Git远程仓库和本地仓库协同工作精讲
Git远程仓库和本地仓库协同工作精讲
要了解git远程仓库和本地仓库是如何协同工作的,首先要理解清楚以下几个关键的概念。
Remote references
Remote references are references (pointers) in your remote repositories, including branches, tags, and so on.
远程仓库其实就是一个git仓库。所以Remote references就是另一台电脑上的一个git仓库的原汁原味的应用。
Remote-tracking branches
但是我们在实际中,基本不使用Remote references,而是使用Remote-tracking branches.
Remote-tracking branches are references to the state of remote branches.
- They’re local references that you can’t move, Git moves them for you whenever you do any network communication(这里并不是网络良好就会保持一致,而是人为通过命令使得一致之后。但不言而喻,没有网的话,是根本不可通的), to make sure they accurately represent the state of the remote repository.
- Think of them as bookmarks, to remind you where the branches in your remote repositories were the last time you connected to them.
- Remote-tracking branch names take the form
/ . For instance, if you wanted to see what the master branch on your origin remote looked like as of the last time you communicated with it, you would check the origin/master branch.- if you were working on an issue with a partner and they pushed up an iss53 branch, you might have your own local iss53 branch, but the branch on the server would be represented by the remote-tracking origin/iss53
接下来我将用实例讲解
Let’s say you have a Git server on your network at git.ourcompany.com. If you clone from this, Git’s clone command automatically names it origin for you, pulls down all its data, creates a pointer to where its master branch is, and names it origin/master locally. Git also gives you your own local master starting at the same place as origin’s master branch, so you have something to work from.
- origin并没有什么特殊的含义,仅代表一个git远程仓库而已。
首先我将讲一下git clone命令到底做了什么
假设现在在远程有这么一个仓库:[email protected]:project.git,我在本地运行git clone命令。
则发生的事情是这样的。
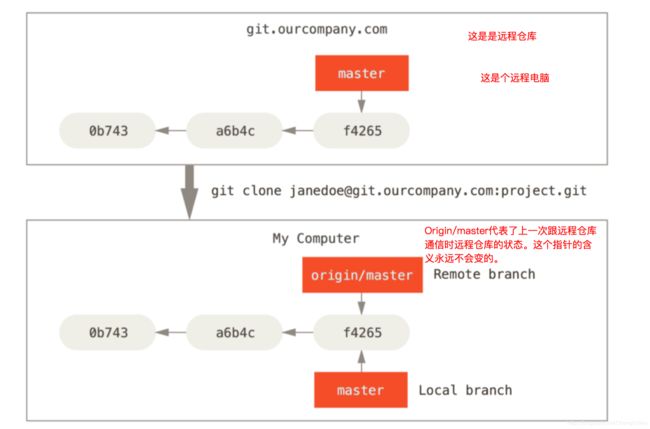
可以看到本地存在两个分支。一个是origin/master,这是远程分支的映像。本地的master分支也从origin/master当前的状况开始。
If you do some work on your local branch—master, and in the meantime, someone else pushes to git.ourcompany.com and update its master branch, then your histories move forward differently(这里的history指的是本地的master). Also, as long as you stay out of contact with your origin server, your origin/master pointer doesn’t move.
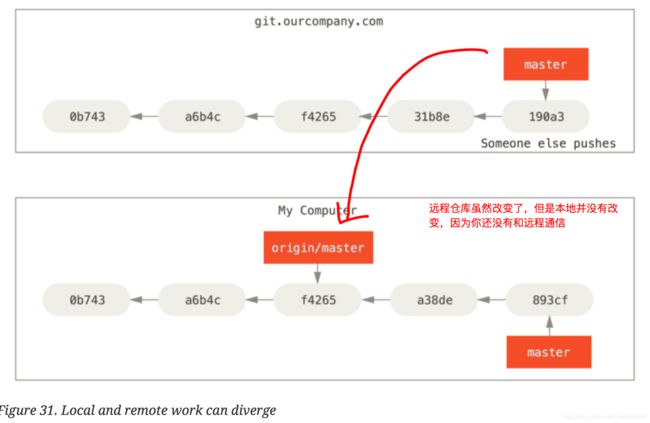
OK, 到底如何才能让本地的origin/master和远程的server进行联系了?
需要运行一个git fetch
在我们这个例子中,即为git fetch origin命令。这个命令执行的步骤到底是怎样的呢?
- Looks up which server “origin” is (in this case, its’ git.ourcompany.com)
- fetch any data from it that you don’t yet have(这里有没有是与本地的origin/master做比较的,而不是与本地的master做比较)
- updates your local database, moving your origin/master pointer to its new, more up-to-date position.
多个远程仓库如何协同工作
To demonstrate having multiple remote servers and what remote branches for those remote projects look like, let’s assume you have another Git server that is used only for development by one of your sprint teams. This server is at git.team1.ourcompany.com. You can add it as a new remote reference to the project you’re currently working on by running the git remote add command.
git remote add teamone git://git.team1.ourcompany.com
We name this remote teamone, which will be your shortname for that whole URL.
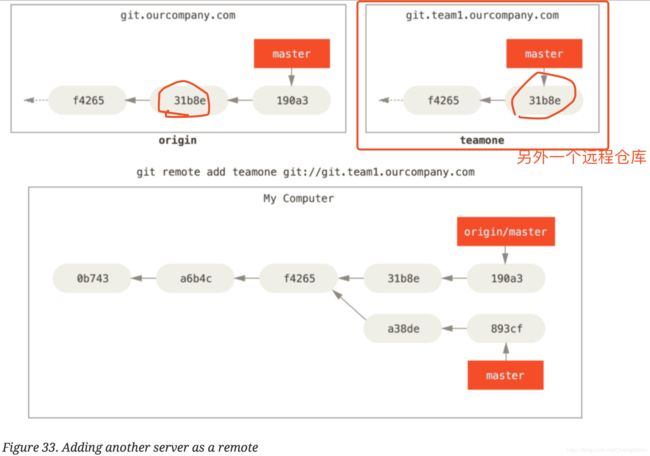
Now,we can run
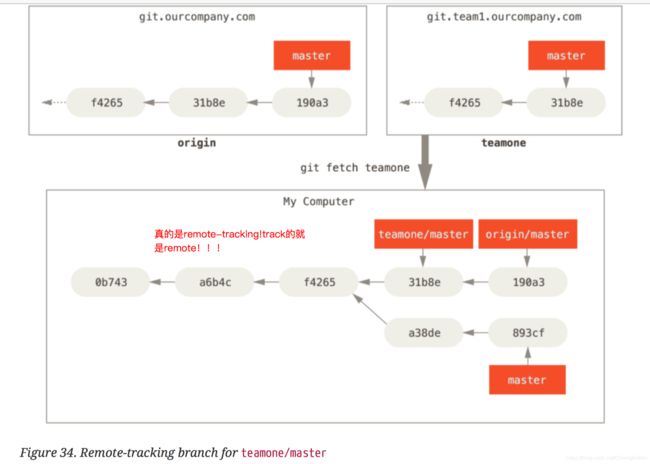
git fetch teamone
to fetch everything the remote teamone server has that you don’t have yet.(这个地方到底是和谁做比较?,我也没有搞清楚,搞清楚了之后更新)
Because the remote teamone server has a subset of the data your origin server has right now, Git fetches not data but sets a remote-tracking branch called teamone/master to point to the commit that teamone has as its master branch.
Push命令详解
When you want to share a branch with the world, you need to push it up to a remote to which you have write access. Your local branches aren’t automatically synchronized to the remotes you write to–you have to explicitly push the branches you want to share.
存在几种情况:
- 远程并不存在与本地同名的分支
这个时候当我推送上去的时候,则会自动在远程服务器创建一个与我本地相同的分支。例如:
git push origin serverfix
这句话的意思是:将本地serverfix分支的内容推送到远程服务器origin上。然而在服务器上的仓库中并不存在这样一个分支。所以运行此命令完毕后,去Github上查看的时候,会发现多了一个名为serverfix的分支。 - 未完待续!具体参考progit https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2 3.5节!