翻译:@shiweifu
本文链接:http://segmentfault.com/blog/shiweifu
原文链接:http://rubymotion-tutorial.com/10-api-driven-example/
目标读者:["想了解RubyMotion开发模式", "想学习RubyMotion", "逗比"]
我们将创建一个使用Colr JSON API作为后端的应用。用户输入颜色的16进制值( #3B5998)他们会看见标签的颜色发生对应的变化。他们可以往里添加新的颜色。
我们先考虑下程序的结构。会有两个Controller:一个用来搜索,一个用来显示颜色。这两个Controller外面都套着UINavigationController。我们还需要Model:Color、Tag,它可能并不精美,但能工作。
初始化
使用motion create Colr 命令初始化一个新的项目,添加bubble-wrap 到你的 Rakefile。接下来我们在./app 中创建两个目录:./app/models/ 和 ./app/controllers。
Models
首先,让我们先看下模型。Colr API 的 Color JSON 结构如下:
{
"timestamp": 1285886579,
"hex": "ff00ff",
"id": 3976,
"tags": [{
"timestamp": 1108110851,
"id": 2583,
"name": "fuchsia"
}]
}
我们的 Colors 需要timestamp,hex, id, tags这些属性,特别注意的是,tags属性将包含多个Tag对象
创建./app/models/color.rb然后填写 Model 代码:
class Color
PROPERTIES = [:timestamp, :hex, :id, :tags]
PROPERTIES.each { |prop|
attr_accessor prop
}
def initialize(hash = )
hash.each { |key, value|
if PROPERTIES.member? key.to_sym
self.send((key.to_s + "=").to_s, value)
end
}
end
...
PROPERTIES 这块是个小trick,很容易就定义了属性。需要稍微说一下的是tags这个属性,让它始终返回一个Tag Model的数组。
...
def tags
@tags ||= []
end
def tags=(tags)
if tags.first.is_a? Hash
tags = tags.collect |tag| Tag.new(tag)
end
tags.each { |tag|
if not tag.is_a? Tag
raise "Wrong class for attempted tag #tag.inspect"
end
}
@tags = tags
end
end
我们覆盖了#tags 的getter和setter,所以当tags没有值的时候,将返回一个空的数组。#tags=保证解析和返回Tag对象数组。我们接下来编看看TagModel里面都有啥。
创建并打开./app/models/tag.rb,接口返回的数据如下所示:
{
"timestamp": 1108110851,
"id": 2583,
"name": "fuchsia"
}
创建TagModel的类,代码短且友好:
class Tag
PROPERTIES = [:timestamp, :id, :name]
PROPERTIES.each { |prop|
attr_accessor prop
}
def initialize(hash = )
hash.each { |key, value|
if PROPERTIES.member? key.to_sym
self.send((key.to_s + "=").to_s, value)
end
}
end
end
Controllers
模型都已经定义好了,你的好友「控制器君」即将上线。创建./app/controllers/search_controller.rb和./app/controllers/color_controller.rb 俩文件,把最基本的实现先写上去:
class SearchController < UIViewController
def viewDidLoad
super
self.title = "Search"
end
end
class ColorController < UIViewController
def viewDidLoad
super
self.title = "Color"
end
end
将我们的控制器带上UINavigationController和UIWindow,甩给AppDelegate:
class AppDelegate
def application(application, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions)
@window = UIWindow.alloc.initWithFrame(UIScreen.mainScreen.bounds)
@search_controller = SearchController.alloc.initWithNibName(nil, bundle:nil)
