史上最全的ElasticSearch教程(一)索引的增删改查
1.7.API
Elasticsearch提供了Rest风格的API,即http请求接口,而且也提供了各种语言的客户端API
1.7.1.Rest风格API
文档地址:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/index.html
1.7.2.客户端API
Elasticsearch支持的客户端非常多:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/index.html
点击Java Rest Client后,你会发现又有两个:
Low Level Rest Client是低级别封装,提供一些基础功能,但更灵活
High Level Rest Client,是在Low Level Rest Client基础上进行的高级别封装,功能更丰富和完善,而且API会变的简单
1.7.3.如何学习
建议先学习Rest风格API,了解发起请求的底层实现,请求体格式等。
2.操作索引
2.1.基本概念
Elasticsearch也是基于Lucene的全文检索库,本质也是存储数据,很多概念与MySQL类似的。
对比关系:
索引(indices)--------------------------------Databases 数据库
类型(type)-----------------------------Table 数据表
文档(Document)----------------Row 行
字段(Field)-------------------Columns 列
详细说明:
| 概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 索引库(indices) | indices是index的复数,代表许多的索引, |
| 类型(type) | 类型是模拟mysql中的table概念,一个索引库下可以有不同类型的索引,比如商品索引,订单索引,其数据格式不同。不过这会导致索引库混乱,因此未来版本中会移除这个概念 |
| 文档(document) | 存入索引库原始的数据。比如每一条商品信息,就是一个文档 |
| 字段(field) | 文档中的属性 |
| 映射配置(mappings) | 字段的数据类型、属性、是否索引、是否存储等特性 |
是不是与Lucene和solr中的概念类似。
另外,在SolrCloud中,有一些集群相关的概念,在Elasticsearch也有类似的:
- 索引集(Indices,index的复数):逻辑上的完整索引
- 分片(shard):数据拆分后的各个部分
- 副本(replica):每个分片的复制
要注意的是:Elasticsearch本身就是分布式的,因此即便你只有一个节点,Elasticsearch默认也会对你的数据进行分片和副本操作,当你向集群添加新数据时,数据也会在新加入的节点中进行平衡。
2.2.创建索引
2.2.1.语法
Elasticsearch采用Rest风格API,因此其API就是一次http请求,你可以用任何工具发起http请求
创建索引的请求格式:
-
请求方式:PUT
-
请求路径:/索引库名
-
请求参数:json格式:
{ "settings": { "number_of_shards": 3, "number_of_replicas": 2 } }- settings:索引库的设置
- number_of_shards:分片数量
- number_of_replicas:副本数量
- settings:索引库的设置
2.2.2.测试
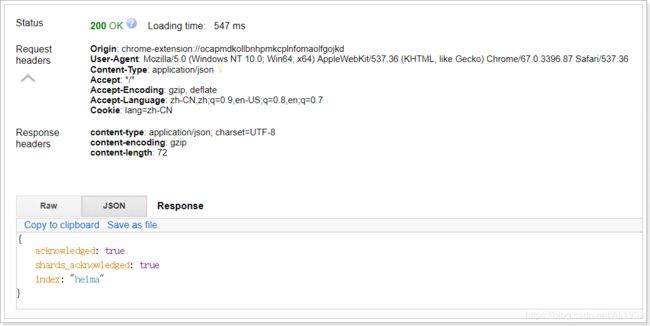
我们先用RestClient来试试
响应:
可以看到索引创建成功了。
2.2.3.使用kibana创建
kibana的控制台,可以对http请求进行简化,示例:
相当于是省去了elasticsearch的服务器地址
而且还有语法提示,非常舒服。
2.3.查看索引设置
语法
Get请求可以帮我们查看索引信息,格式:
GET /索引库名
或者,我们可以使用*来查询所有索引库配置:
2.4.删除索引
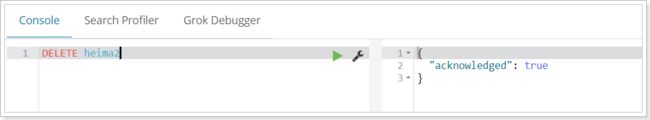
删除索引使用DELETE请求
语法
DELETE /索引库名
示例
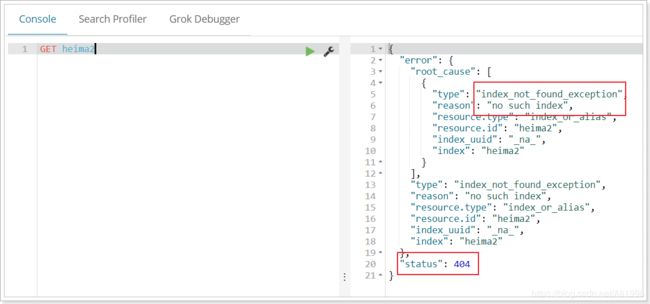
再次查看heima2:
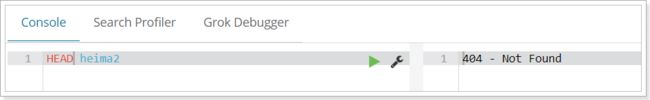
当然,我们也可以用HEAD请求,查看索引是否存在:
2.5.映射配置
索引有了,接下来肯定是添加数据。但是,在添加数据之前必须定义映射。
什么是映射?
