Muduo分析及总结(二)Channel
Channel类
- 每个Channel对象自始至终只属于一个EventLoop,因此每个Channel对象都只属于某一个IO线程。
- 每个Channel对象自始至终只负责一个文件描述符(fd)的IO事件分发,但它并不拥有这个fd,也不会在析构的时候关闭这个fd。
- Muduo用户一般不直接使用Channel,而会使用更上层的封装,如TcpConnection。
- Channel的生命期由其owner calss负责管理。
- Channel的成员函数都只能在IO线程调用,因此更新数据成员都不必加锁。
一、回调触发时序图
这里只展现了有事件产生时,如何调用的Channel回调函数的一个大致流程。
二、源码分析
由于Channel类相对来说比较简单,这里只分析下源码。
1、Channel.h
class Channel : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef boost::function EventCallback; //事件回调
typedef boost::function ReadEventCallback; //读事件回调,带有事件参数
Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd);
~Channel();
void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);//当通道产生事件时,EventLoop首先调用的方法。
void setReadCallback(const ReadEventCallback& cb) //设置读回调
{ readCallback_ = cb; }
void setWriteCallback(const EventCallback& cb) //设置写回调
{ writeCallback_ = cb; }
void setCloseCallback(const EventCallback& cb) //设置关闭回调
{ closeCallback_ = cb; }
void setErrorCallback(const EventCallback& cb) //设置错误回调
{ errorCallback_ = cb; }
//tie此方法是防止Channel类还在执行,上层调用导致
//Channel提前释放而出现的异常问题,下文会详细解释。
/// Tie this channel to the owner object managed by shared_ptr,
/// prevent the owner object being destroyed in handleEvent.
void tie(const boost::shared_ptr&);
int fd() const { return fd_; } //Channel拥有的fd
int events() const { return events_; } //Channel当前处理的事件类型
void set_revents(int revt) { revents_ = revt; } // used by pollers
// int revents() const { return revents_; }
//检查当前Channel是否未处理任何事件
bool isNoneEvent() const { return events_ == kNoneEvent; }
//使能读,并更新通道信息
void enableReading() { events_ |= kReadEvent; update(); }
// void disableReading() { events_ &= ~kReadEvent; update(); }
//使能写
void enableWriting() { events_ |= kWriteEvent; update(); }
//停止所有写事件
void disableWriting() { events_ &= ~kWriteEvent; update(); }
//停止所有事件
void disableAll() { events_ = kNoneEvent; update(); }
bool isWriting() const { return events_ & kWriteEvent; }
// for Poller
int index() { return index_; } //每个Channel在Poller管理时都有一个index
void set_index(int idx) { index_ = idx; }
// for debug
string reventsToString() const; //事件信息转换,便于调试
void doNotLogHup() { logHup_ = false; } //是否输出POLLHUP挂起日志
EventLoop* ownerLoop() { return loop_; }
void remove();
private:
void update();
//事件处理方法类
void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);
//事件
static const int kNoneEvent;
static const int kReadEvent;
static const int kWriteEvent;
EventLoop* loop_;
const int fd_;
int events_;
int revents_;
int index_; // used by Poller.
