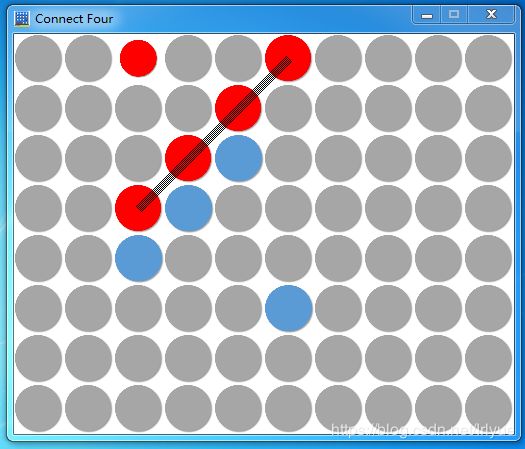
Connect Four四子棋c++程序 - 碰撞检测(2)
文章目录
- 碰撞检测
上一篇文章里已经完成了四子棋的主要游戏逻辑和画面渲染,现在我们把“碰撞检测”添加上去。这里的碰撞检测就是 检测当前玩家下子以后是否有超过4个棋子连成一条线了。这一部分要完成的工作有:
- 检测是否有超过4个棋子连在一起的情形;
- 如果有,要把那条直线在游戏中显示出来。
碰撞检测
超过4个棋子连成一条线有如下三种情况:
- 它们在水平方向连成一条线;
- 它们在竖直方向连成一条线;
- 它们在斜对角线上连成一条线(这里又有两种情况)。
要如何检测呢?首先我们这里只考虑最简单的情形:一旦有人连成4个棋子了,游戏就结束(也就是说不是积分制的那种)。然后我们来确定一下要检测的区域:
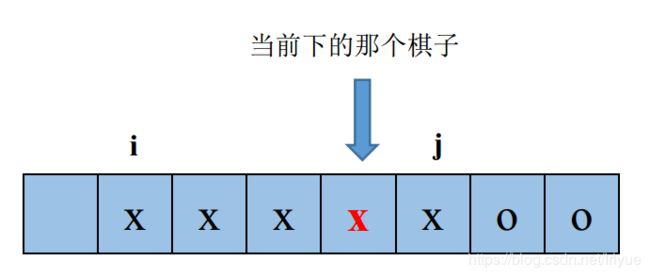
如果此时存在4个棋子连成一条直线,那么当前玩家下的那个棋子一定是其中4个棋子之一
这样就很简单了,我们可以从当前玩家下的那个棋子位置着手进行检测,举个水平方向的例子:
- 先一直往右边走,直至走出棋盘或者遇到不是当前玩家的棋子,记录下最右边的位置i;
- 然后在回到原来的位置往左边走,同样直至走出棋盘或者遇到不是当前玩家的棋子,记录下最左边的未知j。
接着计算这串棋子的个数n = i - j,如果n >= 4,那么就表明当前玩家赢了。类似地,我们按照相同的原理检测其他走向的直线。
因为一些变量在不同函数之间都会使用,我们先定义几个新的类成员变量:
int _startPos = -1; // 用来记录位置i
int _endPos = -1; // 用来记录位置j
bool _connected = false; // 当前棋局是否有4个棋子连成一条线
下面直接来看检测代码:
void checkCollision() {
if (_lastPos != -1) {
checkFromPos(_lastPos);
}
}
void checkFromPos(int pos) {
int tx = pos % _nbWGrids, ty = pos / _nbWGrids;
int i, j, x, y;
// check horizontally
y = ty;
for (x = pos % _nbWGrids; x < pos % _nbWGrids + 4; x++) {
if (x >= _nbWGrids || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
i = (x - 1) + y * _nbWGrids;
for (x = pos % _nbWGrids; x > pos % _nbWGrids - 4; x--) {
if (x < 0 || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
j = (x + 1) + y * _nbWGrids;
if (i - j >= 3) {
_connected = true;
_startPos = i;
_endPos = _startPos - 3;
return;
}
// check vertically
x = tx;
for (y = pos / _nbWGrids; y < pos / _nbWGrids + 4; y++) {
if (y >= _nbHGrids || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
i = x + (y - 1) * _nbWGrids;
for (y = pos / _nbWGrids; y > pos / _nbWGrids - 4; y--) {
if (y < 0 || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
j = x + (y + 1) * _nbWGrids;
if (i - j >= 3 * _nbWGrids) {
_connected = true;
_startPos = i;
_endPos = i - 3 * _nbWGrids;
return;
}
// check diagonally
// case 1: top left -> bottom right
for (x = pos % _nbWGrids, y = pos / _nbWGrids; x < pos % _nbWGrids + 4; x++, y++) {
if (x >= _nbWGrids || y >= _nbHGrids || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
i = (x - 1) + (y - 1) * _nbWGrids;
for (x = pos % _nbWGrids, y = pos / _nbWGrids; x > pos % _nbWGrids - 4; x--, y--) {
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
j = (x + 1) + (y + 1) * _nbWGrids;
