java中的Io(二)
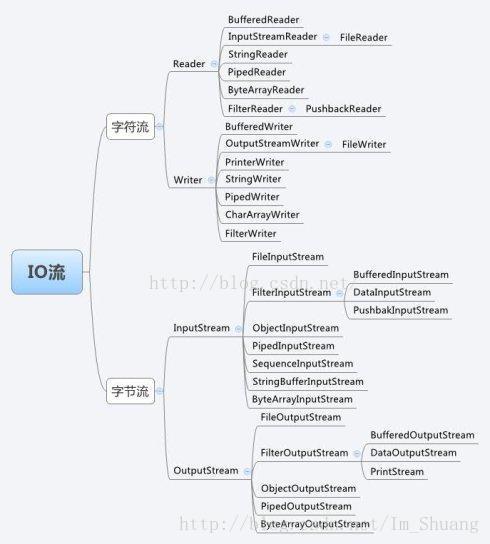
Java.IO流类库
java.io包中包含了流式I/O所需要的所有类。在java.io包中有四个基本类:InputStream、OutputStream及Reader、Writer类.
一. 字节流InputStream/OutputStream
1. InputStream 抽象类
InputStream 为字节输入流,它本身为一个抽象类,必须依靠其他子类实现各种功能,此抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。
InputStream为输入字节数据用的类,它提供了三种重载的read方法。
(1) public abstract int read()
(2) public int read(byte b[])
(3)public int read (byte b[],int off,int len):从输入流中len个字节的数据,放到偏移量为off的数组中。
(4) public int close()
2. OutputStream抽象类
(1).public void write(byte b[]);
(2) public void write(byte b[] ,int off,int len);
(3) public abstract void write(int b);
3.文件输入流:FileInputStream类
使用方法1:
File fin = new File("d:/abc.text");
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(fin);
使用方法2:
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("d:/abc.txt");
程序举例:将InputFromFile.java的程序的内容显示在显示器上
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
FileInputStream rf = new FileInputStream("F:/User/zss/Desktop/new1.txt");
int n=512;
byte buffer[]=new byte[n];
while((rf.read(buffer,0,n)!=-1)&&(n>0)){
System.out.println(new String(buffer));
}
System.out.println();
rf.close();
} catch(IOException IOe){
System.out.println(IOe.toString());
}
}
}方式1:
File f = new File("d:/myjava/write.txt");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:/myjava/write.txt");
方式2:
FileOuputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:/myjava/write.txt");
方式3:构造函数将 FileDescriptor()对象作为其参数。
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor();
FileOutputStream f2=new FileOutputStream(fd);
方式4:构造函数将文件名作为其第一参数,将布尔值作为第二参数。
* @param file the file to be opened for writing.
* @param append if true, then bytes will be written
* to the end of the file rather than the beginning
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt",true);
程序举例:使用键盘输入一段文章,将文章保存在文件write.txt中
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
System.out.println("please input from keyboard:");
int count,n=512;
byte buffer[] = new byte[n];
count=System.in.read(buffer);
FileOutputStream wf= new FileOutputStream("F:/User/zss/Desktop/new1.txt");//创建输出流
wf.write(buffer, 0, count);//从偏移量为0开始的count个字节写到输出流
wf.close();//关闭输出流
System.out.println("save to the new1.txt");//每次保存会覆盖掉上次的内容
} catch(IOException IOe){
System.out.println("file write error!");
}
}
}
BufferInputStream:当向缓冲区写入数据时,数据先写入缓冲区,待缓冲区写满后,系统一次性将数据发送给设备。
BufferOutputStream:当从缓冲区读取数据时,系统先从缓冲区读取数据,待缓冲区为空时候,系统再从输入设备读取数据到缓冲区。
1)将文件读入内存
将BufferInputStream与FileInputStream相连
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("fie.txt");
BufferInputStream bin = new BufferInputStream(in);
2)将内存写入文件
FileOutputStream out= new FileOutputStream("file.txt");
BufferOutputStream bin = new BufferOutputStream(out);
3)键盘输入流读到内存
将BufferReader与标准的的数据流相接
InputStreamReader sin = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferReader bin = new BufferReader(sin);
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
InputStreamReader sin = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(sin);
FileWriter out = new FileWriter("F:/User/zhushuangshuang/Desktop/new1.txt");
BufferedWriter bout = new BufferedWriter(out);
String s;
while ((s = bin.readLine()).length() > 0) {
bout.write(s, 0, s.length());
}
} catch(IOException IOe){
System.out.println("file write error!");
}
}
}
1. Reader抽象类
用于读取字符流的抽象类,子类必须实现的方法只有read(char[] ,int ,int)和close()。但是,多数子类将重写此定义的方法。代表类:FileReader:用来读取字符文件
2.
2. Writer抽象类