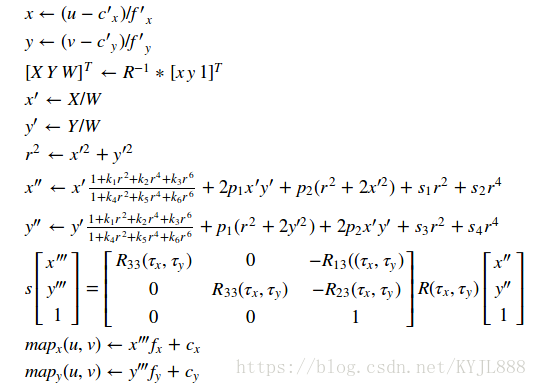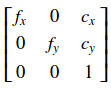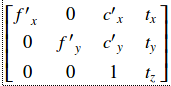{畸变矫正}图像去畸变opencv各种方法与matlab各种方法-联合分析(一统江湖)
opencv 畸变矫正分析
参考 https://docs.opencv.org/3.3.0/da/d54/group__imgproc__transform.html#ga69f2545a8b62a6b0fc2ee060dc30559d
理论分析
方法一undistort() 与matlab标定去畸变显示相同
undistort()
| void cv::undistort | ( | InputArray | src, |
| OutputArray | dst, | ||
| InputArray | cameraMatrix, | ||
| InputArray | distCoeffs, | ||
| InputArray | newCameraMatrix = noArray() |
||
| ) |
矫正图像以补偿镜头失真。
该功能可转换图像以补偿径向和切向镜头失真。该函数只是cv :: initUndistortRectifyMap (带有单位R)和cv :: remap (带双线性插值)的组合。 有关正在执行的转换的详细信息,请参阅前一个函数。
目标图像中的源像中没有对应像素的像素用零(黑色)填充。
可以通过newCameraMatrix来调节在校正图像中可见的源图像的特定子集。 您可以使用cv :: getOptimalNewCameraMatrix根据您的要求计算相应的newCameraMatrix。
可以使用cv :: calibrateCamera确定相机矩阵和失真参数。 如果图像的分辨率与校准阶段使用的分辨率不同,则需要相应地缩放\(f_x,f_y,c_x 和(c_y),而畸变系数保持不变。(分辨率与内参和畸变的关系)
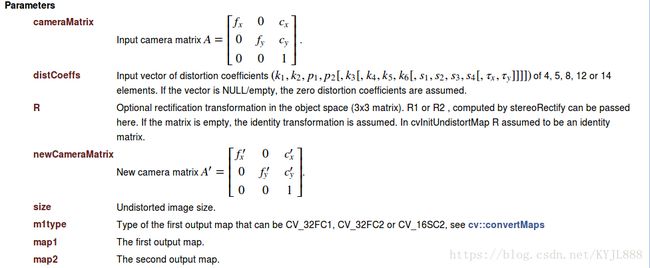
参数
| SRC | 输入(失真)图像。 |
| DST | 输出(校正)图像,其大小和类型与src相同。 |
| cameraMatrix | 输入相机矩阵\(A = \ vecthreethree {f_x} {0} {c_x} {0} {f_y} {c_y} {0} {0} {1} \)。 |
| distCoeffs | 失真系数的输入矢量\((k_1,k_2,p_1,p_2 [,k_3 [,k_4,k_5,k_6 [,s_1,s_2,s_3,s_4 [,\ tau_x,\ tau_y]]]])\)of 4 ,5,8,12或14个元素。 如果向量为NULL /空,则假定零失真系数。 |
| newCameraMatrix | 扭曲图像的相机矩阵。 默认情况下,它与cameraMatrix相同,但您可以通过使用不同的矩阵来扩展和移动结果。 |
方法二 cv::initUndistortRectifyMap and cv::remap
initUndistortRectifyMap()
| void cv :: initUndistortRectifyMap | ( | InputArray | cameraMatrix , |
| InputArray | distcoeffs , | ||
| InputArray | R , | ||
| InputArray | newCameraMatrix , | ||
| 尺寸 | 大小 , | ||
| INT | m1type , | ||
| OutputArray | map1 , | ||
| OutputArray | MAP2 | ||
| ) |
计算不失真和整改转换图。
该函数计算联合不失真和整流变换,并以重映射的映射形式表示结果。 未失真的图像看起来像原始图像,就像使用相机矩阵= newCameraMatrix和零失真一样使用相机拍摄。 在单目相机的情况下,newCameraMatrix通常等于cameraMatrix,或者可以通过cv :: getOptimalNewCameraMatrix计算,以便更好地控制缩放。 在立体相机的情况下,newCameraMatrix通常设置为由cv :: stereoRectify计算的P1或P2。
此外,根据R的说法,这款新相机在坐标空间中的定向也不同。例如,有助于对齐立体相机的两个镜头,使两个图像上的极线变为水平并具有相同的y坐标(在水平对齐立体相机的情况)。
该函数实际构建了重映射使用的逆映射算法的映射。 也就是说,对于目标(校正和校正)图像中的每个像素\((u,v)\),该函数计算源图像中的对应坐标(即,来自相机的原始图像)。 应用以下过程:
其中\((k_1,k_2,p_1,p_2 [,k_3 [,k_4,k_5,k_6 [,s_1,s_2,s_3,s_4 [,\ tau_x,\ tau_y]]]])\)是失真系数(矫正系数)
在立体相机的情况下,此功能被调用两次:在每个摄像头 ,在stereoRectify之后调用,在此之后调用cv :: stereoCalibrate 。 但是如果没有校准立体相机,仍然可以使用cv :: stereoRectifyUncalibrated直接从基本矩阵计算校正变换。 对于每个相机,该函数计算单应性H作为像素域中的整流变换,而不是3D空间中的旋转矩阵R. R可以从H计算得到
