Andrdoid 注解和 meta-data 的基本使用(Kotlin)
文章目录
- 第一章 注解
- 一、基本使用
- 二、元注解
- 1.@Retention
- 2.@MustBeDocumented
- 2.1.Kotlin使用dokka生成javadoc
- 2.2.dokka使用方式
- 3.@Target
- 4.@Inherited
- 5.@Repeatable
- 6.系统自带注解
- 6.1.@SupressWarning
- 6.2.@Deprecated
- 6.3.@Override
- 第二章 meta-data
- 基本使用
- 参考文章
第一章 注解
一、基本使用
1.首先声明注解类
annotation class MyAnnotation(val value: String, val name: String)
2.在Activity中使用反射调用
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val methods = javaClass.declaredMethods
methods.forEach {
if (it.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation::class.java)) {
val annotation = it.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation::class.java)
Log.d("~~~", "value = ${annotation.value}, name = ${annotation.name}")
}
}
}
@MyAnnotation("1.0","Cassin")
fun testAnnotation(){
}
}
运行程序,Log控制台显示如下:
~~~: value = 1.0, name = Cassin
二、元注解
1.@Retention
@Retention标志了注解存活的时间
@Retention的源码如下:
/**
* This meta-annotation determines whether an annotation is stored in binary output and visible for reflection. By default, both are true.
*
* @property value necessary annotation retention (RUNTIME, BINARY or SOURCE)
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
public annotation class Retention(val value: AnnotationRetention = AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
其中,AnnotationRentention源码如下:
/**
* Contains the list of possible annotation's retentions.
*
* Determines how an annotation is stored in binary output.
*/
public enum class AnnotationRetention {
/** Annotation isn't stored in binary output */
SOURCE,
/** Annotation is stored in binary output, but invisible for reflection */
BINARY,
/** Annotation is stored in binary output and visible for reflection (default retention) */
RUNTIME
}
根据源码的注释,可知:
- @Retention设置为SOURCE时,注解仅存活在源码中,不会存储到二进制输出文件中。
- 设置为BINARY时,注解会存储到二进制输出文件中,但是对反射不可见。
- 设置为RUNTIME时,注解会存储到二进制输出文件中,并且对反射可见。
对于同一个注解设置不同的@Retention,笔者测试结果是:
AnnotationRetention.BINARY注解打包出的apk体积最大
AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME注解打包出的apk体积第二大
AnnotationRetention.SOURCE注解打包出的apk体积最小
如果注解是用来配置程序运行必需的参数,则Retention必须是AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME,否则打包出来的apk无法获取配置的参数。
2.@MustBeDocumented
表示将注解添加到Javadoc中,默认为不添加。
@MustBeDocumented的源码如下:
/**
* This meta-annotation determines that an annotation is a part of public API and therefore should be included in the generated
* documentation for the element to which the annotation is applied.
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
public annotation class MustBeDocumented
这里顺便讲一下Kotlin怎么生成Javadoc
2.1.Kotlin使用dokka生成javadoc
dokka库的github地址为:https://github.com/Kotlin/dokka
2.2.dokka使用方式
1.在project的build.gradle中添加:
classpath 'org.jetbrains.dokka:dokka-android-gradle-plugin:0.9.18'
2.在app模块的build.gradle中添加:
apply plugin: 'org.jetbrains.dokka-android'
task javadoc(type: Javadoc) {
source = android.sourceSets.main.java.srcDirs
options.encoding = "UTF-8"
classpath += project.files(android.getBootClasspath().join(File.pathSeparator))
}
task dokkaJavadoc(type: org.jetbrains.dokka.gradle.DokkaTask) {
outputFormat = "javadoc"
outputDirectory = javadoc.destinationDir
}
task generateJavadoc(type: Jar, dependsOn: dokkaJavadoc) {
group = 'jar'
classifier = 'javadoc'
from javadoc.destinationDir
}
artifacts {
archives generateJavadoc
}
sync之后,打开terminal,Windows环境下,输入:
gradlew generateJavadoc
Mac环境下,输入:
./gradlew generateJavadoc
Build Success之后,在app模块下的 build/libs 文件夹下会生成一个app-javadoc.jar,使用解压工具将其解压,就可以看到每个类对应的html格式的javadoc了。
上例中,不添加@MustBeDocumented生成的javadoc如下:
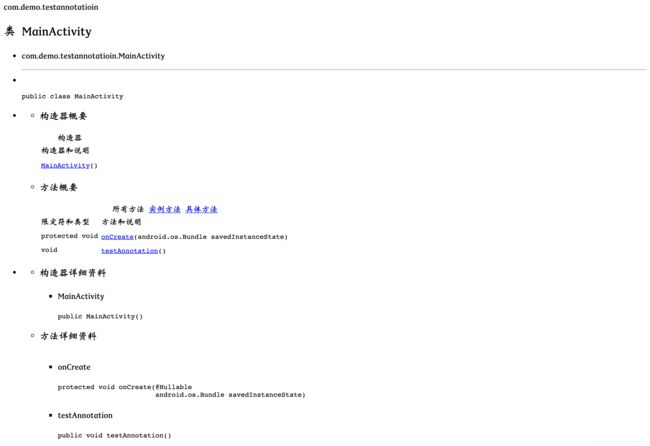
添加了@MustBeDocumented生成的javadoc如下:

3.@Target
Target指定此注解能够对哪些类型进行注解。
@Target源码如下:
/**
* This meta-annotation indicates the kinds of code elements which are possible targets of an annotation.
