SpringDataRedis踩坑记录
这几天做的功能涉及到Redis缓存,踩了不少坑,这里记录下来。
1、SpringBoot自动配置的RedisTemplate
在SpringBoot中可以在properties配置文件中配置spring.redis.*相关属性,SpringBoot就会自动帮你创建相关Redis连接以及RedisTemplate相关对象。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ JedisConnection.class, RedisOperations.class, Jedis.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
// Redis连接的自动配置
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(GenericObjectPool.class)
protected static class RedisConnectionConfiguration { ... }
/**
* RedisTemplate相关配置,SpringBoot会为我们生成两个RedisTemplate
*/
@Configuration
protected static class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Object>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(StringRedisTemplate.class)
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
}
大多数情况下使用SpringBoot默认的配置即可。
2、StringRedisTemplate与RedisTemplate
SpringBoot默认为我们配置了两个RedisTemplate,其中StringRedisTemplate继承自RedisTemplate。
public class StringRedisTemplate extends RedisTemplate<String, String> {
public StringRedisTemplate() {
// StringRedisTemplate默认使用StringRedisSerializer进行序列化
RedisSerializer<String> stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
setKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
setValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
setHashValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
}
public StringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
this();
setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
afterPropertiesSet();
}
protected RedisConnection preProcessConnection(RedisConnection connection, boolean existingConnection) {
return new DefaultStringRedisConnection(connection);
}
}
两者的区别:
1、StringRedisTemplate使用StringRedisSerializer进行序列化,而RedisTemplate默认使用JdkSerializationRedisSerializer进行序列化。
2、StringRedisTemplate对RedisConnection进行了一层包装。主要是因为RedisConnection的所有操作都是基于字节数组的,DefaultStringRedisConnection会把所有的结果转成String,包装了StringRedisSerializer并对批量操作数据进行批量序列化和反序列化,具体可以参考SetConverter,ListConverter,MapConverter的实现。
Spring Data Redis为了适配各种Redis客户端实现,抽象了一个RedisConnection接口。
事实上如果直接使用Jedis客户端,其实更方便,Jedis已经对String类型做了编解码处理。
package redis.clients.jedis;
public class Client extends BinaryClient implements Commands {
...
public void hset(final String key, final String field, final String value) {
hset(SafeEncoder.encode(key), SafeEncoder.encode(field), SafeEncoder.encode(value));
}
public void hget(final String key, final String field) {
hget(SafeEncoder.encode(key), SafeEncoder.encode(field));
}
...
}
//
package redis.clients.util;
public final class SafeEncoder {
private SafeEncoder(){
throw new InstantiationError( "Must not instantiate this class" );
}
public static byte[][] encodeMany(final String... strs) {
byte[][] many = new byte[strs.length][];
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
many[i] = encode(strs[i]);
}
return many;
}
public static byte[] encode(final String str) {
try {
if (str == null) {
throw new JedisDataException("value sent to redis cannot be null");
}
return str.getBytes(Protocol.CHARSET);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new JedisException(e);
}
}
public static String encode(final byte[] data) {
try {
return new String(data, Protocol.CHARSET);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new JedisException(e);
}
}
}
3、使用RedisTemplate
使用RedisTemplate很简单,因为SpringBoot已经为我们创建了RedisTemplate和StringRedisTemplate,所以我们直接在需要使用的Bean里面注入就行:
@Component
public class Example {
// 因为StringRedisTemplate继承自RedisTemplate才会注入普通的RedisTemplate
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
}
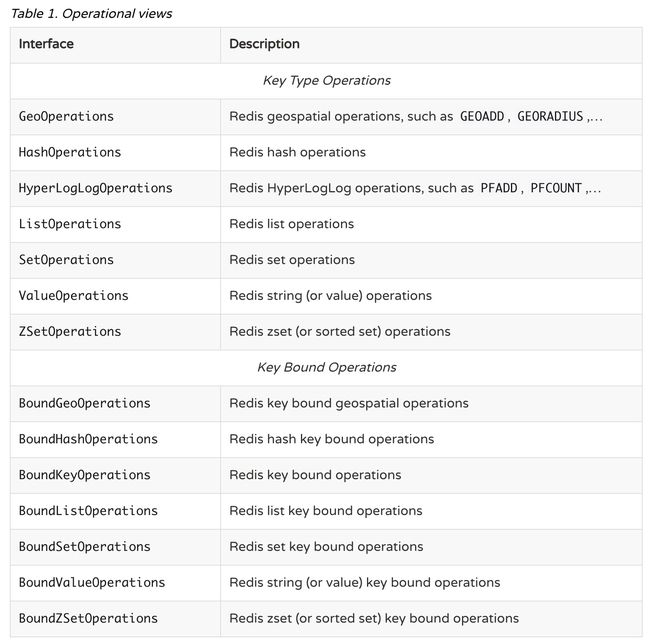
4、使用RedisTemplate的操作视图
RedisTemplate按照Redis的命令分组为我们提供了相应的操作视图:
@Component
public class Example {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate template;
public void doSomething() {
template.opsForList().leftPush("my-list", "value");
template.opsForSet().add("my-set", "member1", "member2");
...
