深入理解Spring源码之剖析AOP(注解配置方式)
先贴出整篇文章的测试代码:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.atguigu.aop.MathCalculator;
import com.atguigu.bean.Boss;
import com.atguigu.bean.Car;
import com.atguigu.bean.Color;
import com.atguigu.bean.AwareBean;
import com.atguigu.config.MainConfigOfAOP;
import com.atguigu.config.MainConifgOfAutowired;
import com.atguigu.dao.BookDao;
import com.atguigu.service.BookService;
public class IOCTest_AOP {
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfAOP.class);
MathCalculator mathCalculator = applicationContext.getBean(MathCalculator.class);
mathCalculator.div(1, 0);
applicationContext.close();
}
}import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AopInfrastructureBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import com.atguigu.aop.MathCalculator;
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfAOP {
//业务逻辑类加入容器中
@Bean
public MathCalculator calculator(){
return new MathCalculator();
}
//切面类加入到容器中
@Bean
public LogAspects logAspects(){
return new LogAspects();
}
}import java.util.Arrays;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
/**
* 切面类
*
* @Aspect: 告诉Spring当前类是一个切面类
*
*/
@Aspect
public class LogAspects {
//抽取公共的切入点表达式
//1、本类引用
//2、其他的切面引用
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.MathCalculator.*(..))")
public void pointCut(){};
//@Before在目标方法之前切入;切入点表达式(指定在哪个方法切入)
@Before("pointCut()")
public void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println(""+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"运行。。。@Before:参数列表是:{"+Arrays.asList(args)+"}");
}
@After("com.atguigu.aop.LogAspects.pointCut()")
public void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println(""+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"结束。。。@After");
}
//JoinPoint一定要出现在参数表的第一位
@AfterReturning(value="pointCut()",returning="result")
public void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
System.out.println(""+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"正常返回。。。@AfterReturning:运行结果:{"+result+"}");
}
@AfterThrowing(value="pointCut()",throwing="exception")
public void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
System.out.println(""+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"异常。。。异常信息:{"+exception+"}");
}
}public class MathCalculator {
public int div(int i,int j){
System.out.println("MathCalculator...div...");
return i/j;
}
}
AOP的基本概念和使用步骤
AOP:【动态代理】
指在程序运行期间动态的将某段代码切入到指定方法指定位置进行运行的编程方式;
1、导入aop模块;Spring AOP:(spring-aspects)
2、定义一个业务逻辑类(MathCalculator);在业务逻辑运行的时候将日志进行打印(方法之前、方法运行结束、方法出现异常,xxx)
3、定义一个日志切面类(LogAspects):切面类里面的方法需要动态感知MathCalculator.div运行到哪里然后执行;
通知方法:
前置通知(@Before):logStart:在目标方法(div)运行之前运行
后置通知(@After):logEnd:在目标方法(div)运行结束之后运行(无论方法正常结束还是异常结束)
返回通知(@AfterReturning):logReturn:在目标方法(div)正常返回之后运行
异常通知(@AfterThrowing):logException:在目标方法(div)出现异常以后运行
环绕通知(@Around):动态代理,手动推进目标方法运行(joinPoint.procced())
4、给切面类的目标方法标注何时何地运行(通知注解);
5、将切面类和业务逻辑类(目标方法所在类)都加入到容器中;
6、必须告诉Spring哪个类是切面类(给切面类上加一个注解:@Aspect)
7、给配置类中加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 【开启基于注解的aop模式】
在Spring中很多的 @EnableXXX;
三步:
1)、将业务逻辑组件和切面类都加入到容器中;告诉Spring哪个是切面类(@Aspect)
2)、在切面类上的每一个通知方法上标注通知注解,告诉Spring何时何地运行(切入点表达式)
3)、开启基于注解的aop模式;@EnableAspectJAutoProxy一、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy和AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator分析
AOP原理:【看给容器中注册了什么组件,这个组件什么时候工作,这个组件的功能是什么?】
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
1、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy是什么?
