使用Tensorboard——TensorFlow可视化2
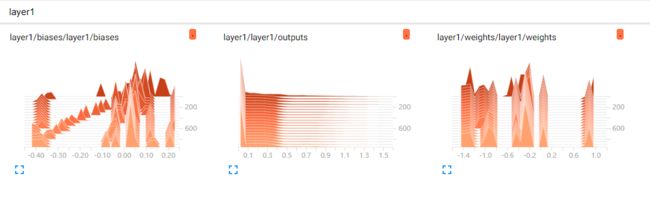
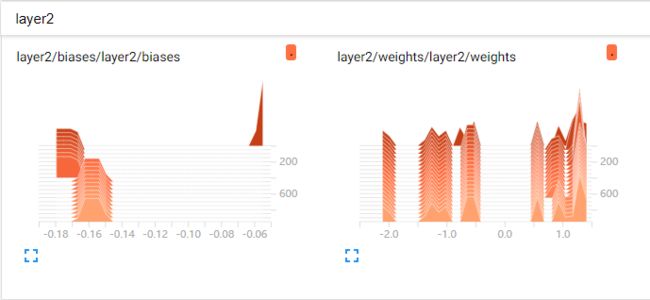
效果如下列图所示。
代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #构造添加一个神经层的函数 def add_layer(inputs,in_size,out_size,n_layer,activation_function=None): layer_name='layer%s' % n_layer with tf.name_scope(layer_name):#define layer name,图层的名字叫layer with tf.name_scope('weights'):#define weights name Weights=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]), name='W') #老版的TensorFlow的该函数为 tf.histogram_summary() tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+'/weights',Weights) with tf.name_scope('biases'):#define biases biases=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1, name='b')#biases的建议值不为0,故加上0.1 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): Wx_plus_b=tf.matmul(inputs,Weights)+biases if activation_function is None: outputs=Wx_plus_b else: outputs=activation_function(Wx_plus_b) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/outputs', outputs) return outputs #导入数据 x_data=np.linspace(-1,1,300,dtype=np.float32)[:,np.newaxis] noise=np.random.normal(0,0.05,x_data.shape).astype(np.float32) y_data=np.square(x_data)-0.5+noise #None代表无论输入有多少都可以,因为输入只有一个特征,所以这里是1 with tf.name_scope('inputs'):#形成一个大的图层,包围xs和ys,图层的名字叫inputs xs=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='x_in')#为xs指定名称为x_in ys=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='y_in')#为ys指定名称为y_in #搭建网络 #输入层为1层、隐藏层为10层、输出层也为1层的神经网络 #添加隐藏层 L1=add_layer(xs,1,10,n_layer=1,activation_function=tf.nn.relu)#使用TensorFlow自带的激励函数tf.nn.relu #此处的10为隐藏层的10个输出,将它作为输出层的输入;1则表示输出层只有一个输出 #计算所得的prediction的值即是所求的预测值 #添加输出层 prediction=add_layer(L1,10,1,n_layer=2,activation_function=None) #计算预测值prediction和真实值的误差,对二者差的平方求和再取平均 with tf.name_scope('loss'): loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) #老版的TensorFlow的该函数为tf.scalar_summary() tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)#观看loss的变化很重要 #使用梯度下降算法来最小化误差loss,学习率为0.1 with tf.name_scope('train'): train_step=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) #初始化所有变量 init=tf.global_variables_initializer() #定义Session,用来执行初始化操作 sess=tf.Session() #老版的TensorFlow的该函数为tf.merge_all_summaries() merged=tf.summary.merge_all()#将所有的summary合并打包 writer=tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/",sess.graph)#将整个 框架加载到一个文件 sess.run(init) #plot the real data fig=plt.figure()#生成一个图片框 ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)#连续画图 ax.scatter(x_data,y_data)#画散点图 plt.ion()#程序遇到show会暂停,故用它保持程序持续运行 plt.show() #训练 for i in range(1000): sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) if i % 50 ==0: result=sess.run(merged,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) writer.add_summary(result,i)#将result加入到 summary中,i是训练的次数 print(sess.run(loss,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data})) #先抹除当前的线,再画新的线 try: #抹除当前的线,因第一次没有线可以抹除,会报错,所以用try来捕捉异常 ax.lines.remove(lines[0]) except Exception: pass prediction_value=sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={xs:x_data}) #plot the prediction #画一条曲线,红色,宽度为5 lines=ax.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw=5) plt.pause(0.1)#让线条停顿0.1秒 #让画图框运行完不会消失 plt.ioff() plt.show()
学自 莫烦 PYTHON