@navigation_controller = UINavigationController.alloc.initWithRootViewController(@search_controller)
@window.rootViewController = @navigation_controller
@window.makeKeyAndVisible
true
end
end
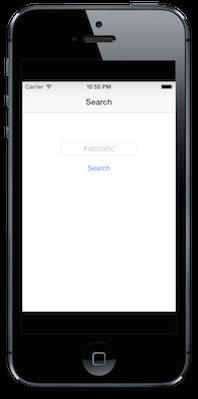
代码堆砌完了,是时候看看成果了,执行rake命令,在屏幕中会出现:
一切都很好,该看看SearchController里面都有啥了。
SearchController
(译者著:原文是系列文章,之前的部分从未出现过UITextField,所以这里假设UITextField从未出现过,不然接不上。)
我们将使用一个之前从未提到过的控件UITextField来接受用户的输入,当用户点击Search按钮时候,我们将发起一个API请求,这时界面不接受任何输入,直到请求结束。如果请求成功完成,我们会push一个ColorController给用户展示结果,否则的话会给个出错提示。
以下是SearchController的初始化时干活的代码:
def viewDidLoad
super
self.title = "Search"
self.view.backgroundColor = UIColor.whiteColor
@text_field = UITextField.alloc.initWithFrame [[0,0], [160, 26]]
@text_field.placeholder = "#abcabc"
@text_field.textAlignment = UITextAlignmentCenter
@text_field.autocapitalizationType = UITextAutocapitalizationTypeNone
@text_field.borderStyle = UITextBorderStyleRoundedRect
@text_field.center = CGPointMake(self.view.frame.size.width / 2, self.view.frame.size.height / 2 - 100)
self.view.addSubview @text_field
@search = UIButton.buttonWithType(UIButtonTypeRoundedRect)
@search.setTitle("Search", forState:UIControlStateNormal)
@search.setTitle("Loading", forState:UIControlStateDisabled)
@search.sizeToFit
@search.center = CGPointMake(self.view.frame.size.width / 2, @text_field.center.y + 40)
self.view.addSubview @search
end
self.view.frame.size.height / 2 - 100设置座标和大小的代码是我个人习惯,设置UIControlStateDisabled是为了统一配置阻塞时的样式。UITextBorderStyleRoundedRect是为了设置UITexitField的样式,带来更好的观感。
rake再执行,现在看到的样子:
(译者注:BubbleWrap是RubyMotion官方开发的一个库,里面封装了很多用Cocoa写起来很蛋疼的地方,使代码更加「Ruby」)
该处理事件了。还记得我之前提到过BubbleWrap屌屌的么?使用它我们不用再像过去写傻傻的addTarget:action:forControlEvents啥啥啥的来添加事件,代码清晰很多:
def viewDidLoad
...
self.view.addSubview @search
@search.when(UIControlEventTouchUpInside) do
@search.enabled = false
@text_field.enabled = false
hex = @text_field.text
# chop off any leading #s
hex = hex[1..-1] if hex[0] == "#"
Color.find(hex) do |color|
@search.enabled = true
@text_field.enabled = true
end
end
end
when 方法在所有UIControl的子类都可以用。使用UIControlEvent开头的那些标识事件位作为参数。当请求发出后,我们临时禁用UI。
(译者注:作者的意思应该是每个颜色都写一段代码去获取,有疑问去看原文吧,如果不是这样,记得指正 T.T)Color.find这个方法是哪来的?在这里,我们将 URL 处理的代码放到模型里,而不是放到控制器里。当需要得到一个Color对象的时候,只需要我们传递个block进去,不用在控制器中去写重复的代码了。
给Color类添加find类方法:
class Color
...
def self.find(hex, &block)