bool logHup_;
boost::weak_ptr tie_; //用于tie()方法
bool tied_; //用于tie()方法
bool eventHandling_; //表示当前是否正在处理事件
ReadEventCallback readCallback_;
EventCallback writeCallback_;
EventCallback closeCallback_;
EventCallback errorCallback_;
};
2、Channel.cc
//读写事件值初始化
const int Channel::kNoneEvent = 0;
const int Channel::kReadEvent = POLLIN | POLLPRI;
const int Channel::kWriteEvent = POLLOUT;
Channel::Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd__)
: loop_(loop),
fd_(fd__),
events_(0),
revents_(0),
index_(-1),
logHup_(true),
tied_(false),
eventHandling_(false)
{
}
Channel::~Channel()
{
//析构时,如果当前Channel
//事件还在处理,则异常。
assert(!eventHandling_);
}
void Channel::tie(const boost::shared_ptr& obj)
{
//捆绑Channel的拥有者,防止Channel还在使用时,
//拥有者将Channel析构了。
tie_ = obj;
tied_ = true;
}
void Channel::update()
{
//调用EventLoop更新此通道信息
loop_->updateChannel(this);
}
void Channel::remove()
{
//当前无任何事件的情况下,
//移除Channel管理队列中本Channel。
assert(isNoneEvent());
loop_->removeChannel(this);
}
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
boost::shared_ptr guard;
if (tied_)
{
//捆绑了Channel的拥有者的处理方式。
//tie_用的是boost::weak_ptr,所以
//要先lock获取下,然后判断是否可用。
guard = tie_.lock();
if (guard)
{
//事件处理
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
else
{
//事件处理
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
//事件处理时,设置下此状态,
//Channel析构时,用到此状态
eventHandling_ = true;
if ((revents_ & POLLHUP) && !(revents_ & POLLIN))
{
//文件描述符挂起,并且不是读事件
//POLLHUP 描述符挂起,比如管道的写端被关闭后,读端描述符将收到此事件
if (logHup_)
{
LOG_WARN << "Channel::handle_event() POLLHUP";
}
if (closeCallback_) closeCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & POLLNVAL)
{
//指定的文件描述符非法,
//输出日志便于errorCallback_区分错误。
LOG_WARN << "Channel::handle_event() POLLNVAL";
}
if (revents_ & (POLLERR | POLLNVAL))
{
//POLLERR 指定的描述符发生错误。
//POLLNVAL 指定的描述符非法(描述符未打开)。
if (errorCallback_) errorCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & (POLLIN | POLLPRI | POLLRDHUP))
{
//POLLIN 普通数据可读(普通数据+优先级数据)
//POLLPRI 紧急数据(优先级数据)
//POLLRDHUP TCP连接被对方关闭,或者对方关闭了写操作,由GNU引入。
if (readCallback_) readCallback_(receiveTime);
}
if (revents_ & POLLOUT)
{
//数据可写
if (writeCallback_) writeCallback_();
}
eventHandling_ = false;
}
//此方法就是将对应的事件转换为字符串输出,便于调试。
string Channel::reventsToString() const
{
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << fd_ << ": ";
if (revents_ & POLLIN)
oss << "IN ";
if (revents_ & POLLPRI)
oss << "PRI ";
if (revents_ & POLLOUT)
oss << "OUT ";
if (revents_ & POLLHUP)
oss << "HUP ";
if (revents_ & POLLRDHUP)
oss << "RDHUP ";
if (revents_ & POLLERR)
oss << "ERR ";
if (revents_ & POLLNVAL)
oss << "NVAL ";
return oss.str().c_str();
}
三、关键点
这里详细说下Channel::tie()方法。
1、作用
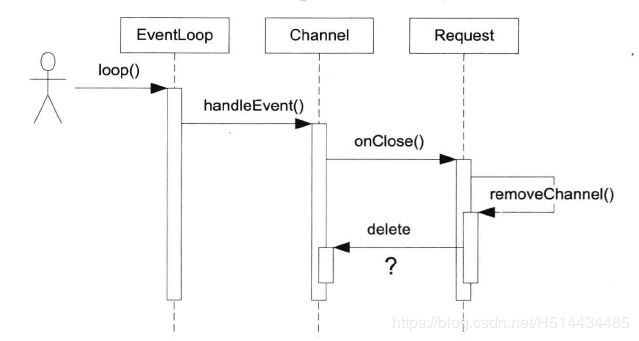
先看一个调用时序图。
图3-1
当对方断开TCP连接,这个IO事件会触发Channel::handleEvent()调用,后者会调用用户提供的CloseCallback,而用户代码在onClose()中有可能析构Channel对象,这就造成了灾难。等于说Channel::handleEvent()执行到一半的时候,其所属的Channel对象本身被销毁了。这时程序立刻core dump就是最好的结果了。
Muduo的解决办法是提供Channel::tie(const boost::shared_ptr
Muduo TcpConnection采用shared_ptr管理对象生命期的原因之一就是因为这个。
2、示例
这里举个TcpClient使用TcpConnection时,TcpConnection调用Channel::tie()的例子。
1)TcpClient设置自己的关闭回调:
void TcpClient::newConnection(int sockfd)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
InetAddress peerAddr(sockets::getPeerAddr(sockfd));
char buf[32];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, ":%s#%d", peerAddr.toHostPort().c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_;
string connName = buf;
InetAddress localAddr(sockets::getLocalAddr(sockfd));
// FIXME poll with zero timeout to double confirm the new connection
// FIXME use make_shared if necessary
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(loop_,
connName,
sockfd,
localAddr,
peerAddr));
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_);
//设置关闭回调
conn->setCloseCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpClient::removeConnection, this, _1)); // FIXME: unsafe
{
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
connection_ = conn;
}
conn->connectEstablished();
}
void TcpClient::removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(loop_ == conn->getLoop());
{
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
assert(connection_ == conn);
connection_.reset();
}
//回调函数中执行TcpConnection::connectDestroyed
loop_->queueInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn));
if (retry_ && connect_)
{
LOG_INFO << "TcpClient::connect[" << this << "] - Reconnecting to "
<< connector_->serverAddress().toHostPort();
connector_->restart();
}
}2) TcpConnection将关闭回调设置到Channel
TcpConnection::TcpConnection(EventLoop* loop,
const string& nameArg,
int sockfd,
const InetAddress& localAddr,
const InetAddress& peerAddr)
: loop_(CHECK_NOTNULL(loop)),
name_(nameArg),
state_(kConnecting),
socket_(new Socket(sockfd)),
channel_(new Channel(loop, sockfd)),
localAddr_(localAddr),
peerAddr_(peerAddr),
highWaterMark_(64*1024*1024)
{
channel_->setReadCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleRead, this, _1));
channel_->setWriteCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleWrite, this));
//设置关闭回调
channel_->setCloseCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleClose, this));
channel_->setErrorCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleError, this));
LOG_DEBUG << "TcpConnection::ctor[" << name_ << "] at " << this
<< " fd=" << sockfd;
socket_->setKeepAlive(true);
}
3) TcpConnection调用Channel::tie()
void TcpConnection::connectEstablished()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(state_ == kConnecting);
setState(kConnected);
//tie调用
channel_->tie(shared_from_this());
channel_->enableReading();
connectionCallback_(shared_from_this());
}4)Channel关闭事件回调
当产生关闭事件时,Channel::handleEvent就好调用TcpConnection::handleClose()
void TcpConnection::handleClose()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "TcpConnection::handleClose state = " << state_;
assert(state_ == kConnected || state_ == kDisconnecting);
// we don't close fd, leave it to dtor, so we can find leaks easily.
setState(kDisconnected);
channel_->disableAll();
TcpConnectionPtr guardThis(shared_from_this());
connectionCallback_(guardThis);
//由上次调用TcpConnection设置的关闭回调
// must be the last line
closeCallback_(guardThis);
}
5)TcpConnection::connectDestroyed
void TcpConnection::connectDestroyed()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
if (state_ == kConnected)
{
setState(kDisconnected);
channel_->disableAll();
connectionCallback_(shared_from_this());
}
//此处会释放Channel
channel_->remove();
}
当有关闭事件时,调用流程如下:
Channel::handleEvent -> TcpConnection::handleClose ->TcpClient::removeConnection ->TcpConnection::connectDestroyed
->channel_->remove()。
- 1、为了在Channel::handleEvent处理期间,防止因其owner对象被修改,进而导致Channel被析构,最后出现不可预估错误。 Channel::tie()的作用就是将Channel的owner对象进行绑定保护起来。
- 2、另外channel->remove的作用是删除channel在Poll中的地址拷贝,而不是销毁channel。channel的销毁由其owner对象决定。