT_FILE)
@echo file $(TARGET).elf >> $(GDBINIT_FILE)
@echo target remote $(DEBUG_HOST):$(DEBUG_PORT) >> $(GDBINIT_FILE)
ifeq ($(DEBUG_BACKEND),simulavr)
@echo load >> $(GDBINIT_FILE)
endif
@echo break main >> $(GDBINIT_FILE)
debug: gdb-config $(TARGET).elf
ifeq ($(DEBUG_BACKEND), avarice)
@echo Starting AVaRICE - Press enter when "waiting to connect" message displays.
#@$(WINSHELL) /c start avarice --jtag $(JTAG_DEV) --erase --program --file \
#$(TARGET).hex $(DEBUG_HOST):$(DEBUG_PORT)
#@$(WINSHELL) /c pause
@$(WINSHELL) avarice --xmega -g --jtag $(JTAG_DEV) --erase --program --file \
$(TARGET).elf:$(DEBUG_PORT)
#@$(WINSHELL) pause
else
@$(WINSHELL) /c start simulavr --gdbserver --device $(MCU) --clock-freq \
$(DEBUG_MFREQ) --port $(DEBUG_PORT)
endif
#@$(WINSHELL) /c start avr-$(DEBUG_UI) --command=$(GDBINIT_FILE)
@$(WINSHELL) $(DEBUG_UI)
# Convert ELF to COFF for use in debugging / simulating in AVR Studio or VMLAB.
COFFCONVERT = $(OBJCOPY) --debugging
COFFCONVERT += --change-section-address .data-0x800000
COFFCONVERT += --change-section-address .bss-0x800000
COFFCONVERT += --change-section-address .noinit-0x800000
COFFCONVERT += --change-section-address .eeprom-0x810000
coff: $(TARGET).elf
@echo
@echo $(MSG_COFF) $(TARGET).cof
$(COFFCONVERT) -O coff-avr $< $(TARGET).cof
extcoff: $(TARGET).elf
@echo
@echo $(MSG_EXTENDED_COFF) $(TARGET).cof
$(COFFCONVERT) -O coff-ext-avr $< $(TARGET).cof
# Create final output files (.hex, .eep) from ELF output file.
%.hex: %.elf
@echo
@echo $(MSG_FLASH) $@
$(OBJCOPY) -O $(FORMAT) -R .eeprom -R .fuse -R .lock $< $@
%.eep: %.elf
@echo
@echo $(MSG_EEPROM) $@
-$(OBJCOPY) -j .eeprom --set-section-flags=.eeprom="alloc,load" \
--change-section-lma .eeprom=0 --no-change-warnings -O $(FORMAT) $< $@ || exit 0
# Create extended listing file from ELF output file.
%.lss: %.elf
@echo
@echo $(MSG_EXTENDED_LISTING) $@
$(OBJDUMP) -h -S -z $< > $@
# Create a symbol table from ELF output file.
%.sym: %.elf
@echo
@echo $(MSG_SYMBOL_TABLE) $@
$(NM) -n $< > $@
# Create library from object files.
.SECONDARY : $(TARGET).a
.PRECIOUS : $(OBJ)
%.a: $(OBJ)
@echo
@echo $(MSG_CREATING_LIBRARY) $@
$(AR) $@ $(OBJ)
# Link: create ELF output file from object files.
.SECONDARY : $(TARGET).elf
.PRECIOUS : $(OBJ)
%.elf: $(OBJ)
@echo
@echo $(MSG_LINKING) $@
$(CC) $(ALL_CFLAGS) $^ --output $@ $(LDFLAGS)
# Compile: create object files from C source files.
$(OBJDIR)/%.o : %.c
@echo
@echo $(MSG_COMPILING) $<
$(CC) -c $(ALL_CFLAGS) $< -o $@
# Compile: create object files from C++ source files.
$(OBJDIR)/%.o : %.cpp
@echo
@echo $(MSG_COMPILING_CPP) $<
$(CC) -c $(ALL_CPPFLAGS) $< -o $@
# Compile: create assembler files from C source files.
%.s : %.c
$(CC) -S $(ALL_CFLAGS) $< -o $@
# Compile: create assembler files from C++ source files.
%.s : %.cpp
$(CC) -S $(ALL_CPPFLAGS) $< -o $@
# Assemble: create object files from assembler source files.
$(OBJDIR)/%.o : %.S
@echo
@echo $(MSG_ASSEMBLING) $<
$(CC) -c $(ALL_ASFLAGS) $< -o $@
# Create preprocessed source for use in sending a bug report.
%.i : %.c
$(CC) -E -mmcu=$(MCU) -I. $(CFLAGS) $< -o $@
# Target: clean project.
clean: begin clean_list end
clean_list :
@echo
@echo $(MSG_CLEANING)
$(REMOVE) $(TARGET).hex
$(REMOVE) $(TARGET).eep
$(REMOVE) $(TARGET).cof
$(REMOVE) $(TARGET).elf
$(REMOVE) $(TARGET).map
$(REMOVE) $(TARGET).sym
$(REMOVE) $(TARGET).lss
$(REMOVE) $(SRC:%.c=$(OBJDIR)/%.o)
$(REMOVE) $(SRC:%.c=$(OBJDIR)/%.lst)
$(REMOVE) $(SRC:.c=.s)
$(REMOVE) $(SRC:.c=.d)
$(REMOVE) $(SRC:.c=.i)
$(REMOVEDIR) .dep
# Create object files directory
$(shell mkdir $(OBJDIR) 2>/dev/null)
# Include the dependency files.
-include $(shell mkdir .dep 2>/dev/null) $(wildcard .dep/*)
# Listing of phony targets.
.PHONY : all begin finish end sizebefore sizeafter gccversion \
build elf hex eep lss sym coff extcoff \
clean clean_list program debug gdb-config