![]()
其中cameraMatrix可以任意选择。
remap()
| void cv :: remap | ( | InputArray | src , |
| OutputArray | dst , | ||
| InputArray | map1 , | ||
| InputArray | map2 , | ||
| INT | 插值 | ||
| INT | borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT , |
||
| const Scalar & | borderValue = Scalar () |
||
|
|
) |
对图像应用通用几何变换。
函数remap使用指定的映射转换源图像:
其中使用可用插值方法之一计算具有非整数坐标的像素值。 \(map_x \)和\(map_y \)可分别编码为\(map_1 \)和\(map_2 \)中的单独浮点映射,或\((x,y)\的交错浮点映射在\(map_1 \)中,或使用convertMaps创建的定点地图。 您可能希望从映射的浮点转换为定点表示的原因是它们可以产生更快(2x)的重映射操作。 在转换的情况下,\(map_1 \)包含对(cvFloor(x),cvFloor(y))和\(map_2 \)包含插值系数表中的索引。
此功能无法就地操作。
参数
| SRC | 来源图片。 |
| DST | 目的地形象。 它与map1的大小相同,与src的大小相同。 |
| MAP1 | (x,y)的第一个映射点或仅具有CV_16SC2,CV_32FC1或CV_32FC2类型的x值。 有关将浮点表示转换为定点以获得速度的详细信息,请参阅convertMaps。 |
| MAP2 | 第二个y值映射分别具有类型CV_16UC1,CV_32FC1或none(空映射,如果map1是(x,y)点)。 |
| 插值 | 插值方法(参见cv :: InterpolationFlags )。 此函数不支持INTER_AREA方法。 |
| borderMode | 像素外推方法(参见cv :: BorderTypes )。 当borderMode = BORDER_TRANSPARENT时,表示目标图像中与源图像中的“异常值”对应的像素未被该函数修改。 |
| borderValue | 在边界不变的情况下使用的值。 默认情况下,它为0。 |
注意 由于当前的实现限制,输入和输出图像的大小应小于32767x32767。
方法三 undistortPoints()
undistortPoints()
| void cv :: undistortPoints | ( | InputArray | src , |
| OutputArray | dst , | ||
| InputArray | cameraMatrix , | ||
| InputArray | distcoeffs , | ||
| InputArray | R = noArray () , |
||
| InputArray | P = noArray () |
||
| ) |
根据观察到的点坐标计算理想点坐标。
该函数类似于cv :: undistort和cv :: initUndistortRectifyMap,但它在稀疏的点集上操作而不是光栅图像。 此函数还对projectPoints执行反向转换。 在3D对象的情况下,它不重建其3D坐标,但是对于平面对象,如果指定了适当的R,则直到旋转向量。
对于每个观察到的点坐标((u,v)),函数计算:
其中, undistort是一种近似迭代算法,用于估计归一化失真点坐标中的归一化原始点坐标(“归一化”意味着坐标不依赖于摄像机内参)。
该功能可用于立体摄像头或单目摄像头(当R为空时)。
参数
实验结果
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/billbliss/article/details/52527182
#include "opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void ReadIntrinsics(Mat &cameraMatrix, Mat &distCoeffs, Size &imageSize, char *IntrinsicsPath)
{
bool FSflag = false;
FileStorage readfs;
FSflag = readfs.open(IntrinsicsPath, FileStorage::READ);
if (FSflag == false) cout << "Cannot open the file" << endl;
readfs["Camera_Matrix"] >> cameraMatrix;
readfs["Distortion_Coefficients"] >> distCoeffs;
readfs["image_Width"] >> imageSize.width;
readfs["image_Height"] >> imageSize.height;