BoundHashOperations<String, Object, Object> hashOps = template.boundHashOps("my-hash");
hashOps.put("name", "holmofy");
hashOps.put("age", "23");
hashOps.put("gender", "male");
}
}
这种随用随调方式的弊端是每次调用opsForXxx()都会创建一个新的视图。
SpringDataRedis可以直接注入视图:
@Component
public class Example {
// 只能用jsr250的@Resource注解注入
@Resource(name="redisTemplate")
private ListOperations<String, String> listOps;
public void addLink(String userId, URL url) {
listOps.leftPush(userId, url.toExternalForm());
}
}
这个功能得益于PropertyEditorSupport,具体可参考该链接
5、RedisSerilizer
因为StringRedisTemplate和RedisTemplate默认使用的序列化不一样,所以在使用视图操作时要注意一些序列化方面的细节:
@Component
public class Example {
@Resource(name = "redisTemplate")
private ValueOperations<String, Object> jdkSerializerValueOps;
@Resource(name = "stringRedisTemplate")
private ValueOperations<String, String> stringSerializerValueOps;
@PostConstruct
public void doSomething() {
jdkSerializerValueOps.set("jdkNumber", 1);
jdkSerializerValueOps.set("jdkString", "1");
stringSerializerValueOps.set("string", "1");
try {
jdkSerializerValueOps.increment("jdkNumber"); //失败
} catch (Exception ignore) { }
try {
jdkSerializerValueOps.increment("jdkString"); //失败
} catch (Exception ignore) { }
try {
stringSerializerValueOps.increment("string"); //成功
} catch (Exception ignore) { }
}
}
经过不同的序列化器保存到Redis中的内容是不一样的,StringRedisTemplate直接转成字符串保存到Redis里面,但RedisTemplate默认使用JdkSerializer会将对象信息存储到Redis中。
JdkSerializer优缺点
优点:序列化存储了类型信息,所以反序列化能直接生成相应对象。
缺点:
1、Redis中存储的内容包括对象头信息,存储了过多的无用内容,浪费Redis内存。
2、Redis中的一些操作不能使用,比如自增自减。
StringRedisSerializer优缺点
优点:
1、使用方便,所有的操作都以字符串形式保存到Redis
2、占用Redis更小
缺点:所有操作只能以字符串形式执行。StringRedisTemplate的key,value等参数都必须是String类型,因为StringRedisSerializer只负责把String转换成byte[]。存储对象时,需要我们手动序列化成字符串;相应地,取对象需要反序列化。
6、其他序列化
目前最新的SpringDataRedis 2.1.5版默认提供了6种序列化方案。
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer
底层使用Jackson进行序列化并存入Redis。对于普通类型(如数值类型,字符串)可以正常反序列化回相应对象。
但如果存入对象时由于没有存入类信息,则无法反序列化。
不过GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer默认为我们开启了Jackson的类型信息的存储:
public GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(String classPropertyTypeName) {
this(new ObjectMapper());
// 使用Jackson的类型功能嵌入反序列化所需的类型信息
// the type hint embedded for deserialization using the default typing feature.
mapper.registerModule(new SimpleModule().addSerializer(new NullValueSerializer(classPropertyTypeName)));
if (StringUtils.hasText(classPropertyTypeName)) {
mapper.enableDefaultTypingAsProperty(DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, classPropertyTypeName);
} else {
mapper.enableDefaultTyping(DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, As.PROPERTY);
}
}
所以当我存入一个对象时,它会把对象的类型信息也序列化存入Redis:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
private class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
}
//{\"@class\":\"com.example.demo.Person\",\"name\":\"Tom\",\"age\":10}
jacksonSerializerValueOps.set("jsonObject", new Person("Tom", 10));
Object obj = jacksonSerializerValueOps.get("jsonObject");
System.out.println(obj.getClass()); // com.example.demo.Person
具体可以参考Jackson相关文档
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer与GenericToStringSerializer
这两种序列化器是针对特定对象类型,前者用的是Jackson,后者用Spring的ConversionService。