cJSON源码解释(二)--解释输入
cJSON解释
把读入的字符串解释成一颗树,具体的结构参考
对这个部分更加详尽的注释可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/zengjfgit/p/4314330.html
/* 跳过空格和回车键,换行符和ascii码小于等于32的字符,cr是回车键,键码值为13,lf是换行键,键码是12,空格的键码值为32*/ static const char *skip(const char *in) { while (in && *in && (unsigned char)*in<=32) in++; return in; } /* Default options for cJSON_Parse */ cJSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value) { return cJSON_ParseWithOpts(value,0,0); } /* Parse an object - create a new root, and populate. */ /*解析一个对象,创建一个新的根节点*/ cJSON *cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value,const char **return_parse_end,int require_null_terminated) { const char *end=0; cJSON *c=cJSON_New_Item(); ep=0; if (!c) return 0; /* memory fail */ end=parse_value(c,skip(value)); if (!end){ cJSON_Delete(c); return 0; } /* parse failure. ep is set. */ /* if we require null-terminated JSON without appended garbage, skip and then check for a null terminator */ if (require_null_terminated) { end=skip(end); if (*end) { cJSON_Delete(c); ep=end; return 0; } } if (return_parse_end) *return_parse_end=end; return c; }
最主要的解释函数就是parese_value(),注意到形参value的值的开头为下面几种情况之一:
分别对应的输入为:
- \”字符串\”
- l数字
- {
- [
- true
- false
- null
当要解释的字符串的前几个字符是null,false或者true的时候,只是简单的设置了节点的type成员字段然后就返回,而遇到剩余的情况时,就需要特别的解释函数
static const char *parse_value(cJSON *item,const char *value) { if (!value) return 0; /* Fail on null. */ if (!strncmp(value,"null",4)){ item->type=cJSON_NULL; return value+4; } if (!strncmp(value,"false",5)){ item->type=cJSON_False; return value+5; } if (!strncmp(value,"true",4)){ item->type=cJSON_True; item->valueint=1; return value+4; } if (*value=='\"'){ return parse_string(item,value); } if (*value=='-' || (*value>='0' && *value<='9')){ return parse_number(item,value); } if (*value=='['){ return parse_array(item,value); } if (*value=='{'){ return parse_object(item,value); } ep=value;return 0; /* failure. */ }
解释字符串
把两个双引号之间的字符串提取出来,遇到特殊字符的时候就进行转义
static const char *parse_string(cJSON *item,const char *str) { const char *ptr=str+1;char *ptr2;char *out;int len=0;unsigned uc,uc2; if (*str!='\"') { ep=str; return 0; } /* not a string! */ while (*ptr!='\"' && *ptr && ++len) if (*ptr++ == '\\') ptr++; /*相当于跳过了\\\”字符*/ out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+1); /* This is how long we need for the string, roughly. */ if (!out) return 0; ptr=str+1;ptr2=out; while (*ptr!='\"' && *ptr) { if (*ptr!='\\') *ptr2++=*ptr++; else { ptr++; switch (*ptr) { case 'b': *ptr2++='\b'; break; case 'f': *ptr2++='\f'; break; case 'n': *ptr2++='\n'; break; case 'r': *ptr2++='\r'; break; case 't': *ptr2++='\t'; break; case 'u': /* transcode utf16 to utf8. */ uc=parse_hex4(ptr+1);ptr+=4; /* get the unicode char. */ if ((uc>=0xDC00 && uc<=0xDFFF) || uc==0) break; /* check for invalid. */ if (uc>=0xD800 && uc<=0xDBFF) /* UTF16 surrogate pairs. */ { if (ptr[1]!='\\' || ptr[2]!='u') break; /* missing second-half of surrogate. */ uc2=parse_hex4(ptr+3);ptr+=6; if (uc2<0xDC00 || uc2>0xDFFF) break; /* invalid second-half of surrogate. */ uc=0x10000 + (((uc&0x3FF)<<10) | (uc2&0x3FF)); } len=4;if (uc<0x80) len=1;else if (uc<0x800) len=2;else if (uc<0x10000) len=3; ptr2+=len; switch (len) { case 4: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6; case 3: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6; case 2: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6; case 1: *--ptr2 =(uc | firstByteMark[len]); } ptr2+=len; break; default: *ptr2++=*ptr; break; } ptr++; } } *ptr2=0; if (*ptr=='\"') ptr++; item->valuestring=out; item->type=cJSON_String; return ptr; }
