Qt学习——Qimage和Mat
一、Qimage
资料来源:http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qimage.html
简介
Qimage类提供独立于硬件的图像描述,其允许直接对像素数据进行访问,同时可以作为绘画对象使用。
Qt提供了四个用于图像数据处理的类:QImage,QPixmap,QBitmap和QPicture。
- QImage:主要用于I / O和对图像像素直接访问和操作。
- QPixmap:主要用于在屏幕上显示图像。
- QBitmap:继承QPixmap的类,用于确保深度为1。
- QPicture:用于记录和重放QPainter命令。
因为QImage是QPaintDevice子类,所以可以使用QPainter直接绘制到QImage格式的图像上。在QImage上使用QPainter时,可以在独立于当前GUI线程之外的另一个线程中执行绘制。
QImage支持所多种图像格式格式。这些包括单色,8位,32位和alpha混合图像。
QImage提供了一系列功能,可用于获取有关图像的各种信息,同时也可用于图像转换。
由于QImage类使用隐式数据共享,因此QImage对象可以按值传递。QImage对象也可以进行流式处理和比较。
存储在QImage中的每个像素由整数表示,其大小取决于图像格式。
注意
- 如果想在Qt的静态版本中加载QImage对象,需参阅http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/plugins-howto.html。
- 不支持在QImage :: Format_Indexed8格式的QImage上画图。
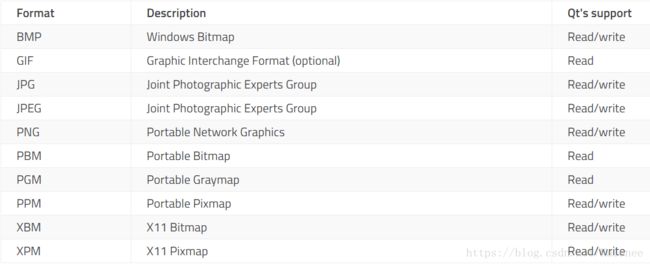
支持图片格式
Qimage格式
| Constant | Value | Description |
| QImage::Format_Invalid | 0 | The image is invalid. |
| QImage::Format_Mono | 1 | The image is stored using 1-bit per pixel. Bytes are packed with the most significant bit (MSB) first. |
| QImage::Format_MonoLSB | 2 | The image is stored using 1-bit per pixel. Bytes are packed with the less significant bit (LSB) first. |
| QImage::Format_Indexed8 | 3 | The image is stored using 8-bit indexes into a colormap. |
| QImage::Format_RGB32 | 4 | The image is stored using a 32-bit RGB format (0xffRRGGBB). |
| QImage::Format_ARGB32 | 5 | The image is stored using a 32-bit ARGB format (0xAARRGGBB). |
| QImage::Format_ARGB32_Premultiplied | 6 | The image is stored using a premultiplied 32-bit ARGB format (0xAARRGGBB), i.e. the red, green, and blue channels are multiplied by the alpha component divided by 255. (If RR, GG, or BB has a higher value than the alpha channel, the results are undefined.) Certain operations (such as image composition using alpha blending) are faster using premultiplied ARGB32 than with plain ARGB32. |
| QImage::Format_RGB16 | 7 | The image is stored using a 16-bit RGB format (5-6-5). |
| QImage::Format_ARGB8565_Premultiplied | 8 | The image is stored using a premultiplied 24-bit ARGB format (8-5-6-5). |
| QImage::Format_RGB666 | 9 | The image is stored using a 24-bit RGB format (6-6-6). The unused most significant bits is always zero. |
| QImage::Format_ARGB6666_Premultiplied | 10 | The image is stored using a premultiplied 24-bit ARGB format (6-6-6-6). |
| QImage::Format_RGB555 | 11 | The image is stored using a 16-bit RGB format (5-5-5). The unused most significant bit is always zero. |
| QImage::Format_ARGB8555_Premultiplied | 12 | The image is stored using a premultiplied 24-bit ARGB format (8-5-5-5). |
| QImage::Format_RGB888 | 13 | The image is stored using a 24-bit RGB format (8-8-8). |
| QImage::Format_RGB444 | 14 | The image is stored using a 16-bit RGB format (4-4-4). The unused bits are always zero. |
| QImage::Format_ARGB4444_Premultiplied | 15 | The image is stored using a premultiplied 16-bit ARGB format (4-4-4-4). |
| QImage::Format_RGBX8888 | 16 | The image is stored using a 32-bit byte-ordered RGB(x) format (8-8-8-8). This is the same as the Format_RGBA8888 except alpha must always be 255. |
| QImage::Format_RGBA8888 | 17 | The image is stored using a 32-bit byte-ordered RGBA format (8-8-8-8). Unlike ARGB32 this is a byte-ordered format, which means the 32bit encoding differs between big endian and little endian architectures, being respectively (0xRRGGBBAA) and (0xAABBGGRR). The order of the colors is the same on any architecture if read as bytes 0xRR,0xGG,0xBB,0xAA. |
| QImage::Format_RGBA8888_Premultiplied | 18 | The image is stored using a premultiplied 32-bit byte-ordered RGBA format (8-8-8-8). |
| QImage::Format_BGR30 | 19 | The image is stored using a 32-bit BGR format (x-10-10-10). |
| QImage::Format_A2BGR30_Premultiplied | 20 | The image is stored using a 32-bit premultiplied ABGR format (2-10-10-10). |
| QImage::Format_RGB30 | 21 | The image is stored using a 32-bit RGB format (x-10-10-10). |
| QImage::Format_A2RGB30_Premultiplied | 22 | The image is stored using a 32-bit premultiplied ARGB format (2-10-10-10). |
| QImage::Format_Alpha8 | 23 | The image is stored using an 8-bit alpha only format. |
不同格式之间可以通过函数进行转换:
QImage QImage::convertToFormat(QImage::Format format, Qt::ImageConversionFlags flags = Qt::AutoColor) const &
QImage QImage::convertToFormat(QImage::Format format, Qt::ImageConversionFlags flags = Qt::AutoColor) &&注意:若使用QPainter,建议采用QImage::Format_ARGB32_Premultiplied代替ARGB32,可以获得更高速度。
二、Mat
Mat用于在OpenCV中实现图像的存储和处理,在官方文档中,在程序编写过程中Mat可以自动分配空间或者自动释放内存,但是在实际编写中依然会出现内存报错或者溢出的问题,其中需要注意的为内存的深拷贝和浅拷贝。
Mat包含两个部分,矩阵头(包含矩阵大小,用于存储的方法,存储矩阵的地址等信息)和指向包含像素值的矩阵的指针(其维度取决于选择的存储方法)。矩阵头的大小是恒定的,但是矩阵本身的大小会随着图像的改变而变化,并且通常大几个数量级。
常用Mat格式及其对应数据格式:
CV_8U: 1-byte unsigned integer (unsigned char).
CV_32S: 4-byte signed integer (int).
CV_32F: 4-byte floating point (float).(1)Mat初始化
1、默认形式
cv::Mat m;
2、指定类型和大小(行列)的二维数组
cv::Mat m(int rows, int cols, int type)
3、有初始化值的指定类型和大小(行列)的二维数组
cv::Mat m(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s);
4、使用预先存在数据定义的指定类型和大小(行列)的二维数组
cv::Mat m(int rows, int cols, int type, void* data, size_t step = AUTO_STEP);
5、指定大小(size)和类型的二维数组
cv::Mat m(cv::Size sz, int type, const Scalar& s);
6、使用预先存在的数据定义的指定大小(size)和类型的二维数组
cv::Mat m(cv::Size sz, int type, void* data, size_t step = AUTO_STEP);
7、指定类型的多维数组
cv::Mat m(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type);
8、有初始化值的指定类型多维数组
cv::Mat m(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s);
9、使用预先存在的数据定义的指定类型的多维数组
cv::Mat m(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, void* data, size_t step = AUTO_STEP);(2)Mat深拷贝和浅拷贝
//浅拷贝:
Mat A;
A = image // 第一种方式
Mat A(image); // 第二种方式
//浅copy为共享相同存储空间,但拥有不同的矩阵头。当图像矩阵发生变化时,两者相关联,都会变化。
//深拷贝
Mat A,B;
A = image.clone(); // 第一种方式
image.copyTo(B); // 第二种方式
//深拷贝为真正的复制了一个新的图像矩阵,此时image,A,B三者相互没有影响。
三、Qimage和Mat转换
(1) Qimage转换为Mat
cv::Mat MainWindow::QImage2cvMat(const QImage& image)
{
switch(image.format())
{
// 8-bit, 4 channel
case QImage::Format_ARGB32:
break;
case QImage::Format_ARGB32_Premultiplied:
{
cv::Mat mat(image.height(), image.width(),
CV_8UC4,
(void*)image.constBits(),
image.bytesPerLine());
return mat.clone();
}
// 8-bit, 3 channel
case QImage::Format_RGB32:
{
cv::Mat mat(image.height(),image.width(),
CV_8UC4,
(void*)image.constBits(),
image.bytesPerLine());
// drop the all-white alpha channel
cv::cvtColor(mat, mat, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
return mat.clone();
}
case QImage::Format_RGB888:
{
QImage swapped = inImage.rgbSwapped();
cv::Mat mat(swapped.height(), swapped.width(),
CV_8UC3,
(void*)image.constBits(),
image.bytesPerLine());
return mat.clone();
}
// 8-bit, 1 channel
case QImage::Format_Indexed8:
{
cv::Mat mat(image.height(),image.width(),
CV_8UC1,
(void*)image.constBits(),
image.bytesPerLine());
return mat.clone();
}
// wrong
default:
qDebug() << "ERROR: QImage could not be converted to Mat.";
break;
}
return cv::Mat();
}(2) Mat转换为Qimage
QImage MatToQImage(const cv::Mat& mat)
{
switch (mat.type())
{
// 8-bit, 4 channel
case CV_8UC4:
{
QImage image(mat.data,
mat.cols, mat.rows,
static_cast(mat.step),
QImage::Format_ARGB32);
return image;
}
// 8-bit, 3 channel
case CV_8UC3:
{
QImage image(mat.data,
mat.cols, mat.rows,
static_cast(mat.step),
QImage::Format_RGB888);
return image.rgbSwapped();
}
// 8-bit, 1 channel
case CV_8UC1:
{
#if QT_VERSION >= QT_VERSION_CHECK(5, 5, 0)
QImage image(mat.data,
mat.cols, mat.rows,
static_cast(mat.step),
QImage::Format_Grayscale8);
#else
static QVector sColorTable;
// only create our color table the first time
if (sColorTable.isEmpty())
{
sColorTable.resize( 256 );
for ( int i = 0; i < 256; ++i )
{
sColorTable[i] = qRgb( i, i, i );
}
}
QImage image(mat.data,
mat.cols, mat.rows,
static_cast(mat.step),
QImage::Format_Indexed8 );
image.setColorTable(sColorTable);
#endif
return image;
}
// wrong
default:
qDebug() << "ERROR: Mat could not be converted to QImage.";
break;
}
return QImage();
}
参考
http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qimage.html
https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.1/d3/d63/classcv_1_1Mat.html
https://blog.csdn.net/guduruyu/article/details/66973415
https://blog.csdn.net/dancing_night/article/details/51545524