Coursera吴恩达Deep Learning.ai第一课第四周Building your Deep Neural Network: Step by Step
Building your Deep Neural Network: Step by Step
您将构建一个深层神经网络,拥有您想要的多个层!
完成此任务后,您将能够:
- 使用ReLU等非线性单位来改善您的模型。
- 构建更深层的神经网络(具有多于1个隐藏层)。
- 实现易于使用的神经网络类。
符号:
1 - 包
- numpy是使用Python进行科学计算的主要软件包。
- matplotlib是一个用Python绘制图形的库。
- dnn_utils为这款笔记本提供了一些必要的功能。
- testCases提供了一些测试用例来评估函数的正确性
- np.random.seed(1)用于保持所有随机函数调用一致。 它将帮助我们评估您的工作。 请不要改变种子。
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from testCases import *
from dnn_utils import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
np.random.seed(1)
2 - 作业概要
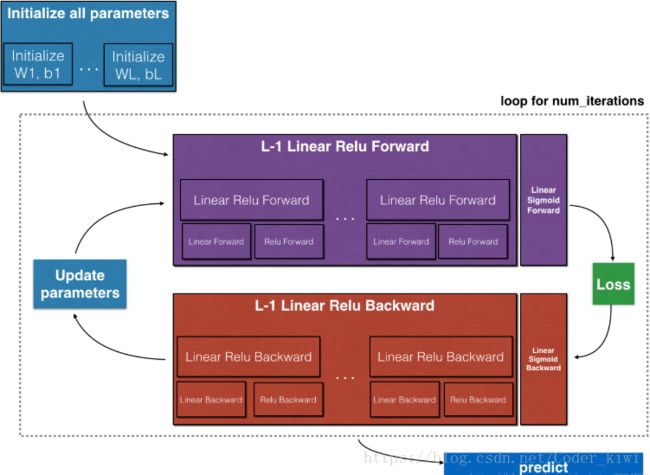
要构建您的神经网络,您将实现几个“辅助函数”。这些辅助函数将用于下一个任务,以构建一个双层神经网络和一个L层神经网络。以下是此作业的概要,您将:
- 初始化双层网络和L层神经网络的参数。
- 实现前向传播模块(如下图中的紫色所示)。
-
完成图层前向传播步骤的LINEAR部分(得到Z [1])。
-
我们为您提供ACTIVATION功能(relu / sigmoid)。
-
将前两个步骤组合成一个新的[LINEAR-> ACTIVATION]前向功能。
-
堆叠[LINEAR-> RELU]前向功能L-1时间(对于第1层到第L-1层)并在末尾添加[LINEAR-> SIGMOID](对于最后一层L)。这为您提供了一个新的L_model_forward函数。
- 计算损失。
- 实现后向传播模块(下图中以红色表示)。
- 完成图层向后传播步骤的LINEAR部分。
-
我们给你ACTIVATE函数的渐变(relu_backward / sigmoid_backward)
-
将前两个步骤组合成一个新的[LINEAR-> ACTIVATION]向后功能。
-
向后堆叠[LINEAR-> RELU] L-1次并在新的L_model_backward函数中向后添加[LINEAR-> SIGMOID]
- 最后更新参数。
注意:对于每个前向功能,都有相应的后向功能。在转发模块的每一步中,您都会将一些值存储在缓存中。缓存的值对计算渐变很有用。在反向传播模块中,您将使用缓存来计算渐变。此作业将向您显示如何执行这些步骤。
3 - 初始化
您将编写两个辅助函数来初始化模型的参数。第一个函数将用于初始化双层模型的参数。第二个将把这个初始化过程推广到L层。
3.1 - 2层神经网络
练习:创建并初始化2层神经网络的参数。
说明:
- 模型的结构是:LINEAR - > RELU - > LINEAR - > SIGMOID。
- 对权重矩阵使用随机初始化。使用正确形状的np.random.randn(shape)* 0.01。
- 对偏差使用零初始化。使用np.zeros(shape)。
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
Argument:
n_x -- size of the input layer
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
n_y -- size of the output layer
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)
b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)
W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)
b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)
"""
np.random.seed(1)
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h) * 0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert(b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert(W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert(b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
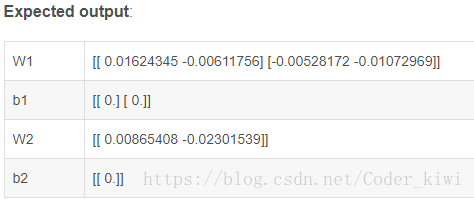
return parameters parameters = initialize_parameters(2,2,1)
print("W1 = " + str(parameters["W1"]))
print("b1 = " + str(parameters["b1"]))
print("W2 = " + str(parameters["W2"]))
print("b2 = " + str(parameters["b2"]))
3.2 - L层神经网络
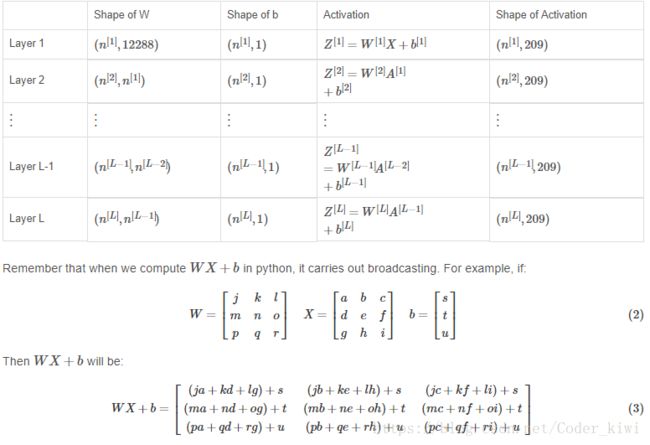
更深层的L层神经网络的初始化更复杂,因为有更多的权重矩阵和偏置向量。 完成initialize_parameters_deep后,您应确保每个图层之间的尺寸匹配。 回想一下,n [l]是层l中的单元数。 因此,例如,如果我们的输入X的大小是(12288,209)(m = 209个例子)那么:
练习:实现L层神经网络的初始化。
说明:
- 模型的结构是[LINEAR - > RELU]×(L-1) - > LINEAR - > SIGMOID。即,它具有L-1层,使用ReLU激活函数,接着是具有S形激活函数的输出层。
- 对权重矩阵使用随机初始化。使用np.random.rand(shape)* 0.01。
- 对偏差使用零初始化。使用np.zeros(shape)。
- 我们将在变量layer_dims中存储n [l],即不同层中的单元数。例如,上周的“平面数据分类模型”的layer_dims将是[2,4,1]:有两个输入,一个隐藏层有4个隐藏单元,一个输出层有一个输出单元。因此,W1的形状为(4,2),b1为(4,1),W2为(1,4),b2为(1,1)。现在你将它推广到L层!
- 这是L = 1(单层神经网络)的实现。它应该激励你实现一般情况(L层神经网络)。
if L == 1:
parameters["W" + str(L)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[1], layer_dims[0]) * 0.01
parameters["b" + str(L)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[1], 1))# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters_deep
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
"""
Arguments:
layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":
Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1)
"""
np.random.seed(3)
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1]) * 0.01
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]))
assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))
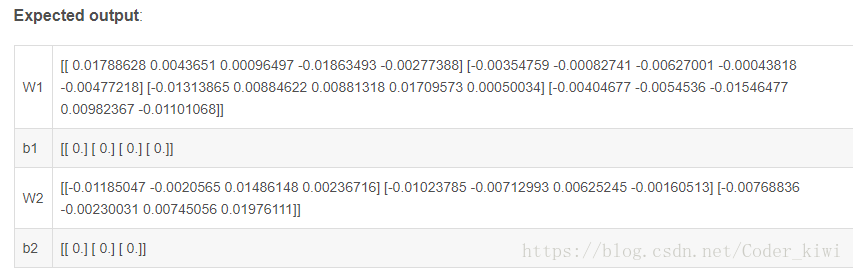
return parametersparameters = initialize_parameters_deep([5,4,3])
print("W1 = " + str(parameters["W1"]))
print("b1 = " + str(parameters["b1"]))
print("W2 = " + str(parameters["W2"]))
print("b2 = " + str(parameters["b2"]))4 - 前向传播模块
4.1 - 线性前向
现在您已经初始化了参数,您将进行前向传播模块。 您将首先实现一些基本功能,稍后您将在实现模型时使用这些功能。 您将按此顺序完成三个功能:
- LINEAR
- LINEAR - > ACTIVATION,其中ACTIVATION将是ReLU或Sigmoid。
- [LINEAR - > RELU]×(L-1) - > LINEAR - > SIGMOID(整个模型)
练习:构建前向传播的线性部分。
提醒:该单位的数学表示为![]() 。 您可能还会发现np.dot()很有用。 如果您的尺寸不匹配,打印W.shape可能会有所帮助。
。 您可能还会发现np.dot()很有用。 如果您的尺寸不匹配,打印W.shape可能会有所帮助。
# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_forward
def linear_forward(A, W, b):
"""
Implement the linear part of a layer's forward propagation.