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class):给容器中导入AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar
利用AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar自定义给容器中注册bean;BeanDefinetion
internalAutoProxyCreator=AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
给容器中注册一个AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator;
2、 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator:
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
->AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
->AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
->AbstractAutoProxyCreator
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware
关注后置处理器(在bean初始化完成前后做事情)、自动装配BeanFactory
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.setBeanFactory()
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.有后置处理器的逻辑;
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.setBeanFactory()-》initBeanFactory()
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.initBeanFactory()
=======创建和注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的过程========
1)、传入配置类,创建ioc容器
2)、注册配置类,调用refresh()刷新容器;
3)、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);注册bean的后置处理器来方便拦截bean的创建;
3.1)、先获取ioc容器已经定义了的需要创建对象的所有BeanPostProcessor
3.2)、给容器中加别的BeanPostProcessor
3.3)、优先注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor;
3.4)、再给容器中注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor;
3.5)、注册没实现优先级接口的BeanPostProcessor;
3.6)、注册BeanPostProcessor,实际上就是创建BeanPostProcessor对象,保存在容器中;
创建internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanPostProcessor【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator】
3.6.1)、创建Bean的实例
3.6.2)、populateBean;给bean的各种属性赋值
3.6.3)、initializeBean:初始化bean;
3.6.3.1)、invokeAwareMethods():处理Aware接口的方法回调
3.6.3.2)、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization():应用后置处
理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization()
3.6.3.3)、invokeInitMethods();执行自定义的初始化方法
3.6.3.4)、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization();执行后置处
理器的postProcessAfterInitialization();
3.6.4)、BeanPostProcessor(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator)创建成
功;--》aspectJAdvisorsBuilder
3.7)、把BeanPostProcessor注册到BeanFactory中;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
=======AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator执行时机========
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 继承了 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
4)、finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);完成BeanFactory初始化工作;创建剩下的单实
例bean
4.1)、遍历获取容器中所有的Bean,依次创建对象getBean(beanName); getBean->doGetBean()-
>getSingleton()->
4.2)、创建bean【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在所有bean创建之前会有一个拦
截,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,会调用
【postProcessBeforeInstantiation()】
4.2.1)、先从缓存中获取当前bean,如果能获取到,说明bean是之前被创建过的,直接使用,否则再创建;只要创建好的Bean都会被缓存起来
4.2.2)、createBean();创建bean;AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 会在任
何bean创建之前先尝试返回bean的实例【BeanPostProcessor是在Bean对象创建完成
初始化 前后调用的】【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是在创建Bean实例
之前先尝试用后置处理器返回对象的
4.2.2.1)、resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);解析
BeforeInstantiation希望后置处理器在此能返回一个代理对象;如果能返
回代理对象就使用,如果不能就继续
4.2.2.1.1)、后置处理器先尝试返回对象;bean =
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation():
拿到所有后 置处理器,如果是
