JDK容器与并发—Map—ConcurrentSkipListMap
概述
基于跳表实现的ConcurrentNavigableMap。
1)containsKey、get、put、remove等操作的平均时间复杂度为log(n);size非固定时间操作,因异步特性,需要遍历所有节点才能确定size,且可能不是正确的值如果遍历过程中有修改;批量操作:putAll、equals、toArray、containsValue、clear非原子性。
2)增删改查操作并发线程安全;
3)迭代器是弱一致性的:map创建时或之后某个时间点的,不抛出ConcurrentModificationException,可能与其他操作并发执行。升序视图及迭代器比降序的要快;
数据结构
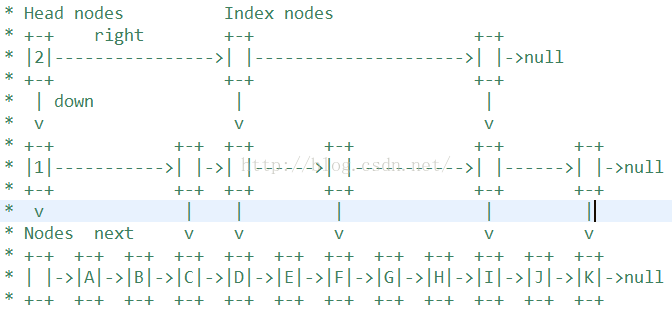
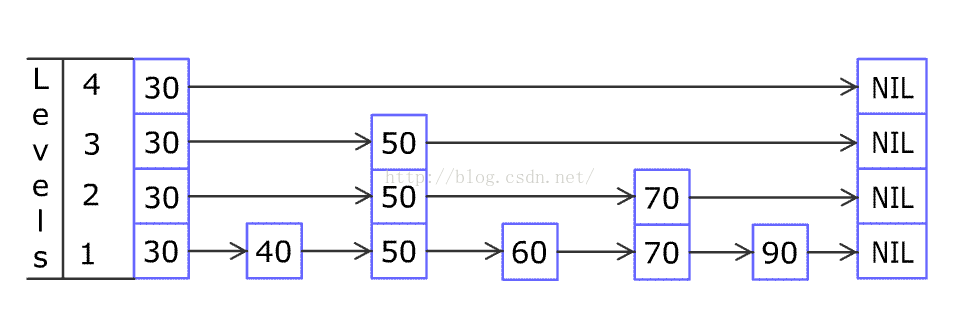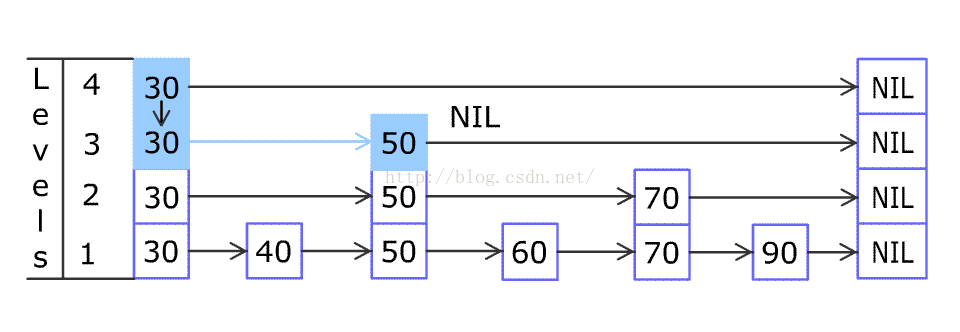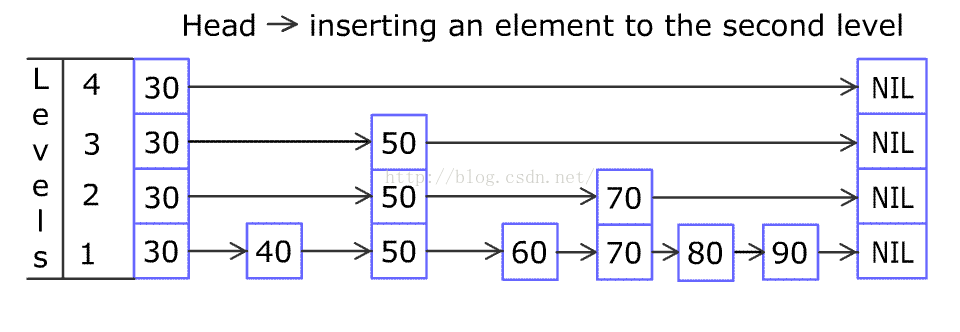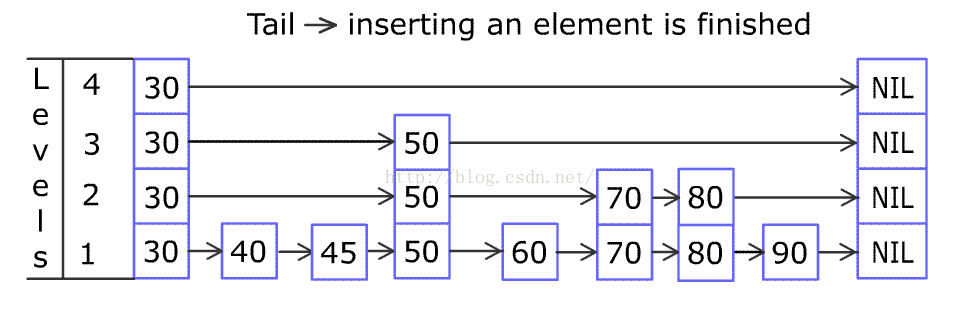
基于链表,有三种类型节点Node、Index、HeadIndex,底层为Node单链表有序层(升序),其他层为基于Node层的Index层即索引层,可能有多个索引层。
相对于单链表,跳表查找节点很快是在于:通过HeadIndex维护索引层次,通过Index从最上层开始往下查找元素,一步步缩小查找范围,到了最底层Node单链表层,就只需要比较很少的元素就可以找到待查找的元素节点。
// Node节点,拥有key-value对
// 单链表,有序,第一个节点为head.node标记节点,中间可能会穿插些删除标记节点(即marker节点)
static final class Node {
final K key;
volatile Object value; // value为Object类型,便于区分删除标记节点、head.node标记节点
volatile Node next;
/**
* Creates a new regular node.
*/
Node(K key, Object value, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
// 创建一个删除标记节点
// 删除标记节点的value为this,以区分其他Node节点;
// key为null,其他场合会用到,但不能用作区分,因为head.node的key也为null
Node(Node next) {
this.key = null;
this.value = this;
this.next = next;
}
// CAS value属性
boolean casValue(Object cmp, Object val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);
}
// CAS next属性
boolean casNext(Node cmp, Node val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
// 是否为删除标记节点