Arguments:
A -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)
W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)
Returns:
Z -- the input of the activation function, also called pre-activation parameter
cache -- a python dictionary containing "A", "W" and "b" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
Z = np.dot(W, A) + b
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))
cache = (A, W, b)
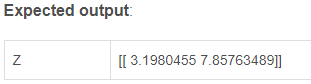
return Z, cacheA, W, b = linear_forward_test_case()
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A, W, b)
print("Z = " + str(Z))4.2 - 线性激活转发
在此笔记本中,您将使用两个激活功能:
为方便起见,您将把两个函数(线性和激活)分组为一个函数(LINEAR-> ACTIVATION)。 因此,您将实现一个函数,该函数执行LINEAR前进步骤,然后执行ACTIVATION前进步骤。
练习:实现LINEAR-> ACTIVATION图层的前向传播。 数学关系是:![]() 其中激活“g”可以是sigmoid()或relu()。 使用linear_forward()和正确的激活函数。
其中激活“g”可以是sigmoid()或relu()。 使用linear_forward()和正确的激活函数。
# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_activation_forward
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
"""
Implement the forward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer
Arguments:
A_prev -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)
W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)
activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"
Returns:
A -- the output of the activation function, also called the post-activation value
cache -- a python dictionary containing "linear_cache" and "activation_cache";
stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
if activation == "sigmoid":
# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
Z, linear_cache = np.dot(W, A_prev) + b, (A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)
### END CODE HERE ###
elif activation == "relu":
# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
Z, linear_cache = np.dot(W, A_prev) + b, (A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = relu(Z)
### END CODE HERE ###
assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))
cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)
return A, cacheA_prev, W, b = linear_activation_forward_test_case()
A, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation = "sigmoid")
print("With sigmoid: A = " + str(A))
A, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation = "relu")
print("With ReLU: A = " + str(A))注意:在深度学习中,“[LINEAR-> ACTIVATION]”计算在神经网络中计为单层,而不是两层。
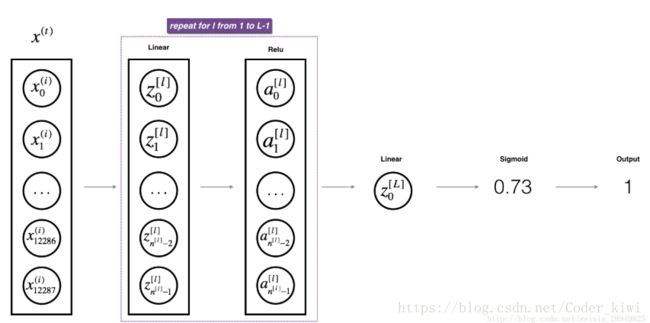
d)L层模型
为了在实现L层神经网络时更加方便,您需要一个能够复制前一个(使用RELU的linear_activation_forward)L-1次的函数,然后使用一个带有SIGMOID的linear_activation_forward。
练习:实现上述模型的前向传播。
指令:在下面的代码中,变量AL将表示![]() 。(有时也称为Yhat,即这是
。(有时也称为Yhat,即这是![]() 。)
。)
提示:
- 使用您之前编写的功能。
- 使用for循环复制[LINEAR-> RELU](L-1)次。
- 不要忘记跟踪“缓存”列表中的缓存。 要向列表中添加新值c,可以使用list.append(c)。
# GRADED FUNCTION: L_model_forward
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
"""
Implement forward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID computation
Arguments:
X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep()
Returns:
AL -- last post-activation value
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_relu_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-2)
the cache of linear_sigmoid_forward() (there is one, indexed L-1)
"""
caches = []
A = X
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)], activation = "relu")
caches.append(cache)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], activation = "sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(AL.shape == (1,X.shape[1]))
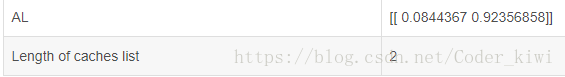
return AL, cachesX, parameters = L_model_forward_test_case()
AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
print("AL = " + str(AL))
print("Length of caches list = " + str(len(caches)))现在,您有一个完整的前向传播,它接受输入X并输出包含您的预测的行向量![]() 。 它还记录“caches”中的所有中间值。 使用
。 它还记录“caches”中的所有中间值。 使用![]() ,您可以计算预测的成本。
,您可以计算预测的成本。
5 - 成本函数
现在,您将实现向前和向后传播。 您需要计算成本,因为您要检查您的模型是否实际学习。
练习:使用以下公式计算交叉熵成本J:
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_cost
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
"""
Implement the cost function defined by equation (7).
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector corresponding to your label predictions, shape (1, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (for example: containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), shape (1, number of examples)
Returns:
cost -- cross-entropy cost
"""
m = Y.shape[1]
# Compute loss from aL and y.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 lines of code)
cost = -1./m * np.sum(Y * np.log(AL) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - AL))
### END CODE HERE ###
cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect (e.g. this turns [[17]] into 17).
assert(cost.shape == ())
return costY, AL = compute_cost_test_case()
print("cost = " + str(compute_cost(AL, Y)))6 - 后向传播模块
就像前向传播一样,您将实现反向传播的辅助函数。 请记住,反向传播用于计算损失函数相对于参数的梯度。
提醒:
现在,类似于前向传播,您将分三个步骤构建向后传播:
- 向后LINEAR。
- LINEAR - > ACTIVATION,ACTIVATION计算ReLU或S形激活的导数。
- [LINEAR - > RELU]×(L-1) - > LINEAR - > SIGMOID向后(整个模型)。
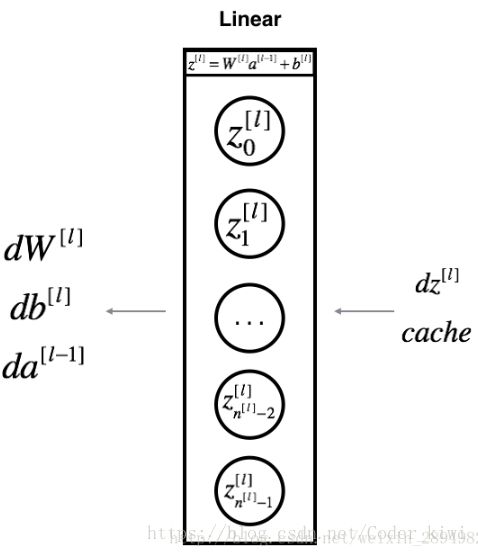
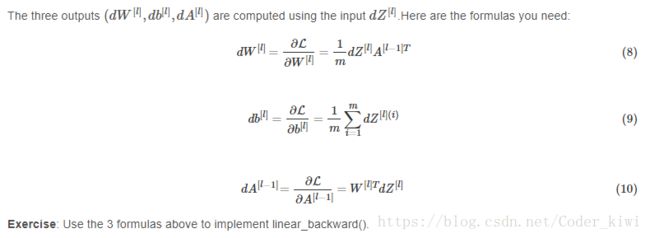
6.1 - 线性向后
对于层l,线性部分是:![]() (随后是激活)。
(随后是激活)。
# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_backward
def linear_backward(dZ, cache):
"""
Implement the linear portion of backward propagation for a single layer (layer l)
Arguments:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the linear output (of current layer l)
cache -- tuple of values (A_prev, W, b) coming from the forward propagation in the current layer
Returns:
dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev
dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W
db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b
"""
A_prev, W, b = cache
m = A_prev.shape[1]
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)
dW = 1./m * np.dot(dZ, A_prev.T)
db = 1./m * np.sum(dZ)
dA_prev = np.dot(W.T, dZ)
### END CODE HERE ###
assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)
assert (dW.shape == W.shape)
assert (isinstance(db, float))
return dA_prev, dW, db# Set up some test inputs
dZ, linear_cache = linear_backward_test_case()
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
print ("dA_prev = "+ str(dA_prev))
print ("dW = " + str(dW))
print ("db = " + str(db))6.2 - 向后线性激活
接下来,您将创建一个合并两个辅助函数的函数:linear_backward和激活linear_activation_backward的后退步骤。
# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_activation_backward
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient for current layer l
cache -- tuple of values (linear_cache, activation_cache) we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"
Returns:
dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev
dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W
db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b
"""
linear_cache, activation_cache = cache
if activation == "relu":
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
### END CODE HERE ###
elif activation == "sigmoid":
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
### END CODE HERE ###
return dA_prev, dW, dbAL, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_backward_test_case()
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_activation_backward(AL, linear_activation_cache, activation = "sigmoid")
print ("sigmoid:")
print ("dA_prev = "+ str(dA_prev))
print ("dW = " + str(dW))
print ("db = " + str(db) + "\n")
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_activation_backward(AL, linear_activation_cache, activation = "relu")
print ("relu:")
print ("dA_prev = "+ str(dA_prev))
print ("dW = " + str(dW))