if (i - j >= 3 * (_nbWGrids + 1)) {
_connected = true;
_startPos = i;
_endPos = _startPos - 3 * (_nbWGrids + 1);
return;
}
// case 2: top right -> bottom left
for (x = pos % _nbWGrids, y = pos / _nbWGrids; x > pos % _nbWGrids - 4; x--, y++) {
if (x < 0 || y >= _nbHGrids || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
i = (x + 1) + (y - 1) * _nbWGrids;
for (x = pos % _nbWGrids, y = pos / _nbWGrids; x < pos % _nbWGrids + 4; x++, y--) {
if (x >= _nbWGrids || y < 0 || _contents[x + y * _nbWGrids] != _contents[pos])
break;
}
j = (x - 1) + (y + 1) * _nbWGrids;
if (i - j >= 3 * (_nbWGrids - 1)) {
_connected = true;
_startPos = i;
_endPos = _startPos - 3 * (_nbWGrids - 1);
return;
}
}
这段代码看似很长,但其实是重复了三次,水平、垂直和对角线分别检测。然后记得把检测代码添加到游戏主循环里:
void run() {
_running = true;
Uint32 tic, elapsed;
while (_running) {
tic = SDL_GetTicks();
handleEvent();
clearScreen();
checkCollision(); // <--- here
renderScreen();
SDL_RenderPresent(gRenderer);
elapsed = SDL_GetTicks() - tic;
if (elapsed < 30)
SDL_Delay(30 - elapsed);
}
}
另外,如果有四个棋子连在一起了,我们还要在上面画一条线:
void renderConnectLine() {
if (_connected) {
SDL_SetRenderDrawColor(gRenderer, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff);
int x1 = static_cast<int>((_startPos % _nbWGrids) * GRID_SIZE + 0.5 * GRID_SIZE);
int y1 = static_cast<int>((_startPos / _nbWGrids) * GRID_SIZE + 0.5 * GRID_SIZE);
int x2 = static_cast<int>((_endPos % _nbWGrids) * GRID_SIZE + 0.5 * GRID_SIZE);
int y2 = static_cast<int>((_endPos / _nbWGrids) * GRID_SIZE + 0.5 * GRID_SIZE);
drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, 10);
}
}
void drawLine(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int thickness = 1) {
if (y1 == y2) {
for (int i = 0; i < thickness; i++) {
int dx = 0;
int dy = i - thickness / 2;
SDL_RenderDrawLine(gRenderer, x1 + dx, y1 + dy, x2 + dx, y2 + dy);
}
}
else {
double k = -(x1 - x2) / (y1 - y2);
double theta = atan(k);
for (int i = 0; i < thickness; i++) {
int dx = static_cast<int>(cos(theta) * (i - thickness / 2));
int dy = static_cast<int>(sin(theta) * (i - thickness / 2));
SDL_RenderDrawLine(gRenderer, x1 + dx, y1 + dy, x2 + dx, y2 + dy);
}
}
}
因为自己没有找到比较好的方式来画一定宽度的直线,所以自己写了一个辅助函数来做这个工作,有些许bug,希望后面有时间再来完善。
同时记得把renderConnectLine()添加到renderScreen()里:
void renderScreen() {
renderPieces();
renderPiecePreview();
renderConnectLine(); // <---here
}