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;就执行
postProcessBeforeInstantiation
if (bean != null) {
bean =
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
4.2.2.2)、doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);真正的去创建一个bean
例;和3.6流程一样;二、 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator注册创建和执行时机
实践:观察AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator注册创建:
notice:eclipse里搜索jar包里的类名快捷键Ctrl+Shift+T
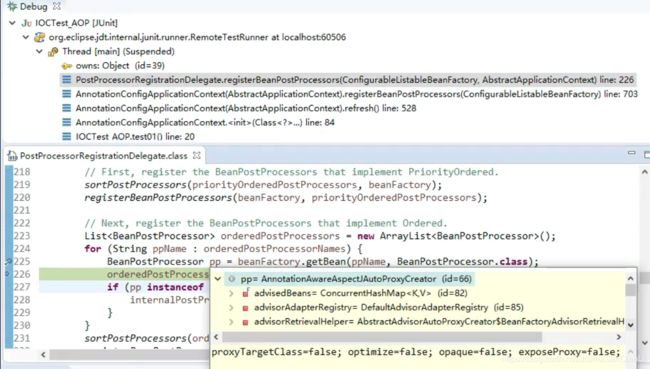
断点打在AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类的setBeanFactory方法下,调用过程如下:
对应过程
1)、传入配置类,创建ioc容器
2)、注册配置类,调用refresh()刷新容器;
3)、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);注册bean的后置处理器来方便拦截bean的创建;
断点打在PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate类的registerBeanPostProcessors方法的
beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class)行上,调用过程如下:
对应过程3)registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);注册bean的后置处理器来方便拦截bean的创建
断点打在AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法上 调用过程如下:
对应过程4.2)创建bean【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在所有bean创建之前会有一个拦截,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,会调用 【postProcessBeforeInstantiation()】
================================================================================================
下面从整体剖析下 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】 的作用:
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】 的作用:
1)、每一个bean创建之前,调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation();
关心MathCalculator和LogAspect的创建
1.1)、判断当前bean是否在advisedBeans中(保存了所有需要增强bean)
1.2)、判断当前bean是否是基础类型的Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、
AopInfrastructureBean,或者是否是切面(@Aspect)
1.3)、是否需要跳过
1.3.1)、获取候选的增强器(切面里面的通知方法)【List
candidateAdvisors】
每一个封装的通知方法的增强器是 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor;
判断每一个增强器是否是 AspectJPointcutAdvisor 类型的;返回true
1.3.2)、永远返回false
2)、创建对象
postProcessAfterInitialization;
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);//包装如果需要的情况下
2.1)、获取当前bean的所有增强器(通知方法) Object[] specificInterceptors
2.1.1、找到候选的所有的增强器(找哪些通知方法是需要切入当前bean方法的)
2.1.2、获取到能在bean使用的增强器。
2.1.3、给增强器排序
2.2)、保存当前bean在advisedBeans中;
2.3)、如果当前bean需要增强,创建当前bean的代理对象;
2.3.1)、获取所有增强器(通知方法)
2.3.2)、保存到proxyFactory
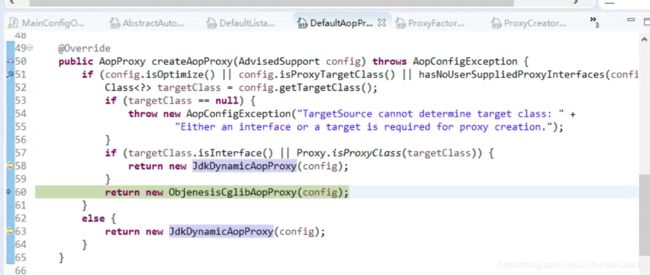
2.3.3)、创建代理对象:Spring自动决定
JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);jdk动态代理;
ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);cglib的动态代理;
2.4)、给容器中返回当前组件使用cglib增强了的代理对象;
2.5)、以后容器中获取到的就是这个组件的代理对象,执行目标方法的时候,代理对象就会执行通知
方法的流程;
3)、目标方法执行 ;
容器中保存了组件的代理对象(cglib增强后的对象),这个对象里面保存了详细信息(比如增强
器,目标对象,xxx);
3.1)、CglibAopProxy.intercept();拦截目标方法的执行
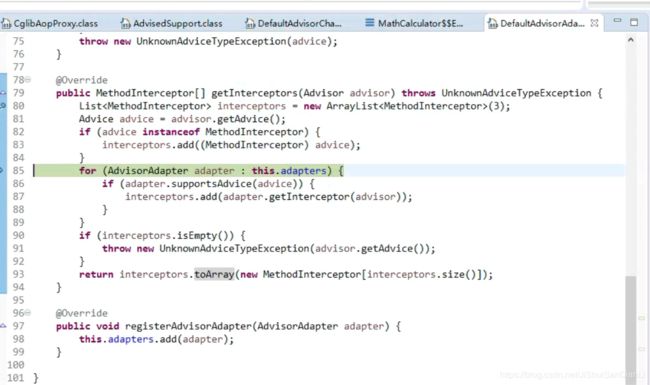
3.2)、根据ProxyFactory对象获取将要执行的目标方法拦截器链;
List 三、创建AOP代理
断点打在AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization(Object, String) 方法
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}进入wrapIfNecessary方法->进入createProxy方法->buildAdvisors方法返回, 如下图可以查看四个增强器
logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint)
logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint)
logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result)
logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception)
断点进入proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader())后可以看到创建了个LogAspects类AOP的cglib代理
org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory: 0 interfaces []; 5
advisors [org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR,