BW::HTTP.get("http://www.colr.org/json/color/#hex") do |response|
p response.body.to_str
# for now, pass nil.
block.call(nil)
end
end
end
(译者注:RubyMotion中的block。如果困惑或者想深入研究,可以去看看Ruby的lambda,还有RubyMotion的block传递)
有些困惑?我们使用简单的HTTP.get去请求服务器,得到数据,然后通过&block传出去。调用的时候,请求调用完毕后,会执行调用的时候do/end之间的代码。通过.call(some, variables)执行do |some, variables|。
再rake一下,来个数据测试一下这个方法,如:3B5998。你将在终端中看到:
(main)> "\"colors\": [{\"timestamp\": 1285886579, \"hex\": \"ff00ff\", \"id\": 3976, \"tags\": [{\"timestamp\": 1108110851, \"id\": 2583, \"name\": \"fuchsia\"}, {\"timestamp\": 1108110864, \"id\": 3810, \"name\": \"magenta\"}, {\"timestamp\": 1108110870, \"id\": 4166, \"name\": \"magic\"}, {\"timestamp\": 1108110851, \"id\": 2626, \"name\": \"pink\"}, {\"timestamp\": 1240447803, \"id\": 24479, \"name\": \"rgba8b24ff00ff\"}, {\"timestamp\": 1108110864, \"id\": 3810, \"name\": \"magenta\"}]], \"schemes\": [], \"schemes_history\": , \"success\": true, \"colors_history\": \"ff00ff\": [{\"d_count\": 0, \"id\": \"4166\", \"a_count\": 1, \"name\": \"magic\"}, {\"d_count\": 0, \"id\": \"2626\", \"a_count\": 1, \"name\": \"pink\"}, {\"d_count\": 0, \"id\": \"24479\", \"a_count\": 1, \"name\": \"rgba8b24ff00ff\"}, {\"d_count\": 0, \"id\": \"3810\", \"a_count\": 1, \"name\": \"magenta\"}], \"messages\": [], \"new_color\": \"ff00ff\"}\n"
WTF!!一坨JSON字符串啊,亲我不想要字符串啊,能不能给我Ruby的Hash?
在BubbleWrap里已经集成了解析JSON的方法:BW::JSON.parse,开箱即用:
def self.find(hex, &block)
BW::HTTP.get("http://www.colr.org/json/color/#hex") do |response|
result_data = BW::JSON.parse(response.body.to_str)
color_data = result_data["colors"][0]
# Colr will return a color with id == -1 if no color was found
color = Color.new(color_data)
if color.id.to_i == -1
block.call(nil)
else
block.call(color)
end
end
end
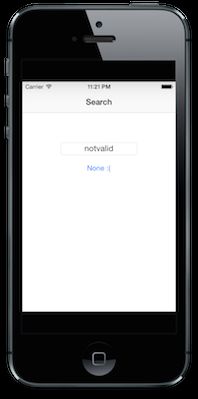
在我们的SearchController中,要做一些对无效输入的校验:
def viewDidLoad
...
Color.find(hex) do |color|
if color.nil?
@search.setTitle("None :(", forState: UIControlStateNormal)
else
@search.setTitle("Search", forState: UIControlStateNormal)
self.open_color(color)
end
@search.enabled = true
@text_field.enabled = true
end
end
end
def open_color(color)
p "Opening #color"
end
一切看起来很好。当遇到无效的JSON的时候界面上会给出明确的反馈:
现在改补上 open_color 方法的代码了。它push一个ColorController,然后在其中显示颜色。
def open_color(color)
self.navigationController.pushViewController(ColorController.alloc.initWithColor(color), animated:true)
end
ColorController
我们要自定义ColorController的构造函数。这个Controller的视图有两部分:一个UITableView,用来显示颜色标记,一个Section 显示具体颜色和添加新的标记。当我们想要标记一个颜色的时候,我们要发一个请求,然后再刷新让它显示出来。
不嘴炮了,看看代码:
class ColorController < UIViewController
attr_accessor :color
def initWithColor(color)
initWithNibName(nil, bundle:nil)
self.color = color
self
end
...
当重载一个iOS SDK 构造函数的时候,你需要做两件事:调用它的父构造函数;在函数结尾的时候返回初始化过的它自己。在RubyMotion中,你不能像标准Ruby一样初始化。
初始化完毕,该布局了:
def viewDidLoad
super
self.title = self.color.hex
# You must comment out the following line if you are developing on iOS < 7.
self.edgesForExtendedLayout = UIRectEdgeNone
# A light grey background to separate the Tag table from the Color info
@info_container = UIView.alloc.initWithFrame [[0, 0], [self.view.frame.size.width, 110]]
@info_container.backgroundColor = UIColor.lightGrayColor
self.view.addSubview @info_container
# A visual preview of the actual color
@color_view = UIView.alloc.initWithFrame [[10, 10], [90, 90]]
# String#to_color is another handy BubbbleWrap addition!
@color_view.backgroundColor = String.new(self.color.hex).to_color
self.view.addSubview @color_view
# Displays the hex code of our color
@color_label = UILabel.alloc.initWithFrame [[110, 30], [0, 0]]
@color_label.text = self.color.hex
@color_label.sizeToFit
self.view.addSubview @color_label
# Where we enter the new tag
@text_field = UITextField.alloc.initWithFrame [[110, 60], [100, 26]]
@text_field.placeholder = "tag"
@text_field.textAlignment = UITextAlignmentCenter
@text_field.autocapitalizationType = UITextAutocapitalizationTypeNone
@text_field.borderStyle = UITextBorderStyleRoundedRect
self.view.addSubview @text_field
# Tapping this adds the tag.
@add = UIButton.buttonWithType(UIButtonTypeRoundedRect)
@add.setTitle("Add", forState:UIControlStateNormal)
@add.setTitle("Adding...", forState:UIControlStateDisabled)
@add.setTitleColor(UIColor.lightGrayColor, forState:UIControlStateDisabled)
@add.sizeToFit
@add.frame = [[@text_field.frame.origin.x + @text_field.frame.size.width + 10, @text_field.frame.origin.y],
@add.frame.size]
self.view.addSubview(@add)
# The table for our color's tags.
table_frame = [[0, @info_container.frame.size.height],
[self.view.bounds.size.width, self.view.bounds.size.height - @info_container.frame.size.height - self.navigationController.navigationBar.frame.size.height]]
@table_view = UITableView.alloc.initWithFrame(table_frame, style:UITableViewStylePlain)
self.view.addSubview(@table_view)
end
……好大一坨代码啊!不要慌,这些代码很容易理解,我们只是添加了几个子view。
rake一下试试看?
额……真的很丑啊……
处理tags没啥特别的,就是实现一个delegate。
def viewDidLoad
...
@table_view.dataSource = self
end
def tableView(tableView, numberOfRowsInSection:section)
self.color.tags.count
end
def tableView(tableView, cellForRowAtIndexPath:indexPath)
@reuseIdentifier ||= "CELL_IDENTIFIER"
cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier(@reuseIdentifier) || begin
UITableViewCell.alloc.initWithStyle(UITableViewCellStyleDefault, reuseIdentifier:@reuseIdentifier)
end
cell.textLabel.text = self.color.tags[indexPath.row].name
cell
end
再次运行rake,有点意思了吧?
!()[http://rubymotion-tutorial.com/10-api-driven-example/images/4.png]
接下来要添加新的tags,有多种方法去实现。你可以老老实实的Tag.create(tag),也可以使用Ruby的黑魔法color.tags << tag,但为了体现出Color和Tag存在联系,我们这么做:color.add_tag(tag, &block)。
这个方法实现如下::
def add_tag(tag, &block)
BW::HTTP.post("http://www.colr.org/js/color/#{self.hex}/addtag/", payload: {tags: tag}) do |response|
block.call
end
end
最后那个参数是在请求执行结束后回调的。好的做法是分别处理成功和失败两种情况,这个例子为了简单,就先不考虑了。
现在给ColorController的按钮添加事件处理代码。我们想在Tag被发送到服务器之后,根据当前服务器返回的数据刷新:
def viewDidLoad
...
self.view.addSubview(@add)
@add.when(UIControlEventTouchUpInside) do
@add.enabled = false
@text_field.enabled = false
self.color.add_tag(@text_field.text) do
refresh
end
end
...
end
def refresh
Color.find(self.color.hex) do |color|
self.color = color
@table_view.reloadData
@add.enabled = true
@text_field.enabled = true
end
end
我们给@add按钮添加了UIControlEventTouchUpInside事件,在事件触发的时候,会POST添加请求给服务器。当请求处理结束,我们刷新页面。这将触发Color.find,重设我们的数据。
rake一下,添加tag试试?
时候到溜
这片冗长的教程终于要结束了。在教程中,我们分离了Controller和Model,因为要保持示例足够小,没怎么考虑View,如果要考虑View,就需要引入KVO或类似的技术。作为预览,本文的示例已经足够给力了。
到底讲了点啥?
- 使用
Model处理你的JSON数据,而不是使用Dictionary或Hash - 把请求放到了
Model中 -
Controller响应用户事件 - 在请求执行过程中,阻塞界面