Logger框架源码解析
在移动软件开发中,我们经常会用到很多框架,如网络框架retrofit,图片加载框架glide,数据库框架litepal,日志框架Logger等。这些框架对应用都很重要,日志框架也是其中重要的一部分。因为很多操作如调试,优化,修改bug等都需要通过日志来验证我们的想法,所以日志框架就成项目的必需。本篇博文将会介绍Logger日志框架,主要从源码的角度分析。
一、什么是Logger框架?
Simple, pretty and powerful logger for android。简单,功能强大日志框架,专为Android。
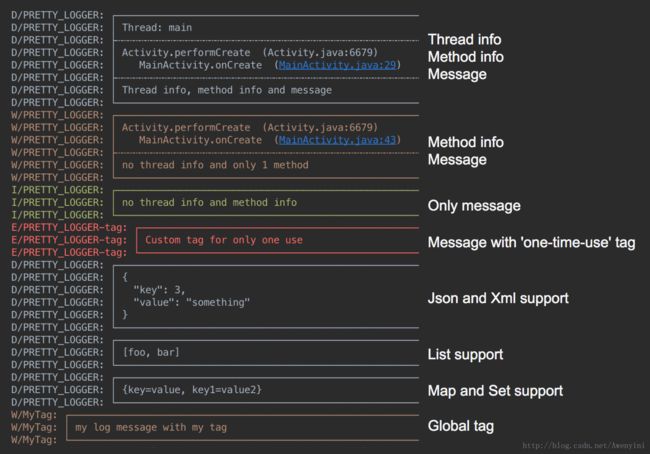
Logger有多强大呢?先让我们来看一张打印日志图:
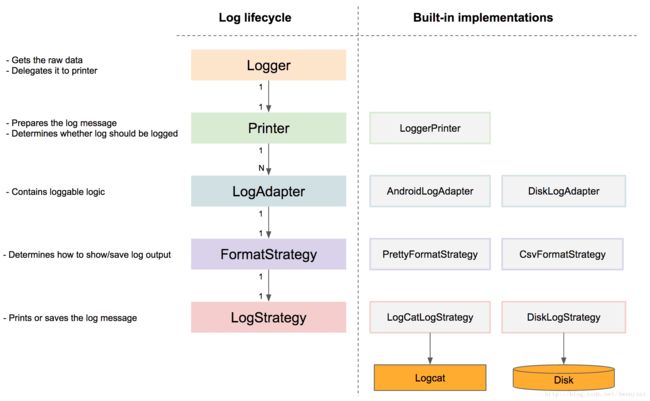
从此图,就可看出Logger打印日志相当强大。Logger框架原理图:
二、Logger源码解析(Json)
Logger源码地址:https://github.com/orhanobut/logger
本篇博文主要采用版本V2.1.1的源码。
1.Logger初始化
Logger.addLogAdapter(new AndroidLogAdapter());//1.初始化我们先来看Logger的初始化,进入Logger类
/**
* But more pretty, simple and powerful
*/
public final class Logger {
private static Printer printer = new LoggerPrinter();
......
public static void addLogAdapter(LogAdapter adapter) {
printer.addAdapter(adapter);
}
......
}Logger的静态方法,主要就是向printer中添加了一个Adapter,通过定义我们知道printer为LoggerPrinter,我们继续看看LoggerPrinter
class LoggerPrinter implements Printer {
private final List logAdapters = new ArrayList<>();
......
@Override public void addAdapter(LogAdapter adapter) {
logAdapters.add(adapter);
}
......
} 从方法名addLogAdapter就知向LogAdapter列表添加LogAdapter,源码下来也的确如此,但这LogAdapters有啥用呢?后面会说到。让我们再来看看AndroidLogAdapter
public class AndroidLogAdapter implements LogAdapter {
private final FormatStrategy formatStrategy;
public AndroidLogAdapter() {
this.formatStrategy = PrettyFormatStrategy.newBuilder().build();
}
public AndroidLogAdapter(FormatStrategy formatStrategy) {
this.formatStrategy = formatStrategy;
}
......
}在AndroidLogAdapter中初始化了FormatStrategy,这类有啥用呢?让我们来看看
public interface FormatStrategy {
void log(int priority, String tag, String message);
}
FormatStrategy就是一个接口,应该是打印日志的。我们来看看他的实现类PrettyFormatStrategy.newBuilder().build(),继续看PrettyFormatStrategy源码
public class PrettyFormatStrategy implements FormatStrategy {
private final int methodCount;
private final int methodOffset;
private final boolean showThreadInfo;
private final LogStrategy logStrategy;
private final String tag;
private PrettyFormatStrategy(Builder builder) {
methodCount = builder.methodCount;
methodOffset = builder.methodOffset;
showThreadInfo = builder.showThreadInfo;
logStrategy = builder.logStrategy;
tag = builder.tag;
}
public static Builder newBuilder() {
return new Builder();
}
public static class Builder {
.......
private Builder() {
}
......
public PrettyFormatStrategy build() {
if (logStrategy == null) {
logStrategy = new LogcatLogStrategy();
}
return new PrettyFormatStrategy(this);
}
}由上易知,主要就是对PrettyFormatStrategy初始化,然后赋值给AndroidLogAdapter的FormatStrategy。PrettyFormatStrategy类对Logger来说是核心类,因为所有日志的打印控制主要也在此类实现,接下来我们会说到。
2.Logger打印日志
Logger.d("Hello world!");//2.debug日志
Logger.json("{ \"key\": 3, \"value\": something}");//3.Json日志i.debug日志,一般日志打印
首先,我们来看一般日志,debug日志,进入Logger源码
public final class Logger {
private static Printer printer = new LoggerPrinter();
.....
public static void d(String message, Object... args) {
printer.d(message, args);
}
public static void d(Object object) {
printer.d(object);
}
public static void e(String message, Object... args) {
printer.e(null, message, args);
}
public static void e(Throwable throwable, String message, Object... args) {
printer.e(throwable, message, args);
}
......
}主要是执行printer中的方法,我们继续看LoggerPrinter
class LoggerPrinter implements Printer {
......
@Override public void d(String message, Object... args) {
log(DEBUG, null, message, args);
}
@Override public void d(Object object) {
log(DEBUG, null, Utils.toString(object));
}
@Override public synchronized void log(int priority, String tag, String message, Throwable throwable) {
.......
for (LogAdapter adapter : logAdapters) {
if (adapter.isLoggable(priority, tag)){
adapter.log(priority, tag, message);
}
}
}
}可以发现,主要就是遍历LogAdapters列表,因为adapter是不同的适配器,不同适配器有不同的打印日志信息格式。从Logger的初始化,我们知道传入的是AndroidLogAdapter并且AndroidLogAdapter中主要执行的是PrettyFormatStrategy中的log方法,这里我们直接看PrettyFormatStrategy中的log方法
@Override public void log(int priority, String onceOnlyTag, String message) {
String tag = formatTag(onceOnlyTag);
logTopBorder(priority, tag);//1.Log顶端的线格式
logHeaderContent(priority, tag, methodCount);//2.log头部内容
//get bytes of message with system's default charset (which is UTF-8 for Android)
byte[] bytes = message.getBytes();
int length = bytes.length;
if (length <= CHUNK_SIZE) {
if (methodCount > 0) {
logDivider(priority, tag);//日志分界线
}
logContent(priority, tag, message);//3.log日志内容
logBottomBorder(priority, tag);//4.log底端线格式
return;
}
if (methodCount > 0) {
logDivider(priority, tag);//日志分界线
}
for (int i = 0; i < length; i += CHUNK_SIZE) {
int count = Math.min(length - i, CHUNK_SIZE);
//create a new String with system's default charset (which is UTF-8 for Android)
logContent(priority, tag, new String(bytes, i, count));//5.log日志内容
}
logBottomBorder(priority, tag);//6.log底端线格式
}此方法是Logger框架打印日志的核心方法,上面图片中的日志,主要就是通过这个方法控制打印的。让我们来看相关方法
public class PrettyFormatStrategy implements FormatStrategy {
private static final char TOP_LEFT_CORNER = '┌';
private static final char BOTTOM_LEFT_CORNER = '└';
private static final char MIDDLE_CORNER = '├';
private static final char HORIZONTAL_LINE = '│';
private static final String DOUBLE_DIVIDER = "────────────────────────────────────────────────────────";
private static final String SINGLE_DIVIDER = "┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄┄";
private static final String TOP_BORDER = TOP_LEFT_CORNER + DOUBLE_DIVIDER + DOUBLE_DIVIDER;
private static final String BOTTOM_BORDER = BOTTOM_LEFT_CORNER + DOUBLE_DIVIDER + DOUBLE_DIVIDER;
private static final String MIDDLE_BORDER = MIDDLE_CORNER + SINGLE_DIVIDER + SINGLE_DIVIDER;
.....
private void logTopBorder(int logType, String tag) {
logChunk(logType, tag, TOP_BORDER);
}
private void logBottomBorder(int logType, String tag) {
logChunk(logType, tag, BOTTOM_BORDER);
}
private void logDivider(int logType, String tag) {
logChunk(logType, tag, MIDDLE_BORDER);
}
private void logContent(int logType, String tag, String chunk) {
String[] lines = chunk.split(System.getProperty("line.separator"));//核心方法
for (String line : lines) {
logChunk(logType, tag, HORIZONTAL_LINE + " " + line);
}
}
private void logChunk(int priority, String tag, String chunk) {
logStrategy.log(priority, tag, chunk);
}
......
}由上易知,最后都调用logChunk()方法,最后主要也是调用了logStrategy的log方法,通过Logger初始化,知logStrategy就是LogcatLogStrategy类,我们来看LogcatLogStrategy中的log方法
import android.util.Log;
public class LogcatLogStrategy implements LogStrategy {
@Override public void log(int priority, String tag, String message) {
Log.println(priority, tag, message);
}
}这里主要调用了android原生的打印日志方法,从而日志就被打印在logCat中了。到这里,一般日志打印就介绍完了,其他日志可以类推的,这里不介绍了。
ii.Json日志的打印
打印调用方法
Logger.json("{ \"key\": 3, \"value\": something}");//3.Json日志从debug日志打印分析中,我们知道PrettyFormatStrategy的log类为打印日志核心方法,对于json日志打印,主要是打印内容的区别,其他打印没有区别,所以这里主要看看打印日志的方法
private void logContent(int logType, String tag, String chunk) {
String[] lines = chunk.split(System.getProperty("line.separator"));//核心方法
for (String line : lines) {
logChunk(logType, tag, HORIZONTAL_LINE + " " + line);
}
}这里知道,对打印内容chunk进行了分割,主要以System.getProperty(“line.separator”)即换行符\n进行分割。从打印Json内容中,我们没有发现换行符,这里需要看看最初调用的方法。由Logger初始化,我们知Logger.json()方法主要就是调用LoggerPrinter中的json方法,这里让我们来看LoggerPrinter.json()方法
@Override public void json(String json) {
if (Utils.isEmpty(json)) {
d("Empty/Null json content");
return;
}
try {
json = json.trim();
if (json.startsWith("{")) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(json);
String message = jsonObject.toString(JSON_INDENT);//1
d(message);
return;
}
if (json.startsWith("[")) {
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray(json);
String message = jsonArray.toString(JSON_INDENT);//2.
d(message);
return;
}
e("Invalid Json");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e("Invalid Json");
}
}通过调试,知道就是在注释中的位置,在进行转化的时候,字符串”{ \”key\”: 3, \”value\”: something}”转为”{\n”key”: 3,\n”value”: something\n}”,从而在打印的时候,就可以分行打印键值对。这样也就再打印json的时候可以分行显示。
到这里,日志Logger框架原理分析就讲解完。其中logger框架还支持打印xml,具体原理如何,这里不做介绍了。
三、总结
Logger日志框架,让Log日志变得整洁,简单,易看,一大功德。其中PrettyFormatStrategy通过静态内部类实现了Logger显示内容配置方式值得借鉴。
四、相关参考文档
Looger官方介绍