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor: expression [pointCut()];
advice method [public void
com.atguigu.aop.LogAspects.logException(org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint,java.lang.Exception)];
perClauseKind=SINGLETON, InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor: expression [pointCut()];
advice method [public void
com.atguigu.aop.LogAspects.logReturn(org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint,java.lang.Object)];
perClauseKind=SINGLETON, InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor: expression
[com.atguigu.aop.LogAspects.pointCut()];
advice method [public void com.atguigu.aop.LogAspects.logEnd(org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint)];
perClauseKind=SINGLETON, InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor: expression [pointCut()];
advice method [public void
com.atguigu.aop.LogAspects.logStart(org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint)]; perClauseKind=SINGLETON];
targetSource [SingletonTargetSource for target object
[com.atguigu.aop.MathCalculator@7d898981]]; proxyTargetClass=true; optimize=false;
opaque=false; exposeProxy=false; frozen=false四、获取拦截器链-MethodInterceptor
AOP拦截器链MethodInterceptor拦截下了mathCalculator.div(1, 0)然后执行所有对应的增强器
断点打在mathCalculator.div(1, 0)
step into mathCalculator.div(1, 0) ->
step return->step into->step return->step into->step return反复几次后进入CglibAopProxy内部类DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的intercept方法->
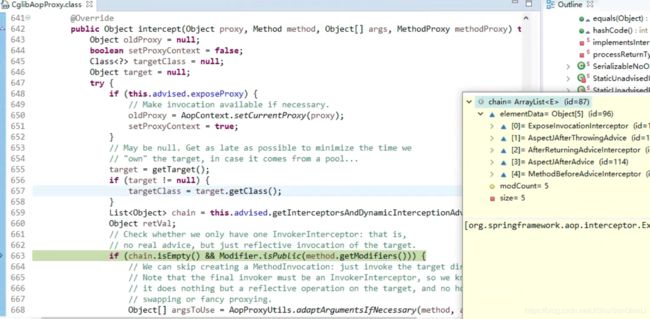
step into advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice->
step into advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice->
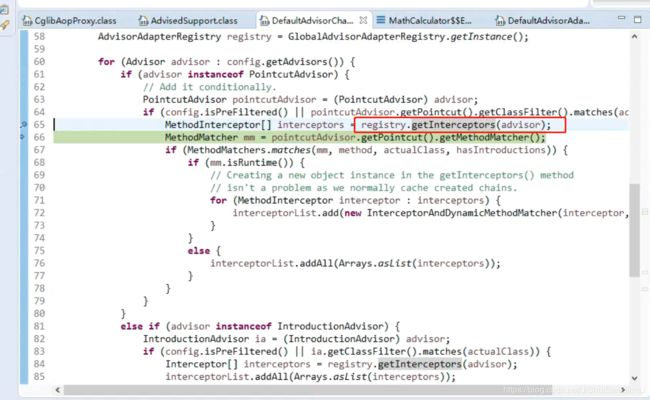
step into registry.getInterceptors(advisor)->
3)、如果没有拦截器链,直接执行目标方法;
拦截器链(每一个通知方法又被包装为方法拦截器,利用MethodInterceptor机制)
4)、如果有拦截器链,把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法,
拦截器链等信息传入创建一个 CglibMethodInvocation 对象,
并调用 Object retVal = mi.proceed();
链式调用通知方法
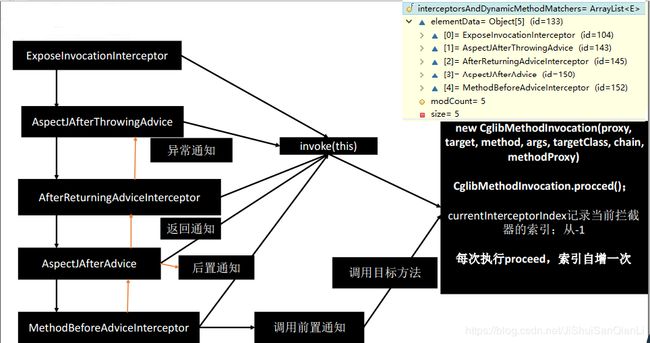
接下来剖析下 new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed()的proceed()方法
源码如下:
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
从上图可以看出前面四次都执行了interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this)分别是下面5个类的invoke,而invoke又执行了mi.proceed() (mi就是CglibMethodInvocation),每次执行变量currentInterceptorIndex就会加1
ExposeInvocationInterceptor的invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
invocation.set(mi);
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice 的invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}AOP总结
1)、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启AOP功能
2)、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 会给容器中注册一个组件 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
3)、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是一个后置处理器;
4)、容器的创建流程:
4.1)、registerBeanPostProcessors()注册后置处理器;创建
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator对象
4.2)、finishBeanFactoryInitialization()初始化剩下的单实例bean
4.2.1)、创建业务逻辑组件和切面组件
4.2.2)、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator拦截组件的创建过程
4.2.3)、组件创建完之后,判断组件是否需要增强是:切面的通知方法,包装成增强器
(Advisor);给业务逻辑组件创建一个代理对象(cglib);
5)、执行目标方法:
5.1)、代理对象执行目标方法
5.2)、CglibAopProxy.intercept();
5.2.1)、得到目标方法的拦截器链(增强器包装成拦截器MethodInterceptor)
5.2.2)、利用拦截器的链式机制,依次进入每一个拦截器进行执行;
5.2.3)、效果:
正常执行:前置通知-》目标方法-》后置通知-》返回通知
出现异常:前置通知-》目标方法-》后置通知-》异常通知