ConcurrentHashMap一篇治愈你的迷茫
都说concurrentHashmap很重要,很好用,今天总结一下,做个笔记。
先捋一下concurrentHashMap的属性
/**
* 这个表的默认初始容量,
* 在构造函数中没有指定的时候使用。
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* 这个表的默认加载因子,不用时使用
* 否则在构造函数中指定。
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* 这个表的默认并发级别,在不使用时使用
* 在构造函数中指定的
*/
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
/**
* 最大容量,如果更高的值隐式使用
* 由具有参数的构造函数指定。 必须
* 是两个<= 1 << 30的幂以确保条目是可索引的
* 使用整数。
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* 每个细分表格的最小容量。 必须是
* 两个,至少两个,以避免立即调整下次使用
*/
static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;
/**
* 允许的最大段数; 用来绑定
* 构造函数参数。。
*/
static final int MAX_SEGMENTS = 1 << 16; // slightly conservative
/**
* 包含大小和包含值的未同步重试次数
* 在诉诸锁定之前的方法。 这是用来避免
* 如果表格经历了不断的修改,那么无限制的重试
* 这将无法获得准确的结果。
*/
static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2;一、先看一下concurrentHashMap的数据结构
看下面,重点是那个Segment[] segments 数组
final int segmentMask;
/**
* Shift value for indexing within segments.
*/
final int segmentShift;
/**
* The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table.
*/
final Segment[] segments;
transient Set keySet;
transient Set> entrySet;
transient Collection values; Segment 的结构,有个HashEntry 数组,并且继承了ReentrantLock ,到这里相信你已经明白了,每个segment都是一个锁,因此concurrentHashMap 的分段锁所得就是这个segment。
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;
/**
* The per-segment table. Elements are accessed via
* entryAt/setEntryAt providing volatile semantics.
*/
transient volatile HashEntry[] table;
/**
* The number of elements. Accessed only either within locks
* or among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.
*/
transient int count;
} HashEntry 结构有next的引用 是个链表结构
static final class HashEntry {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V value;
volatile HashEntry next;
HashEntry(int hash, K key, V value, HashEntry next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
列出上面源码,就清楚可以看出concurrenthashMap 的数据结构了。
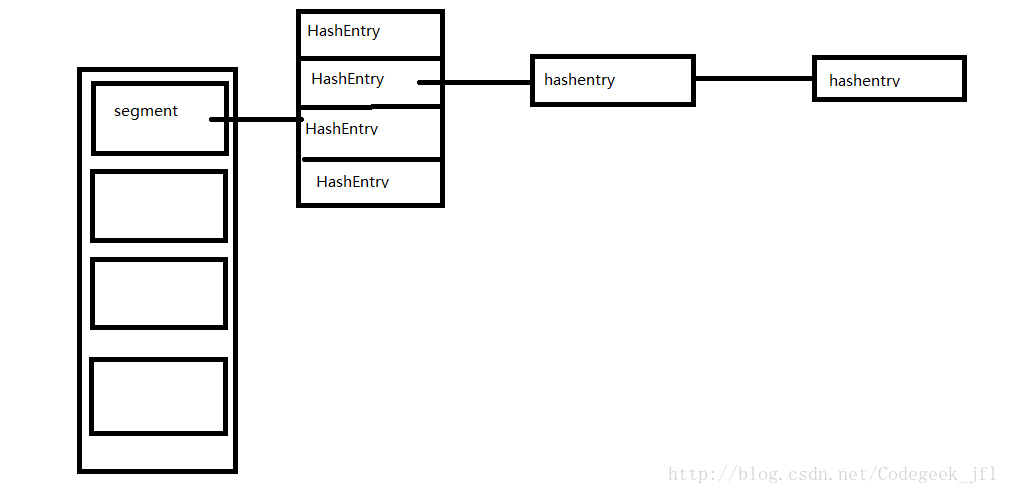
图片画的有点糙,能看出道理就可以了。
concurrenthashMap是一个segment的数组,segment包含一个hashEntry的数组,hashentry是一个链表。
二、来一起走一遍源码
1、初始化
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
//判断加载因子、初始化容量、并发级别参数是否合法
if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//并发级别超过最大值,就设置为最大值
if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS)
concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;
// Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments
//偏移量,定位的时候用
int sshift = 0;
//segment的个数,只能是2的幂次方
int ssize = 1;
while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {
++sshift;
ssize <<= 1;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;
this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
//初始化大小不能大于最大值
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
//下面是计算容量--------------------------
//平均一个segment有所少容量
int c = initialCapacity / ssize;
//必须是2的幂次方
if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)
++c;
//真正的计算容量,2的幂次方
int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;
while (cap < c)
cap <<= 1;
// create segments and segments[0]
Segment s0 =
new Segment(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),
(HashEntry[])new HashEntry[cap]);
Segment[] ss = (Segment[])new Segment[ssize];
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]
this.segments = ss;
}
2、get方法,没有加锁,老的版本还在查到是null的时候,会在加锁的情况下载查一遍。
public V get(Object key) {
Segment s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead
HashEntry[] tab;
int h = hash(key);
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
for (HashEntry e = (HashEntry) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
3、put方法,首先是定位到那个segment,然后调用segment的put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
} 这个就是segment的put方法,分段锁就是在这里。put先判断key是否存在,存在覆盖,不存在,放在链表投。
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
4、remove方法的套路和put是一样的,先定位,然后调用segment的remove。
public V remove(Object key) {
int hash = hash(key);
Segment s = segmentForHash(hash);
return s == null ? null : s.remove(key, hash, null);
} 这里是segment的remove
final V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
if (!tryLock())
scanAndLock(key, hash);
V oldValue = null;
try {
HashEntry[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry e = entryAt(tab, index);
HashEntry pred = null;
while (e != null) {
K k;
HashEntry next = e.next;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value == v || value.equals(v)) {
if (pred == null)
setEntryAt(tab, index, next);
else
pred.setNext(next);
++modCount;
--count;
oldValue = v;
}
break;
}
pred = e;
e = next;
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}