18muduo_base库源码分析(九)
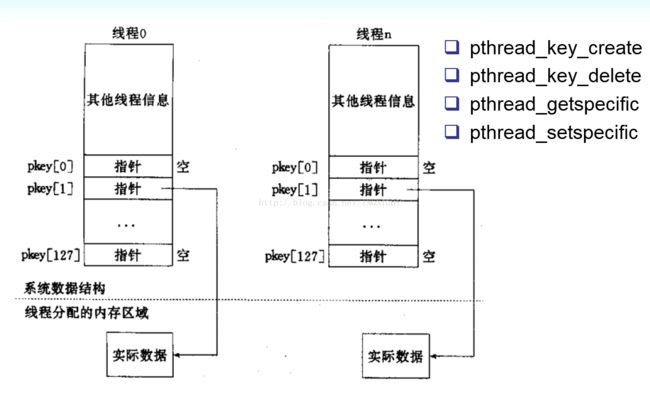
1.线程特定数据
(1)在单线程程序中,我们经常要用到"全局变量"以实现多个函数间共享数据。
(2)在多线程环境下,由于数据空间是共享的,因此全局变量也为所有线程所共有。
(3)但有时应用程序设计中有必要提供线程私有的全局变量,仅在某个线程中有效,但却可以跨多个函数访问。
(4)POSIX线程库通过维护一定的数据结构来解决这个问题,这个些数据称为(Thread-specific Data,或 TSD)。
(5)线程特定数据也称为线程本地存储TLS(Thread-local storage)
(6)对于POD类型的线程本地存储,可以用__thread关键字
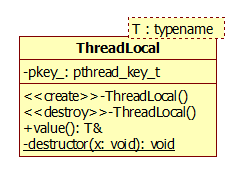
2.ThreadLocal类图
3.代码
ThreadLocal.h
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_THREADLOCAL_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_THREADLOCAL_H
#include
#include
namespace muduo
{
template
class ThreadLocal : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
ThreadLocal()
{
pthread_key_create(&pkey_, &ThreadLocal::destructor);
}
~ThreadLocal()
{
pthread_key_delete(pkey_);
}
T& value()
{
T* perThreadValue = static_cast(pthread_getspecific(pkey_));
if (!perThreadValue) {
T* newObj = new T();
pthread_setspecific(pkey_, newObj);
perThreadValue = newObj;
}
return *perThreadValue;
}
private:
static void destructor(void *x)
{
T* obj = static_cast(x);
typedef char T_must_be_complete_type[sizeof(T) == 0 ? -1 : 1];
delete obj;
}
private:
pthread_key_t pkey_;
};
}
#endif
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Test : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
Test()
{
printf("tid=%d, constructing %p\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this);
}
~Test()
{
printf("tid=%d, destructing %p %s\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this, name_.c_str());
}
const std::string& name() const { return name_; }
void setName(const std::string& n) { name_ = n; }
private:
std::string name_;
};
muduo::ThreadLocal testObj1;
muduo::ThreadLocal testObj2;
void print()
{
printf("tid=%d, obj1 %p name=%s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
&testObj1.value(),
testObj1.value().name().c_str());
printf("tid=%d, obj2 %p name=%s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
&testObj2.value(),
testObj2.value().name().c_str());
}
void threadFunc()
{
print();
testObj1.value().setName("changed 1");
testObj2.value().setName("changed 42");
print();
}
int main()
{
testObj1.value().setName("main one");
print();
muduo::Thread t1(threadFunc);
t1.start();
t1.join();
testObj2.value().setName("main two");
print();
pthread_exit(0);
运行结果
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Test : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
Test()
{
printf("tid=%d, constructing %p\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this);
}
~Test()
{
printf("tid=%d, destructing %p %s\n", muduo::CurrentThread::tid(), this, name_.c_str());
}
const std::string& name() const { return name_; }
void setName(const std::string& n) { name_ = n; }
private:
std::string name_;
};
#define STL muduo::Singleton >::instance().value()
void print()
{
printf("tid=%d, %p name=%s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
&STL,
STL.name().c_str());
}
void threadFunc(const char* changeTo)
{
print();
STL.setName(changeTo);
sleep(1);
print();
}
int main()
{
STL.setName("main one");
muduo::Thread t1(boost::bind(threadFunc, "thread1"));
muduo::Thread t2(boost::bind(threadFunc, "thread2"));
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
print();
t2.join();
pthread_exit(0);
}