Java学习-数据操作高级篇
一、封装类(包装类)
1.数字封装类:Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Float,Double ,这些类都是抽象类Number的子类;
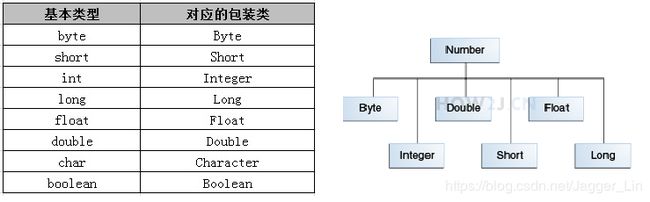
2.基本类型转封装类
- 方法1:通过构造方法:
int i = 10;//基本类型
Integer it = new Integer(i);//转换
- 方法2:自动装箱:
//分开写
int i =10;
Integer it = i;
//合并写
Integer it = 10;
3.封装类转基本类型
- 方法1:调用对象的intValue()方法
int i = it.intValue();
- 方法2:自动拆箱
int i = it;
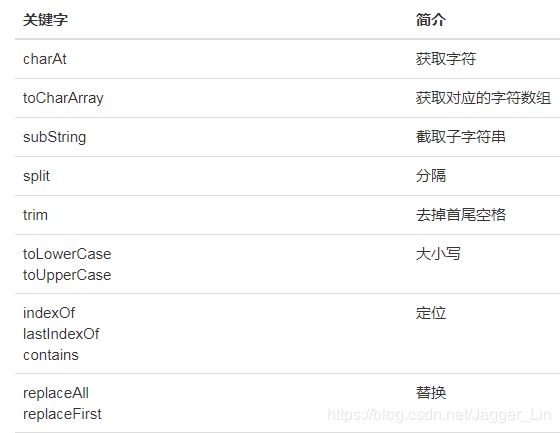
二、字符串与String
字符串即字符的组合,在Java中我们使用的都是字符串对象;
1.创建字符串对象的各种场景
1) 每当有一个字面值出现的时候,虚拟机就会创建一个字符串;
2) 调用String的构造方法创建一个字符串对象;
3) 通过其他类型转换为字符串对象;
4) 通过+加号进行字符串拼接也会创建新的字符串对象;
String xm ="小明"; // 1.字面值,虚拟机碰到字面值就会创建一个字符串对象
String xh = new String("小红"); // 2.创建了两个字符串对象
char[] xl = new char[]{'小','李'};
String s = new String(xl);// 3.通过字符数组创建一个字符串对象
String str= xm+ xh + s;// 4.通过+加号进行字符串拼接
3.字符串的比较
- 是否为同一个对象
//使用 == 判断是否为一个对象
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = new String(s1);
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//结果:true,同一个对象
System.out.println(s1 == s3);//结果:false,不是同一个对象
- 比较字符串内容
// 使用equals进行字符串内容的比较(区分大小写) ,使用equalsIgnoreCase可以忽略大小写判断内容是否一致;
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = "Hello";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//结果:false
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));//结果:true
4.注意:
1)String 被修饰为final,所以是不能被继承的;
2)字符串对象是不可改变的(immutable),一旦创建好这个字符串,里面的内容 永远 不能改变;
三、数字与字符串
1.数字转字符串
- 方法1: 使用String类的静态方法valueOf()
int i = 1;
String s = String.valueOf(i);
- 方法2: 先把基本类型装箱为对象,然后调用对象的toString()方法
Integer it = i;
String s = it.toString();
2.字符串转数字
- 方法1: 使用Integer类中的parseInt()方法
String s = "11";
int i= Integer.parseInt(s);
- 方法2: 先使用Integer类中的valueOf()方法将字符串转换成Integer对象,再拆箱为int型;(仅做思考题)
//分开写
Integer value = Integer.valueOf(s);
int i = value;
//合并写
int i = Integer.valueOf(s);
四、数组与字符串
1.数组转字符串
- 通过String类的构造方法
//字符数组转字符串
char[] c = new char[] {'h','e','l','l','o'};
String s = new String(c);
//字节数组转字符串
byte[] b = "world".getBytes();
String s1 = new String(b);
2.字符串转数组
- 通过toCharArray()和getBytes()方法
//字符串转字符数组
char[] c1 = s.toCharArray();
//字符串转字节数组
byte[] b = "world".getBytes();
五、格式化输出
1.基础知识
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "小明";
int time = 0;
//通用方法输出:易读性差,编码麻烦
String s = name + "昨天" + time + "点睡觉!";
System.out.println(s);
//格式化输出:简单明了,%s 表示字符串、%d 表示数字、%n 表示换行
String sFormat = "%s昨天%d点睡觉!%n";
System.out.printf(sFormat,name,time);
//printf和format效果相同,查看源代码可以知道printf中直接调用了format
System.out.format(sFormat,name,time);
}
}
console结果:
小明昨天0点睡觉!
小明昨天0点睡觉!
小明昨天0点睡觉!
2.扩展知识
int year = 2020;
//总长度,左对齐,补0,千位分隔符,小数点位数,本地化表达
//直接打印数字
System.out.format("%d%n",year);
//总长度是8,默认右对齐
System.out.format("%8d%n",year);
//总长度是8,左对齐
System.out.format("%-8d%n",year);
//总长度是8,不够补0
System.out.format("%08d%n",year);
//千位分隔符
System.out.format("%,8d%n",year*10000);
//小数点位数
System.out.format("%.2f%n",Math.PI);
//不同国家的千位分隔符
System.out.format(Locale.FRANCE,"%,.2f%n",Math.PI*10000);
System.out.format(Locale.US,"%,.2f%n",Math.PI*10000);
System.out.format(Locale.UK,"%,.2f%n",Math.PI*10000);