*
* If the target meta-annotation is not present on an annotation declaration, the annotation is applicable to the following elements:
* [CLASS], [PROPERTY], [FIELD], [LOCAL_VARIABLE], [VALUE_PARAMETER], [CONSTRUCTOR], [FUNCTION], [PROPERTY_GETTER], [PROPERTY_SETTER].
*
* @property allowedTargets list of allowed annotation targets
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
@MustBeDocumented
public annotation class Target(vararg val allowedTargets: AnnotationTarget)
其中,AnnotationTarget源码如下:
/**
* Contains the list of code elements which are the possible annotation targets
*/
public enum class AnnotationTarget {
/** Class, interface or object, annotation class is also included */
CLASS,
/** Annotation class only */
ANNOTATION_CLASS,
/** Generic type parameter (unsupported yet) */
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/** Property */
PROPERTY,
/** Field, including property's backing field */
FIELD,
/** Local variable */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Value parameter of a function or a constructor */
VALUE_PARAMETER,
/** Constructor only (primary or secondary) */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Function (constructors are not included) */
FUNCTION,
/** Property getter only */
PROPERTY_GETTER,
/** Property setter only */
PROPERTY_SETTER,
/** Type usage */
TYPE,
/** Any expression */
EXPRESSION,
/** File */
FILE,
/** Type alias */
@SinceKotlin("1.1")
TYPEALIAS
}
根据源码可知,@Target各属性的含义是:
- AnnotationTarget.CLASS 可以给一个类型进行注解 , 类 、 接口 、 对象 、 甚至注解类本身
- AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS 可以给一个注解类进行注解
- AnnotationTarget.TYPE_PARAMETER 泛型参数 ( 暂未支持 )
- AnnotationTarget.VALUE_PARAMETER 方法 、 构造函数的参数
- AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY (计算)属性(该注解Java不可见)
- AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_GETTER 属性getter方法
- AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_SETTER 属性setter方法
- AnnotationTarget.FIELD 字段变量 , 包括PROPERTY的备用字段 ( backing field)
- AnnotationTarget.LOCAL_VARIABLE 局部变量
- AnnotationTarget.CONSTRUCTOR 构造函数
- AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION 方法 、 函数 ( 不包括构造函数 )
- AnnotationTarget.FILE 文件整体
- AnnotationTarget.TYPE 泛型支持
- AnnotationTarget.TYPEALIAS 类型别名
- AnnotationTarget.EXPRESSION 表达式
4.@Inherited
表示如果某个类注解了此注解,其子类是否继承此注解,默认不继承。
@Inherited源码如下:
/** * Indicates that an annotation type is automatically inherited. If * an Inherited meta-annotation is present on an annotation type * declaration, and the user queries the annotation type on a class * declaration, and the class declaration has no annotation for this type, * then the class's superclass will automatically be queried for the * annotation type. This process will be repeated until an annotation for this * type is found, or the top of the class hierarchy (Object) * is reached. If no superclass has an annotation for this type, then * the query will indicate that the class in question has no such annotation. * *
Note that this meta-annotation type has no effect if the annotated * type is used to annotate anything other than a class. Note also * that this meta-annotation only causes annotations to be inherited * from superclasses; annotations on implemented interfaces have no * effect. * * @author Joshua Bloch * @since 1.5 * @jls 9.6.3.3 @Inherited */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Inherited { }
我们做个简单的测试:
1.先声明一个不带@Inherited的注解:
annotation class MyAnnotation(val value: String)
2.在BaseActivity中使用此注解:
// 测试父类上的注解能否被继承
@MyAnnotation("superClass")
abstract class BaseActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// 测试父类方法中的注解能否被继承
@MyAnnotation("superFun")
protected fun superFun() {
}
// 测试子类重写父类方法是能否继承注解
@MyAnnotation("superOverrideFun")
open fun superOverrideFun() {
}
// 测试父类抽象方法中的注解能否被继承
@MyAnnotation("superAbstractFun")
protected abstract fun superAbstractFun()
}
3.MainActivity继承BaseActivity
class MainActivity : BaseActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val annotations = javaClass.annotations
annotations.forEach {
if (it is MyAnnotation) {
Log.d("~~~annotations", "value = ${it.value}")
}
}
val methods = javaClass.methods
methods.forEach {
if (it.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation::class.java)) {
val annotation = it.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation::class.java)