boolean isMarker() {
return value == this;
}
// 是否为header node节点
boolean isBaseHeader() {
return value == BASE_HEADER;
}
// 在当前Node节点后增加删除标记节点(采用CAS next方式实现)
boolean appendMarker(Node f) {
return casNext(f, new Node(f));
}
// 推进删除Node节点
// 一般在遍历过程中,如果遇到当前Node的value为null,会调用该方法
void helpDelete(Node b, Node f) {
// 首先检查当前的链接是否为b——>this——>f;
// 再进行推进删除,过程分两步,每一步都采用CAS实现
// 每次只推进一步,以减小推进线程间的干扰
if (f == next && this == b.next) { // 检测是否为b——>this——>f,其中b为前驱节点,f为后继节点
if (f == null || f.value != f) // 待删除节点未进行标记
appendMarker(f);// 链接删除标记节点
else
b.casNext(this, f.next); // 删除当前节点及其删除标记节点,完成删除
}
}
// 获取节点的有效value
V getValidValue() {
Object v = value;
if (v == this || v == BASE_HEADER) // 若为删除标记节点、header node节点,则返回null
return null;
return (V)v;
}
// 对有效键值对封装到不可变的Entry
AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry createSnapshot() {
V v = getValidValue();
if (v == null)
return null;
return new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry(key, v);
}
// UNSAFE mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long valueOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class k = Node.class;
valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("value"));
nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
// 索引节点,用于从最上层往下缩小查找范围
// 逻辑上的双链表,非前后链接,而是上下链接
static class Index {
final Node node; // 索引节点是基于Node节点的
final Index down;// down为final的,简化并发
volatile Index right;
/**
* Creates index node with given values.
*/
Index(Node node, Index down, Index right) {
this.node = node;
this.down = down;
this.right = right;
}
// CAS right属性
final boolean casRight(Index cmp, Index val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, rightOffset, cmp, val);
}
// 其Node节点是否删除
final boolean indexesDeletedNode() {
return node.value == null;
}
// 链接Index节点
// 如果链接过程中,其Node节点已删除,则不链接,以减小与解链接的CAS竞争
/*
* @param succ the expected current successor
* @param newSucc the new successor
* @return true if successful
*/
final boolean link(Index succ, Index newSucc) {
Node n = node;
newSucc.right = succ; // 将newSucc链接进来
return n.value != null && casRight(succ, newSucc); // CAS right
}
// 解链接index节点,如果其Node已删除,则解链接失败
/**
* @param succ the expected current successor
* @return true if successful
*/
final boolean unlink(Index succ) {
return !indexesDeletedNode() && casRight(succ, succ.right);// CAS right
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long rightOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class k = Index.class;
rightOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("right"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
// HeadIndex节点,跟踪索引层次
static final class HeadIndex extends Index {
final int level;// 索引层,从1开始,Node单链表层为0
HeadIndex(Node node, Index down, Index right, int level) {
super(node, down, right);
this.level = level;
}
} JDK中一个实例结构图:
WIKI上关于跳表的解释图:
构造器
无参构造,空Map
public ConcurrentSkipListMap() {
this.comparator = null; // 用Key的Comparable接口排序
initialize();
}
// 带comparator参数构造
public ConcurrentSkipListMap(Comparator comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
initialize();
}
// 带Map参数构造,采用Key的Comparable接口排序
public ConcurrentSkipListMap(Map m) {
this.comparator = null;
initialize();
putAll(m);
}
// 带SortedMap参数构造,采用SortedMap的comparator排序
public ConcurrentSkipListMap(SortedMap m) {
this.comparator = m.comparator();
initialize();
buildFromSorted(m);
} 增删改查
初始化
final void initialize() {
keySet = null;
entrySet = null;
values = null;
descendingMap = null;
randomSeed = seedGenerator.nextInt() | 0x0100; // ensure nonzero
head = new HeadIndex(new Node(null, BASE_HEADER, null),
null, null, 1); // 初始化head节点,空Map
} 增、改
步骤:
1)查找比key小的前驱节点,查找过程中删除待删除Node节点的索引节点;
2)从前驱节点开始,遍历底层Node单链表,若已存在相关的key-value对,则CAS替换新的value,返回旧value;若不存在,则确定插入位置;遍历过程中,推进删除待删除的Node节点;
3)用key、value创建新的Node节点,用CAS next方式链接进来;
4)给新的Node节点随机生成一个索引层次,若层次大于0,则给其增加索引节点,返回null。
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return doPut(key, value, false);
}
private V doPut(K kkey, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
Comparable key = comparable(kkey);
for (;;) {
Node b = findPredecessor(key); // 找到前驱节点后,接下来就是在Node单链表层精确找到插入位置
Node n = b.next;
for (;;) {
// 遍历清除Node节点操作同findNode
if (n != null) {
Node f = n.next;
if (n != b.next)
break;
Object v = n.value;
if (v == null) {
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (v == n || b.value == null)
break;
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c > 0) { // key大于n,继续往后找
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
if (c == 0) { // 已有相关的key-value对
if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value))
return (V)v;
else
break; // CAS value失败,则重新开始,失败原因可能是n变成了待删除节点或有其他修改线程修改过
}
// else c < 0; fall through:说明新增的key-value对需要插到b和n之间
}
Node z = new Node(kkey, value, n);
if (!b.casNext(n, z)) // 将新节点z插入b、n之间
break; // 失败了,原因同n != b.next,重来
int level = randomLevel(); // 给新增的Node节点随机生成一个索引层次
if (level > 0)
insertIndex(z, level); // 给z增加索引节点
return null;
}
}
}
// 查找比key小的前驱节点,若没有,则返回head.node
// 一些操作依赖该方法删除索引节点
private Node findPredecessor(Comparable key) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errors
for (;;) {
Index q = head;
Index r = q.right;
// 从索引层最上层开始,往右往下,
// 一直找到最下层索引层(即第一层),从而确定查找范围,以在底层Node单链表遍历精确找到
for (;;) {
if (r != null) { // 在索引层,往右找
Node n = r.node;
K k = n.key;
if (n.value == null) { // 遍历到待删除节点n的索引节点
if (!q.unlink(r))// 删除其索引节点(采用CAS right属性)
//删除失败原因:q被标记为待删除节点或在q后增加新索引节点或已删除了其right节点
break; // 重新开始
r = q.right;// 若删除成功,则获取新的right索引节点,继续找
continue;
}
if (key.compareTo(k) > 0) { // 若key大,说明可能还有小于key的更大的,继续找
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
Index d = q.down;// 当层索引层没有,则往下一层找,进一步缩小查找范围
if (d != null) {// 在下一层索引层,继续找
q = d;
r = d.right;
} else
return q.node;// 确定前驱节点,如果没有则为head.node标记节点
}
}
}
// 给新增的Node节点随机生成一个索引层次
/**
* Returns a random level for inserting a new node.
* Hardwired to k=1, p=0.5, max 31 (see above and
* Pugh's "Skip List Cookbook", sec 3.4).
*
* This uses the simplest of the generators described in George
* Marsaglia's "Xorshift RNGs" paper. This is not a high-quality
* generator but is acceptable here.
*/
private int randomLevel() {
int x = randomSeed;
x ^= x << 13;
x ^= x >>> 17;
randomSeed = x ^= x << 5;
if ((x & 0x80000001) != 0) // test highest and lowest bits
return 0;
int level = 1;
while (((x >>>= 1) & 1) != 0) ++level;
return level;
}
// 为Node节点添加索引节点
/**
* @param z the node
* @param level the level of the index
*/
private void insertIndex(Node z, int level) {
HeadIndex h = head;
int max = h.level; // head的索引层次是最大的
if (level <= max) { // 待添加索引节点的索引层次在head索引层次内,创建索引节点添加进来即可
Index idx = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
idx = new Index(z, idx, null);// 索引节点,从下往上链接
addIndex(idx, h, level); // 将索引节点链接进来
} else { // 增加一层索引层,需要new新层次的HeadIndex
/*
* To reduce interference by other threads checking for
* empty levels in tryReduceLevel, new levels are added
* with initialized right pointers. Which in turn requires
* keeping levels in an array to access them while
* creating new head index nodes from the opposite
* direction.
*/
level = max + 1;
Index[] idxs = (Index[])new Index[level+1];
Index idx = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
idxs[i] = idx = new Index(z, idx, null);
HeadIndex oldh;
int k;
for (;;) {
oldh = head;
int oldLevel = oldh.level;
if (level <= oldLevel) { // 其他线程增加过索引层
k = level;
break; // 同上面的level <= max情况处理
}
HeadIndex newh = oldh;
Node oldbase = oldh.node;
for (int j = oldLevel+1; j <= level; ++j) // 有可能其他线程删除过索引层,所以从oldLevel至level增加HeadIndex
newh = new HeadIndex(oldbase, newh, idxs[j], j); // 创建新层次的HeadIndex且将索引节点idxs相应层次链接进来
if (casHead(oldh, newh)) { // CAS head HeadIndex节点
k = oldLevel;
break;
}
}
addIndex(idxs[k], oldh, k); // 需要将idxs的旧oldLevel层次及下面的索引链接进来
}
}
/**
* 从第indexLevel层往下到第1层,将索引节点链接进来
* @param idx the topmost index node being inserted
* @param h the value of head to use to insert. This must be
* snapshotted by callers to provide correct insertion level
* @param indexLevel the level of the index
*/
private void addIndex(Index idx, HeadIndex h, int indexLevel) {
// Track next level to insert in case of retries
int insertionLevel = indexLevel;
Comparable key = comparable(idx.node.key);
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 过程与findPredecessor类似, 只是多了增加索引节点
for (;;) {
int j = h.level;
Index q = h;
Index r = q.right;
Index t = idx;
for (;;) {
if (r != null) {// 在索引层,往右遍历
Node n = r.node;
// compare before deletion check avoids needing recheck
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (n.value == null) {
if (!q.unlink(r))
break;
r = q.right;
continue;
}
if (c > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
if (j == insertionLevel) { // 可以链接索引节点idx
if (t.indexesDeletedNode()) { // 索引节点的Node节点被标记为待删除节点
findNode(key); // 推进删除索引节点及其Node节点
return; // 不用增加索引节点了
}
if (!q.link(r, t)) // 将第insertionLevel层索引节点链接进来
//删除失败原因:同findPredecessor种的q.unlink(r)
break; // 链接失败,重新开始
if (--insertionLevel == 0) { // 准备链接索引节点idx的下一层索引
if (t.indexesDeletedNode()) // 返回前再次检查索引节点t是否被标记为待删除节点,以进行清理工作
findNode(key);
return; // insertionLevel==0表明已经完成索引节点idx的链接
}
}
if (--j >= insertionLevel && j < indexLevel) // 已链接过索引节点idx的第insertionLevel+1层
t = t.down; // 准备链接索引节点idx的第insertionLevel层
q = q.down; // 准备链接索引节点idx的下一层索引
r = q.right;
}
}
}
// 查找相关key的Node,没有则返回null。
// 遍历Node单链表中,清除待删除节点
// 在doPut、doRemove、findNear等都包含这样的遍历清除操作
// 不能共享这样的清除代码,因为增删改查需要获取Node链表顺序的快照暂存到自身的局部变量,用于并发
// 一些操作依赖此方法删除Node节点
private Node findNode(Comparable key) {
for (;;) {
Node b = findPredecessor(key); // 获取key的前驱节点
Node n = b.next;
for (;;) {
if (n == null)
return null;
Node f = n.next;
// 不是连续的b——>n——>f快照,不能进行后续解链接待删除节点
//变化情况:在b后增加了新节点或删除了其next节点或增加了删除标记节点以删除b,
if (n != b.next)
break; // 重新开始
Object v = n.value;
if (v == null) { // n为待删除节点
n.helpDelete(b, f); // 推进删除节点n
break; // 重新开始
}
// 返回的前驱节点b为待删除节点
// 这里不能直接删除b,因为不知道b的前驱节点,只能重新开始,调用findPredecessor返回更前的节点
if (v == n || b.value == null) // b is deleted
break; // 重新开始
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c == 0)
return n;
if (c < 0)
return null;
b = n;
n = f;
}
}
} 删
步骤:
1)查找比key小的前驱节点;
2)从前驱节点开始,遍历底层Node单链表,若不存在相关的key-value对,则返回null;否则确定Node节点位置;假设确定删除的节点为n,b为其前驱节点,f为其后继节点:
作用:
a)其他增删改查线程遍历到该节点时,都知其为待删除节点;
b)其他增删改查线程可通过CAS修改n的next,推进n的删除。
该步失败,只需要重试即可。
4)在其后添加删除标记节点marker;
a)新增节点不能插入到n的后面;
b)基于CAS方式的删除,可以避免删除上的错误。
5)删除该节点及其删除标记节点;

第4)5)步可能会失败,原因在于其他操作线程在遍历过程中知n的value为null后,会帮助推进删除n,这些帮助操作可以保证没有一个线程因为删除线程的删除操作而阻塞。
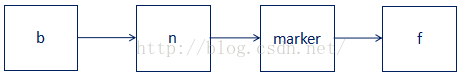
另外,删除需要确保b——>n——>marker——>f链接关系才能进行。
6)用findPredecessor删除其索引节点;
7)若最上层索引层无Node索引节点,则尝试降低索引层次。
8)返回其旧value
public V remove(Object key) {
return doRemove(key, null);
}
// 主要的删除Node节点及其索引节点方法
final V doRemove(Object okey, Object value) {
Comparable key = comparable(okey);
for (;;) {
Node b = findPredecessor(key);
Node n = b.next;
for (;;) {
if (n == null)
return null;
Node f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
Object v = n.value;
if (v == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (v == n || b.value == null) // b is deleted
break;
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c < 0)
return null;
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
if (value != null && !value.equals(v))
return null;
if (!n.casValue(v, null)) // 将value置为null
break;
if (!n.appendMarker(f) || !b.casNext(n, f)) // 添加删除标记节点,删除该节点与其删除标记节点
findNode(key); // 失败则用findNode继续删除
else {
findPredecessor(key); // 用findPredecessor删除其索引节点
if (head.right == null)
tryReduceLevel();
}
return (V)v;
}
}
}
// 当最上三层索引层无Node索引节点,则将最上层索引层去掉。
// 采用CAS方式去掉后,如果其又拥有Node索引节点,则尝试将其恢复。
private void tryReduceLevel() {
HeadIndex h = head;
HeadIndex d;
HeadIndex e;
if (h.level > 3 &&
(d = (HeadIndex)h.down) != null &&
(e = (HeadIndex)d.down) != null &&
e.right == null &&
d.right == null &&
h.right == null &&
casHead(h, d) && // try to set
h.right != null) // recheck
casHead(d, h); // try to backout
} 查
步骤:
1)查找比key小的前驱节点;
2)从前驱节点开始,遍历底层Node单链表,若不存在相关的key-value对,则返回null;否则获取Node节点;
3)判断其value是否为null,如果不为null,则直接返回value;否则重试,原因是其被标记为待删除节点。
public V get(Object key) {
return doGet(key);
}
private V doGet(Object okey) {
Comparable key = comparable(okey);
/*
* Loop needed here and elsewhere in case value field goes
* null just as it is about to be returned, in which case we
* lost a race with a deletion, so must retry.
*/
for (;;) {
Node n = findNode(key);
if (n == null)
return null;
Object v = n.value;
if (v != null)
return (V)v;
}
} 迭代器
基础迭代器为Iter,从first节点开始遍历Node单链表层:
abstract class Iter implements Iterator {
/** the last node returned by next() */
Node lastReturned;
/** the next node to return from next(); */
Node next;
/** Cache of next value field to maintain weak consistency */
V nextValue;
/** Initializes ascending iterator for entire range. */
Iter() {
for (;;) {
next = findFirst();
if (next == null)
break;
Object x = next.value;
if (x != null && x != next) {
nextValue = (V) x;
break;
}
}
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
/** Advances next to higher entry. */
final void advance() {
if (next == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
for (;;) {
next = next.next; // next
if (next == null)
break;
Object x = next.value;
if (x != null && x != next) {
nextValue = (V) x;
break;
}
}
}
public void remove() {
Node l = lastReturned;
if (l == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
// It would not be worth all of the overhead to directly
// unlink from here. Using remove is fast enough.
ConcurrentSkipListMap.this.remove(l.key);
lastReturned = null;
}
} 特性
如何实现增删改查并发线程安全?
1. 采用无锁并发方式;
2.基于final、volatile、CAS方式助于并发;
3. 删除Node节点方式:将该节点的value置为null,且在其后插入一个删除标记节点,即:b——>n——>marker——>f(假设n为待删除Node节点,marker为其删除标记节点,b为n的前驱节点,f为n的删除前的后继节点)这种方式解决了4个问题:
1)与Node插入可并发进行,因为n后为marker标记节点,肯定不会在n后插入新的Node节点;
2)与Node修改可并发进行,因为n的value为null,修改线程对n的CAS修改肯定是失败的;
3)与Node读可并发进行,因为n的value为null,即使读线程匹配到n,也返回的value为null,而在Map中返回null即代表key-value对不存在,n正在删除,所以也表明不存在,尽管不是严格意义上的;
4)所有操作在遍历Node单链表时,可根据以上链接关系,推进删除n和marker。