映射是定义文档的过程,文档包含哪些字段,这些字段是否保存,是否索引,是否分词等
只有配置清楚,Elasticsearch才会帮我们进行索引库的创建(不一定)
2.5.1.创建映射字段
语法
请求方式依然是PUT
PUT /索引库名/_mapping/类型名称
{
"properties": {
"字段名": {
"type": "类型",
"index": true,
"store": true,
"analyzer": "分词器"
}
}
}
-
类型名称:就是前面将的type的概念,类似于数据库中的不同表
字段名:任意填写 ,可以指定许多属性,例如:
-
type:类型,可以是text、long、short、date、integer、object等
-
index:是否索引,默认为true
-
store:是否存储,默认为false
-
analyzer:分词器,这里的
ik_max_word即使用ik分词器
示例
发起请求:
PUT heima/_mapping/goods
{
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": "false"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
}
}
}
响应结果:
{
"acknowledged": true
}
2.5.2.查看映射关系
语法:
GET /索引库名/_mapping
示例:
GET /heima/_mapping
响应:
{
"heima": {
"mappings": {
"goods": {
"properties": {
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}
}
2.5.3.字段属性详解
2.5.3.1.type
Elasticsearch中支持的数据类型非常丰富:
我们说几个关键的:
-
String类型,又分两种:
- text:可分词,不可参与聚合
- keyword:不可分词,数据会作为完整字段进行匹配,可以参与聚合
-
Numerical:数值类型,分两类
- 基本数据类型:long、interger、short、byte、double、float、half_float
- 浮点数的高精度类型:scaled_float
- 需要指定一个精度因子,比如10或100。elasticsearch会把真实值乘以这个因子后存储,取出时再还原。
-
Date:日期类型
elasticsearch可以对日期格式化为字符串存储,但是建议我们存储为毫秒值,存储为long,节省空间。
2.5.3.2.index
index影响字段的索引情况。
- true:字段会被索引,则可以用来进行搜索。默认值就是true
- false:字段不会被索引,不能用来搜索
index的默认值就是true,也就是说你不进行任何配置,所有字段都会被索引。
但是有些字段是我们不希望被索引的,比如商品的图片信息,就需要手动设置index为false。
2.5.3.3.store
是否将数据进行额外存储。
在学习lucene和solr时,我们知道如果一个字段的store设置为false,那么在文档列表中就不会有这个字段的值,用户的搜索结果中不会显示出来。
但是在Elasticsearch中,即便store设置为false,也可以搜索到结果。
原因是Elasticsearch在创建文档索引时,会将文档中的原始数据备份,保存到一个叫做_source的属性中。而且我们可以通过过滤_source来选择哪些要显示,哪些不显示。
而如果设置store为true,就会在_source以外额外存储一份数据,多余,因此一般我们都会将store设置为false,事实上,store的默认值就是false。
2.5.3.4.boost
激励因子,这个与lucene中一样
其它的不再一一讲解,用的不多,大家参考官方文档:
2.6.新增数据
2.6.1.随机生成id
通过POST请求,可以向一个已经存在的索引库中添加数据。
语法:
POST /索引库名/类型名
{
"key":"value"
}
示例:
POST /heima/goods/
{
"title":"小米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":2699.00
}
响应:
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 2
}
通过kibana查看数据:
get _search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{}
}
}
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_version": 1,
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
}
_source:源文档信息,所有的数据都在里面。_id:这条文档的唯一标示,与文档自己的id字段没有关联
2.6.2.自定义id
如果我们想要自己新增的时候指定id,可以这么做:
POST /索引库名/类型/id值
{
...
}
示例:
POST /heima/goods/2
{
"title":"大米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":2899.00
}
得到的数据:
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "大米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2899
}
}
2.6.3.智能判断
在学习Solr时我们发现,我们在新增数据时,只能使用提前配置好映射属性的字段,否则就会报错。
不过在Elasticsearch中并没有这样的规定。
事实上Elasticsearch非常智能,你不需要给索引库设置任何mapping映射,它也可以根据你输入的数据来判断类型,动态添加数据映射。
测试一下:
POST /heima/goods/3
{
"title":"超米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":2899.00,
"stock": 200,
"saleable":true
}
我们额外添加了stock库存,和saleable是否上架两个字段。
来看结果:
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "3",
"_version": 1,
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "超米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2899,
"stock": 200,
"saleable": true
}
}
在看下索引库的映射关系:
{
"heima": {
"mappings": {
"goods": {
"properties": {
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
},
"saleable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"stock": {
"type": "long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}
}
stock和saleable都被成功映射了。
2.7.修改数据
把刚才新增的请求方式改为PUT,就是修改了。不过修改必须指定id,
- id对应文档存在,则修改
- id对应文档不存在,则新增
比如,我们把id为3的数据进行修改:
PUT /heima/goods/3
{
"title":"超大米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":3899.00,
"stock": 100,
"saleable":true
}
结果:
{
"took": 17,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 9,
"successful": 9,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "超大米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 3899,
"stock": 100,
"saleable": true
}
}
]
}
}
2.8.删除数据
删除使用DELETE请求,同样,需要根据id进行删除:
语法
DELETE /索引库名/类型名/id值
示例: