Linux内核驱动编程
Linux内核驱动编程
2015-02-12
驱动程序基础的东西这儿就不罗嗦了,百度上有更好的资料,此处我们只是注重实际用处。
下面我们开始写程序:
一、初步helloword程序
首先是来一个简单的hello。
hello.c代码:
![]()
![]()
1 /******************************
2
3 the first program
4
5 Hello World!
6
7 ******************************/
8
9 #include
10
11 #include
12
13
14
15 static int hello_init(void)
16
17 {
18
19 printk("<0>\nHello, world!\n\n");
20
21 return 0;
22
23 }
24
25
26
27 static void hello_exit(void)
28
29 {
30
31 printk("<0>\nGoodbye,world \n\n");
32
33 }
34
35
36
37 module_init(hello_init);
38
39 module_exit(hello_exit);
40
41 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); //Any version of public GNU license View Code
Make代码:
![]()
![]()
1 ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
2
3 KERNELDIR ?= /home/study/system/linux-2.6.31
4
5 PWD := $(shell pwd)
6
7 modules:
8
9 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
10
11 modules_install:
12
13 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules_install
14
15 clean:
16
17 rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend *.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions *.markers *.order *.symvers
18
19
20
21 else
22
23 obj-m := hello.o
24
25 endifView Code
注意:
①:Makefile中的KERNELDIR ,这个linux源代码的版本是和你的开发板的一模一样,必须修改,否侧或有错误
②:该应用程序必须在开发板上运行,千万注意别再服务器操作系统使用,否则存在破坏系统的危险。
接下来就是,编译->加载,使用以下命令
1 make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-
2
3 //此处为修改为你操作系统上的gcc 交叉编译
4
5 insmod hello.ko
6
7 //加载模块,此时屏幕上会打印,hello,world
8
9 rmmod hello.ko
10
11 //卸载模块,同样会打印 goodsbye world接下来我们对其进行改进
二、改进helloword程序,增加输入模块参数
我们在代码中增加以下代码:
1 static char *name = "LoverXue";
2
3 static int age = 1;
4
5
6
7 module_param(name,charp,S_IRUGO);
8
9 module_param(age,int,S_IRUGO);编译后,加载时,输入以下命令
make CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-
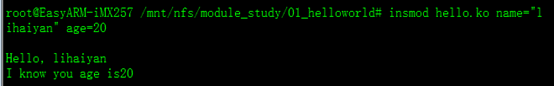
insmod hello.ko name="lihaiyan" age=20结果如下:
附上源代码如下:
hello.c代码:
![]()
![]()
1 /******************************
2
3 the first program
4
5 Hello World!
6
7 ******************************/
8
9
10
11 #include
12
13 #include
14
15
16
17 //module param list
18
19 static char *name = "LoverXue";
20
21 static int age = 1;
22
23
24
25 static int hello_init(void)
26
27 {
28
29 printk("<0>\nHello, %s\nI know you age is%d\n\n",name,age);
30
31 return 0;
32
33 }
34
35
36
37 static void hello_exit(void)
38
39 {
40
41 printk("<0>\nGoodbye,%s\n\n",name);
42
43 }
44
45
46
47 module_init(hello_init);
48
49 module_exit(hello_exit);
50
51 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); //Any version of public GNU license
52
53
54
55 module_param(name,charp,S_IRUGO);
56
57 module_param(age,int,S_IRUGO); View Code
三、改进helloword程序,增加模块之间的依赖
此时,我们的目的是:写两个模块,模块二调用模块一中的函数。
先附上代码,我们看着代码来讲解:
模块一:包含 add_sub.c add_sub.h Makefile 三个文件
add_sub.h
![]()
![]()
1 #ifndef _ADD_SUB_H_
2
3 #define _ADD_SUB_H_
4
5 long add_integer(long a,long b);//function add
6
7 long sub_integer(long a,long b);//function sub
8
9 #endifView Code
add_sub.h 中定义声明了模块二中要调用的函数,函数具体实现,看add_sub.c
add_sub.c
![]()
![]()
1 /*************************************
2
3 add_sub function
4
5 *************************************/
6
7 #include
8
9 #include
10
11
12
13 #include "add_sub.h" //包含函数声明的头文件
14
15
16
17 //returen sum of the two //实现函数
18
19 long add_integer(long a,long b)
20
21 {
22
23 return a+b;
24
25 }
26
27
28
29 //returen subtraction of the two
30
31 long sub_integer(long a,long b)
32
33 {
34
35 return a-b;
36
37 }
38
39 //为了让其他模块可以调用此函数,
40
41 //必须用EXPORT_SYMBOL将函数导出到内核
42
43 //export the function
44
45 EXPORT_SYMBOL(add_integer); /
46
47 EXPORT_SYMBOL(sub_integer);
48
49
50
51 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); View Code
Makefile代码:
![]()
![]()
1 ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
2
3 KERNELDIR ?= /home/study/system/linux-2.6.31
4
5 PWD := $(shell pwd)
6
7 #################################################
8
9 PRINT_INC = $(PWD)/
10
11 EXTRA_CFLAGS += -I $(PRINT_INC)
12
13 #################################################
14
15 modules:
16
17 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
18
19 modules_install:
20
21 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules_install
22
23 clean:
24
25 rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend *.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions *.markers *.order *.symvers
26
27
28
29 else
30
31 obj-m := add_sub.o
32
33 endifView Code
修改前面的代码,必须增加#号内的代码。
此时,我们模块一全部写完。
make 编译。
模块二:包含hello.c Makefile
hello.c代码:
![]()
![]()
1 /******************************
2
3 the first program
4 Hello World!
5 ******************************/
6 #include
7 #include
8
9 //extern module
10 #include "./add/add_sub.h" //包含头文件
11
12 //module param list
13 static char *name = "LoverXue";
14 static int age = 20;
15 static long num1 = 1;
16 static long num2 = 0;
17 static short flag = 1;
18
19 static int hello_init(void)
20 {
21 printk("<0>\nHello, %s\nI know you age is%d\n\n",name,age);
22 if(flag == 1 ){
23 printk("<0>sum of two %ld + %ld = %ld \n", num1,num2,add_integer(num1,num2));
24
25 }else{
26 printk("<0>subtraction of two %ld - %ld = %ld \n", num1,num2,sub_integer(num1,num2));
27 }
28 return 0;
29 }
30
31 static void hello_exit(void)
32 {
33 printk("<0>\nGoodbye,%s\n\n",name);
34 }
35
36 module_init(hello_init);
37 module_exit(hello_exit);
38 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); //Any version of public GNU license
39 MODULE_VERSION("V1.0");
40
41 module_param(name,charp,S_IRUGO);
42 module_param(age,int,S_IRUGO);
43 module_param(num1,long,S_IRUGO);
44 module_param(num2,long,S_IRUGO);
45 module_param(flag,short,S_IRUGO); View Code
Makefile文件代码:
![]()
![]()
1 ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
2
3 KERNELDIR ?= /home/study/system/linux-2.6.31
4
5 PWD := $(shell pwd)
6
7 ##########################################################
8
9 export-objs := /home/study/EasyARM-iMX257/module_study/02_add/add/add_sub.o
10
11 SYMBOL_INC = $(obj)/
12
13 SYMBOL_INC += /home/study/EasyARM-iMX257/module_study/02_add/add
14
15 EXTRA_CFLAGS += -I $(SYMBOL_INC)
16
17 KBUILD_EXTRA_SYMBOLS = /home/study/EasyARM-iMX257/module_study/02_add/add/Module.symvers
18
19 #########################################################
20
21 modules:
22
23 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
24
25 modules_install:
26
27 $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules_install
28
29 clean:
30
31 rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend *.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions *.markers *.order *.symvers
32
33 else
34
35 obj-m := hello.o
36
37 endifView Code
KBUILD_EXTRA_SYMBOLS的意思就是包含我们要调用的模块的Module.symvers,
此处最好使用绝对路径。
编译,
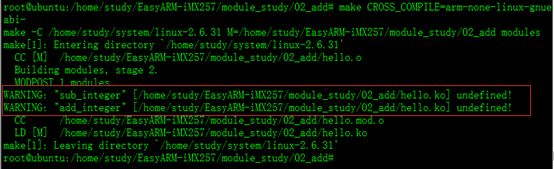
如果编译出错,如图所示。
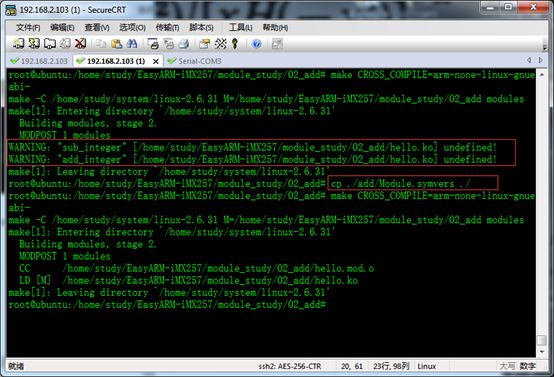
解决方法是;先编译模块一,然后将模块一的Module.symvers拷贝到我们的模块二的目录下,再编译模块二。
如图所示就不会再出这样的错误了。
加载模块
接着就是在开发板中加载模块
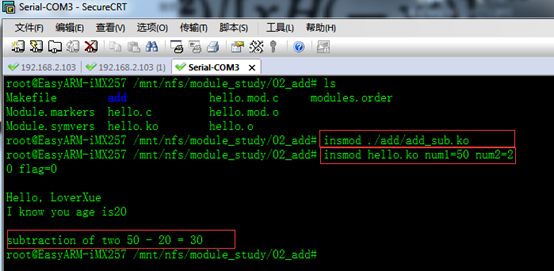
insmod ./add/add_sub.ko
insmod hello.ko num1=50 num2=20 flag=0结果如下:
四、将驱动使用静态编译入内核
接下来,我们来将刚刚写的代码使用静态编译,加入内核
-
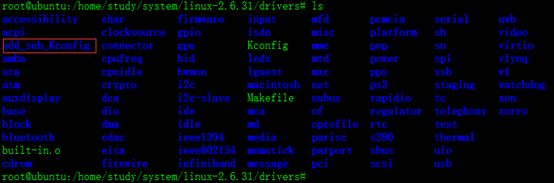
:我们进入内核的driver目录,增加目录add_sub_Kconfig
mkdir add_sub_Kconfig
-
:将我们刚刚写的hello.c add_sub.c add_sub.h 三个文件拷贝入此文件夹
-
:在此文件夹中增加Makefile,Kconfig两个文件,代码如下:
Makefile代码
#drivers/add_sub_Kconfig/Makefile
# Makefile for the ADD_SUB core.
#
obj-$(CONFIG_ADD_SUB) := add_sub.o
obj-$(CONFIG_TEST) := hello.o
Kconfig代码如下:
#drivers/add_sub_Kconfig/Kconfig
menu "ADD_SUB" #main menu //增加主菜单
comment "ADD_SUB"
//增加子菜单
config CONFIG_ADD_SUB #children menu, add the add_sub module
boolean "ADD_SUB support"
default y
#children menu ,add the test menu
config CONFIG_TEST
tristate "ADD_SUB test support"
depends on CONFIG_ADD_SUB #Depends on the config CONFIG_ADD_SUB
default y
endmenu
-
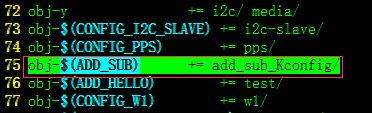
:修改driver下的Makefile,Kconfig 文件代码:
Makefile中增加:
obj-$(ADD_SUB) += add_sub_Kconfig/将上面我们自己写的makefile文件包含进来:
Kconfig中末尾增加以下代码:
将上面我们自己写的Kconfig文件包含进来
source "drivers/add_sub_Kconfig/Kconfig"
source "drivers/test//Kconfig"
-
:修改arch/arm/ 目录下的 Makefile Kconfig
(实验证明只对,只对drivers/Kconfig中修改内容无效,drivers/Kconfig中修改内容无效,还要对arch/arm/Kconfig进行修改,很重要的一步,很多资料上都遗漏了这一步)
在Kconfig中加入代码:
source "drivers/add_sub_Kconfig/Kconfig"
-
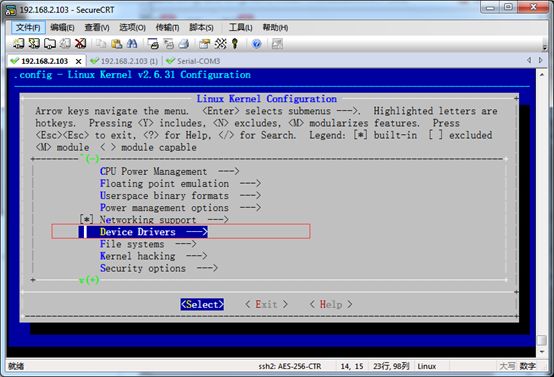
:配置编译
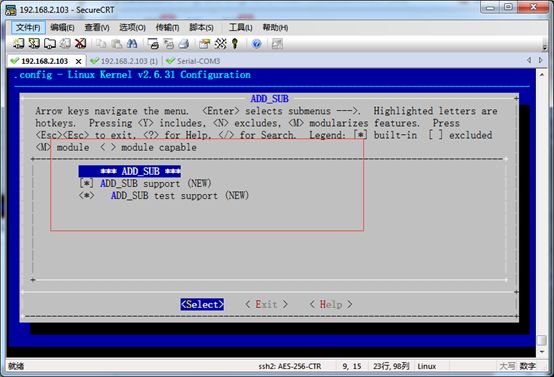
在内核的根目录下执行,make menuconfig 如图所示:
进入Device Drivers 目录
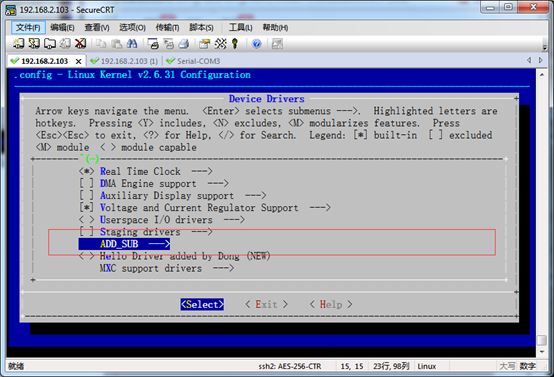
在最后面,我们看到了,我们自定义的模块:ADD_SUB模块
进入ADD_SUB,我们会看到我们写的两个模块全都默认选中了
此时,我们再次编译内核,就会把我们的模板使用静态编译进内核。