print ("db = " + str(db))6.3 - L模型向后
现在,您将为整个网络实现向后功能。回想一下,当您实现L_model_forward函数时,在每次迭代时,您都存储了一个包含(X,W,b和z)的缓存。在反向传播模块中,您将使用这些变量来计算渐变。因此,在L_model_backward函数中,您将从层L开始向后遍历所有隐藏层。在每个步骤中,您将使用层l的缓存值通过层l反向传播。
# GRADED FUNCTION: L_model_backward
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID group
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector, output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward())
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat)
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_activation_forward() with "relu" (it's caches[l], for l in range(L-1) i.e l = 0...L-2)
the cache of linear_activation_forward() with "sigmoid" (it's caches[L-1])
Returns:
grads -- A dictionary with the gradients
grads["dA" + str(l)] = ...
grads["dW" + str(l)] = ...
grads["db" + str(l)] = ...
"""
grads = {}
L = len(caches) # the number of layers
m = AL.shape[1]
Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL
# Initializing the backpropagation
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code)
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
### END CODE HERE ###
# Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "AL, Y, caches". Outputs: "grads["dAL"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"]
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
current_cache = caches[L-1]
grads["dA" + str(L)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, activation = 'sigmoid')
### END CODE HERE ###
for l in reversed(range(L-1)):
# lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients.
# Inputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 2)], caches". Outputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] , grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] , grads["db" + str(l + 1)]
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 5 lines)
current_cache = caches[L - 2 - l]
dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(L)], current_cache, activation = 'relu')
grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] = dA_prev_temp
grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp
grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp
### END CODE HERE ###
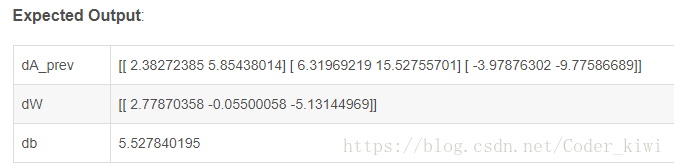
return gradsX_assess, Y_assess, AL, caches = L_model_backward_test_case()
grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y_assess, caches)
print ("dW1 = "+ str(grads["dW1"]))
print ("db1 = "+ str(grads["db1"]))
print ("dA1 = "+ str(grads["dA1"]))
6.4 - 更新参数
在本节中,您将使用渐变下降更新模型的参数:

其中α是学习率。 计算更新的参数后,将它们存储在参数字典中。
练习:使用渐变下降实现update_parameters()以更新参数。
# GRADED FUNCTION: update_parameters
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
"""
Update parameters using gradient descent
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients, output of L_model_backward
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
parameters["W" + str(l)] = ...
parameters["b" + str(l)] = ...
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)
for l in range(L):
parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l+1)]
parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l+1)]
### END CODE HERE ###
return parametersparameters, grads = update_parameters_test_case()
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, 0.1)
print ("W1 = "+ str(parameters["W1"]))
print ("b1 = "+ str(parameters["b1"]))
print ("W2 = "+ str(parameters["W2"]))
print ("b2 = "+ str(parameters["b2"]))
print ("W3 = "+ str(parameters["W3"]))
print ("b3 = "+ str(parameters["b3"]))