cout << cameraMatrix << endl << distCoeffs << endl << imageSize << endl;
readfs.release();
}
void Undistort_img(Mat map1, Mat map2, char *path)
{
Mat img1, img2;
img1 = imread(path);
if (img1.empty()) cout << "Cannot open the image" << endl;
remap(img1, img2, map1, map2, INTER_LINEAR);
// imwrite(path, img2);
imshow("src img", img1);
imshow("dst img", img2);
waitKey();
}
void main()
{
Mat cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, map1, map2;
Size imageSize;
char * IntrinsicsPath = "Intrinsics.yml";
ReadIntrinsics(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imageSize, IntrinsicsPath);
// 去畸变并保留最大图
initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, Mat(),
getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imageSize, 1, imageSize, 0),
imageSize, CV_16SC2, map1, map2);
Undistort_img(map1, map2, "E:/VS13/undistort/undistort/1.bmp");
// 去畸变至全图
initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, Mat(), Mat(),
imageSize, CV_16SC2, map1, map2);
Undistort_img(map1, map2, "E:/VS13/undistort/undistort/1.bmp");
}实验程序
为公布待上传
实验效果图总览
原图
undistort效果图
undistort_p (P= getOptimalNewCameraMatrix)效果图
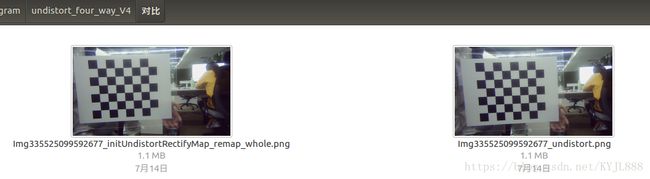
initUndistortRectifyMap_remap_whole 全图显示效果图
initUndistortRectifyMap_remap_max最大像素显示效果
附 对比图,剪切不同
附 错误的标定畸变参数 ,导致的畸变矫正效果不同 (使用K3)
matlab图像畸变矫正undistortImage
参考 http://www.mathworks.com/help/vision/ref/undistortimage.html
通过命令 openExample('vision/CorrectAnImageForLensDistortionExample')句法
[J,newOrigin] = undistortImage(I,cameraParams)
[J,newOrigin] = undistortImage(I,cameraParams,interp)
[J,newOrigin] = undistortImage( ___ ,Name,Value)
代码
%% Correct Image for Lens Distortion
%
%%
% Create a set of calibration images.
images = imageDatastore(fullfile(toolboxdir('vision'),'visiondata', ...
'calibration','mono'));
%%
% Detect calibration pattern.
[imagePoints,boardSize] = detectCheckerboardPoints(images.Files);
%%
% Generate world coordinates of the corners of the squares. The square
% size is in millimeters.
squareSize = 29;
worldPoints = generateCheckerboardPoints(boardSize,squareSize);
%%
% Calibrate the camera.
I = readimage(images,1);
imageSize = [size(I,1),size(I,2)];
cameraParams = estimateCameraParameters(imagePoints,worldPoints, ...
'ImageSize',imageSize);
%%
% Remove lens distortion and display results.
I = images.readimage(1);
J1 = undistortImage(I,cameraParams);
%%
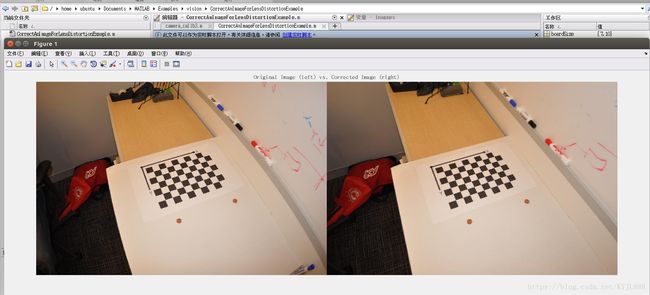
figure; imshowpair(I,J1,'montage');
title('Original Image (left) vs. Corrected Image (right)');
%%
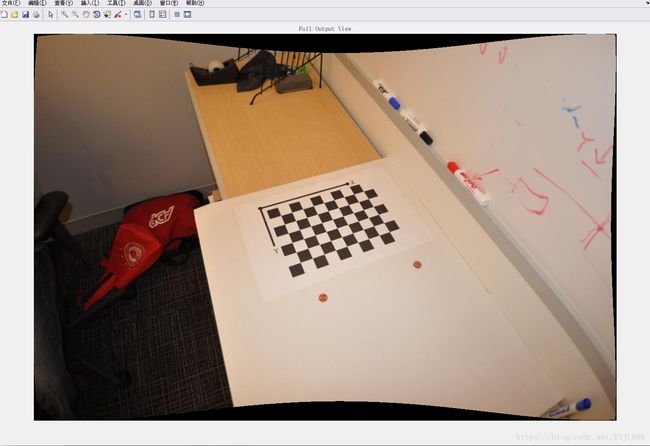
J2 = undistortImage(I,cameraParams,'OutputView','full');
figure;
imshow(J2);
title('Full Output View');效果图
matlab 三种显示方法
'OutputView' - 输出图像的大小'same' (默认)| 'full' | 'valid'
输出图像的大小,指定为逗号分隔对,由' OutputView '和字符向量'same' , 'full'或'valid' 。 将属性设置为'same' ,该函数会将输出图像设置为与输入图像的大小相匹配。 将属性设置为'full' ,输出包括输入图像中的所有像素。 将属性设置为'valid' ,函数会裁剪输出图像以仅包含有效像素。
对于输入图像:
| OutputView | 输出图像 |
|---|---|
'same' |
匹配输入图像的大小。
|
'full' |
输入图像中的所有像素。
|
'valid' |
仅来自输入图像的有效像素。 |
输入参数
全部收缩
I - 输入图像
M -by- N -by-3真彩色图像 | M -by- N 2-D灰度图像
输入图像,以M -by- N -by-3真彩色或M -by- N 2-D灰度指定。 输入图像必须是真实的且非经典的。
数据类型: single | double | int16 | uint8 | uint16 | logical
cameraParams - 用于存储摄像机参数的对象
cameraParameters对象 | cameraIntrinsics对象
摄像机参数,指定为cameraParameters或cameraIntrinsics对象。 您可以使用estimateCameraParameters函数返回cameraParameters对象。 cameraParameters对象包含相机的固有,外在和镜头失真参数。
interp - 插值方法
'linear' (默认)| 'nearest' | 'cubic'
在输入图像上使用的插值方法,指定为字符向量'linear' , 'nearest'或'cubic' 。
名称 - 值对参数
指定可选的逗号分隔的Name,Value参数对。 Name是参数名称, Value是相应的值。 Name必须出现在单引号( ' ' )中。 您可以按任何顺序指定多个名称和值对参数,如Name1,Value1,...,NameN,ValueN 。
示例: 'FillValues' , 0将输出像素填充值设置为0 。
全部收缩
'FillValues' - 输出像素填充值
0 (默认值)| 标量 | 3元素向量
输出像素填充值,指定为由' FillValues '组成的逗号分隔对和包含一个或多个填充值的数组。 当输入图像中对应的逆变换位置完全位于输入图像边界之外时,可以使用输出像素的填充值。 使用2-D灰度输入图像时,必须将FillValues设置为标量。 当您使用truecolor时, FillValues可以是RGB值的标量或3元素向量。
输出参数
全部收缩
J - 无失真的图像
M -by- N -by-3真彩色图像| M -by- N 2-D灰度图像
未失真的图像,以M -by- N -by-3真彩色或M -by- N 2-D灰度返回。
数据类型: single | double | int16 | uint8 | uint16 | logical
newOrigin - 输出图像原点
2元素向量
输出图像原点,作为2元素[ x , y ]向量返回。 该函数根据输入内在坐标设置输出原点位置。 当您将OutputView设置为'same' ,这意味着输出图像与输入图像的大小相同,该函数将newOrigin设置为[0,0] 。
newOrigin输出表示从输出图像J的固有坐标到输入图像I的固有坐标的转换。
| 令P I表示输入图像I的内在坐标中的点。 |
| 令P J表示输出图像J的内在坐标中的相同点。 |
P I = P J + newOrigin
待补充。。。。。。。。。。。。。