Log.d("~~~methods", "${it.name}:value = ${annotation.value}")
}
}
}
override fun superOverrideFun() {
}
override fun superAbstractFun() {
}
}
使用 javaClass.annotations 反射获取类上的所有注解,使用 javaClass.methods 反射获取类中所有方法。运行程序,Log控制台输出如下:
~~~methods: superFun:value = superFun
4.在注解中加上@Inherited:
@Inherited
annotation class MyAnnotation(val value: String)
运行程序,Log控制台输出如下:
~~~annotations: value = superClass
~~~methods: superFun:value = superFun
所以我们可以得出结论:
| 无@Inherited | 有@Inherited | |
|---|---|---|
| 子类能否继承父类的类上的注解 | 否 | 能 |
| 子类能否继承到父类抽象方法的注解 | 否 | 否 |
| 子类能否继承父类方法上的注解 | 能 | 能 |
| 子类重写父类上的方法,能否继承到注解 | 否 | 否 |
5.@Repeatable
表示此注解是否可重复注解。
@Repeatable源码如下:
/**
* This meta-annotation determines that an annotation is applicable twice or more on a single code element
*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS)
public annotation class Repeatable
设置@Repeatable时,注解的@Retention必须被申明为仅存活在源码中,暂不支持其他@Retention。
例如:
声明一个@Repeatable的注解:
@Repeatable
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.SOURCE)
annotation class MyAnnotation(val value: String)
多次使用注解:
@MyAnnotation("a")
@MyAnnotation("b")
@MyAnnotation("c")
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
@MyAnnotation("a")
@MyAnnotation("b")
@MyAnnotation("c")
val field = 1
@MyAnnotation("a")
@MyAnnotation("b")
@MyAnnotation("c")
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
}
@MyAnnotation("a")
@MyAnnotation("b")
@MyAnnotation("c")
fun testAnnotation() {
}
}
6.系统自带注解
6.1.@SupressWarning
@SuppressWarnings注解用来忽略代码警告,源码转换成kotlin如下:
@Target(
AnnotationTarget.CLASS,
AnnotationTarget.FILE,
AnnotationTarget.FIELD,
AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION,
AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_GETTER,
AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_SETTER,
AnnotationTarget.VALUE_PARAMETER,
AnnotationTarget.CONSTRUCTOR,
AnnotationTarget.LOCAL_VARIABLE
)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.SOURCE)
annotation class SuppressWarnings(vararg val value: String)
@Retention是AnnotationRetention.SOURCE,说明只会在源码中保留注解,打包时会忽略此注解。由@Target可知可以在类、文件、字段、方法、getter方法、setter方法、值参数、构造方法、本地变量上使用此注解。
6.2.@Deprecated
@Deprecated标志代码已过时,源码转换成Kotlin如下:
@Target(
AnnotationTarget.CLASS,
AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION,
AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY,
AnnotationTarget.ANNOTATION_CLASS,
AnnotationTarget.CONSTRUCTOR,
AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_SETTER,
AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_GETTER,
AnnotationTarget.TYPEALIAS
)
@MustBeDocumented
public annotation class Deprecated(
val message: String,
val replaceWith: ReplaceWith = ReplaceWith(""),
val level: DeprecationLevel = DeprecationLevel.WARNING
)
@MustBeDocumented标志着此注解会生成到javadoc中,由@Target可知可以在类、方法、属性、注解、构造方法、setter方法、getter方法,类型别名上使用此注解。
6.3.@Override
表示重写方法,源码转换成Kotlin如下:
@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION, AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_GETTER, AnnotationTarget.PROPERTY_SETTER)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.SOURCE)
annotation class Override
@Retention是AnnotationRetention.SOURCE,表示此注解只会在源码中保留,由@Target可知,可以在方法、getter、setter中使用此注解
还有一些系统自带注解,如@SafeVarargs、@FunctionalInterface,有兴趣的读者可以自己了解
第二章 meta-data
基本使用
1.在application中声明meta-data
<meta-data android:name="value_key" android:value="value"/>
<meta-data android:name="resource_key" android:resource="@string/app_name"/>
<meta-data android:name="resource_value" android:value="@string/app_name"/>
2.通过PackageManager调用
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val applicationInfo = packageManager.getApplicationInfo(packageName,PackageManager.GET_META_DATA)
val metaData = applicationInfo.metaData
/**获取meta-data中的参数*/
Log.d("~~~","value_key:${metaData.get("value_key")}\n" +
"resource_key:${getString(metaData.get("resource_key") as Int)}\n" +
"resource_value:${metaData.get("resource_value")}")
}
}
运行程序,显示如下:
~~~: value_key:value
resource_key:TestMetaData
resource_value:TestMetaData
参考文章
- 秒懂,Java 注解 (Annotation)你可以这样学:https://blog.csdn.net/briblue/article/details/73824058
- Kotlin 注解:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ce5b422d93e9
- Android studio 生成带Kotlin文档简易教程:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30034925/article/details/79445072
- 子类可以继承到父类上的注解吗–有结论了:https://elf8848.iteye.com/blog/1621392