如果出现了unicode编码(以\u开头的编码)此时要调用parse_hex4()函数来转换
static unsigned parse_hex4(const char *str) { unsigned h=0; if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0; h=h<<4;str++; if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0; h=h<<4;str++; if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0; h=h<<4;str++; if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0; return h; }
解释数字
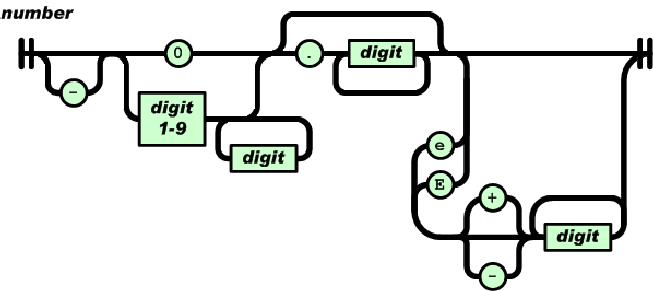
注意这里也可以解释科学计数法
/* Parse the input text to generate a number, and populate the result into item. */ static const char *parse_number(cJSON *item,const char *num) { double n=0,sign=1,scale=0;int subscale=0,signsubscale=1; if (*num=='-') sign=-1,num++; /* Has sign? */ if (*num=='0') num++; /* is zero */ if (*num>='1' && *num<='9') do n=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0'); while (*num>='0' && *num<='9'); /* Number? */ if (*num=='.' && num[1]>='0' && num[1]<='9') { num++; do n=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0'),scale--; while (*num>='0' && *num<='9'); } /* Fractional part? */ if (*num=='e' || *num=='E') /* Exponent? */{ num++; if (*num=='+') num++; else if (*num=='-') signsubscale=-1,num++; /* With sign? */ while (*num>='0' && *num<='9') subscale=(subscale*10)+(*num++ - '0'); /* Number? */ } n=sign*n*pow(10.0,(scale+subscale*signsubscale)); /* number = +/- number.fraction * 10^+/- exponent */ item->valuedouble=n; item->valueint=(int)n; item->type=cJSON_Number; return num; }
解释数组
在读取到一个[(左中括号)时跳转到这里,把数组内用逗号分隔的元素解释成一个双向链表,注意,数组内可能出现嵌套元素,参考:
/* Build an array from input text. */ static const char *parse_array(cJSON *item,const char *value) { cJSON *child; if (*value!='[') {ep=value;return 0;} /* not an array! */ item->type=cJSON_Array; value=skip(value+1); if (*value==']') return value+1; /* empty array. */ item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item(); if (!item->child) return 0; /* memory fail */ value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */ if (!value) return 0; while (*value==',') { cJSON *new_item; if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */ child->next=new_item;new_item->prev=child;child=new_item; value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1))); if (!value) return 0; /* memory fail */ } if (*value==']') return value+1; /* end of array */ ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */ }
解释对象
在读取到一个{(左大括号)时跳转到这里,类似于解释数组,参考:
/* Build an object from the text. */ static const char *parse_object(cJSON *item,const char *value) { cJSON *child; if (*value!='{') { ep=value; return 0; } /* not an object! */ //解释key值 item->type=cJSON_Object; value=skip(value+1); if (*value=='}') return value+1; /* empty array. */ item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item(); if (!item->child) return 0; value=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value))); if (!value) return 0; child->string=child->valuestring;child->valuestring=0; //解释value值 if (*value!=':') { ep=value; return 0; } /* fail! */ value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */ if (!value) return 0; while (*value==',') { cJSON *new_item; if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */ child->next=new_item; new_item->prev=child; child=new_item; value=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value+1))); if (!value) return 0; child->string=child->valuestring; child->valuestring=0; if (*value!=':') { ep=value; return 0; } /* fail! */ value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */ if (!value) return 0; } if (*value=='}') return value+1; /* end of array */ ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */ }