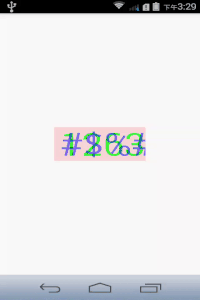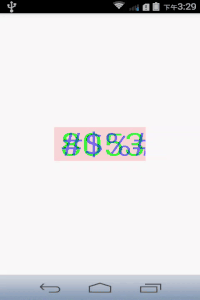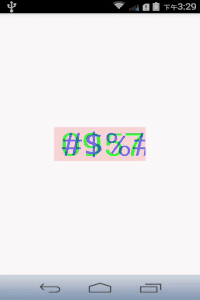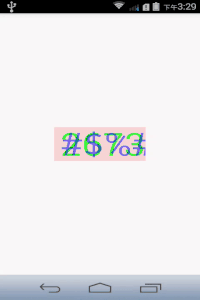android 自定义View基础(2)
android 自定义View基础(2)
本篇文章是学习 hongyang 大神的文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/24252901
的心得体会。
res/values/attrs.xml
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="RandomView">
<attr name="text" format="string|reference"/>
<attr name="textSize" format="dimension|reference"/>
<attr name="textColor" format="color|reference"/>
declare-styleable>
resources>自定义View java代码:
package com.crg.customview2;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.TypedValue;
import android.view.View;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Created by crg on 16-6-11.
*/
public class RandomView extends View{
private String mTextString;
private int mTextColor;
private int mTextSize;
private Paint mPaint;
private Rect mRect;
public RandomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.RandomView);
int count = ta.getIndexCount();
for (int i =0; i < count; i++){
int attr = ta.getIndex(i);
switch (attr){
case R.styleable.RandomView_text:
mTextString = ta.getString(attr);
break;
case R.styleable.RandomView_textSize:
mTextSize = ta.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, 16, getResources().getDisplayMetrics()));
break;
case R.styleable.RandomView_textColor:
mTextColor = ta.getColor(attr, Color.BLACK);
break;
}
}
//资源回收
ta.recycle();
//创建画字体的画笔
mPaint = new Paint();
//设置画笔的字体的大小
mPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
//初始化文字的范围Rect,及文所在的区域
mRect = new Rect();
//根据字体大小,内容,为mRect赋值。
mPaint.getTextBounds(mTextString, 0, mTextString.length(), mRect);
//给View添加点击事件
this.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mTextString = generateRandomText();
//刷新这个view 当view有改变时,调用这个方法系统会调用 onDraw()
//此方法只能在ui线程调用
// invalidate();
//子线程调用 刷新 view,在ui线程也可以用
postInvalidate();
}
});
}
private String generateRandomText() {
Random random = new Random();
Set set = new HashSet();
while (set.size() < 4){
int num = random.nextInt(10);
set.add(num);
}
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (Integer i : set){
stringBuffer.append(i);
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/**
* 如果没有重写 onMeasure()
* wrap_content 属性将不起作用,系统会把 wrap_content 当成 match_parent 处理
*/
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint
* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.
*/
// public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size
* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless
* of how big it wants to be.
*/
// public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up
* to the specified size.
*/
// public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
/*
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//目标宽,即RandomView 的宽 在 onDraw() getMeasuredWidth() 获得此值
int width;
//目标高,即RandomView 的高 在 onDraw() getMeasuredHeight() 获得此值
int height;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
//精确模式,具体数值和match_parent
//
width = widthSize;
} else {
//AT_MOST wrap_content
// UNSPECIFIED
// RandomView 的大小由里面的内容大小决定
width = getPaddingLeft() + mRect.width() + getPaddingRight();
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
height = heightSize;
} else {
height = getPaddingTop() + mRect.height() + getPaddingTop();
}
//绘制结果
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);*/
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//画出要显示的内容
//给画笔设置颜色 半透明的蓝色
// int color = 0x000000ff;
// int color = Color.argb(127, 0, 0, 255);
mPaint.setColor(mTextColor);
//第一步,先画背景的矩形
//画一个矩形,从左上角作为起点,getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight() 就是布局文件里设置的宽和高,及
//这个view的大小
canvas.drawRect(0, 0, getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight(), mPaint);
//画view里面要显示的文字
//带透明的绿色
int color = 0xbc00ff00;
mPaint.setColor(color);
canvas.drawText(mTextString, 0, mTextString.length(), getWidth()/2 - mRect.width()/2, getHeight()/2 + mRect.height()/2, mPaint);
}
}
xml布局文件使用:
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:random="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.crg.customview2.MainActivity">
<com.crg.customview2.RandomView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
random:text = "1263"
random:textSize = "60sp"
random:textColor = "#23ff0000"
/>
RelativeLayout>
效果:
我们使用时,宽和高,都是给定的具体值,
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"换成:
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
random:text = "1263"
random:textSize = "60sp"
random:textColor = "#23ff0000"原因是:我们没有重写
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/**
* 如果没有重写 onMeasure()
* wrap_content 属性将不起作用,系统会把 wrap_content 当成 match_parent 处理
*/
}
系统会把 wrap_content 测量为:match_parent。
最后加点阴影干扰,做成简单的验证码:
//制作简单的验证码
int colorshade = Color.argb(127, 0, 0, 255);
mPaint.setColor(colorshade);
canvas.drawText("#$%&", 0, mTextString.length(), getWidth()/2 - mRect.width()/2, getHeight()/2 + mRect.height()/2, mPaint);效果如下:
参考源码:
https://github.com/aloe-all/RandomView