x-pack 介绍
elk 的系统组件 x-pack 一个集安全、警报、监视、报告和图形功能于身的扩展,轻松开启或关闭那你想要的功能。
效果图
1.监控概览

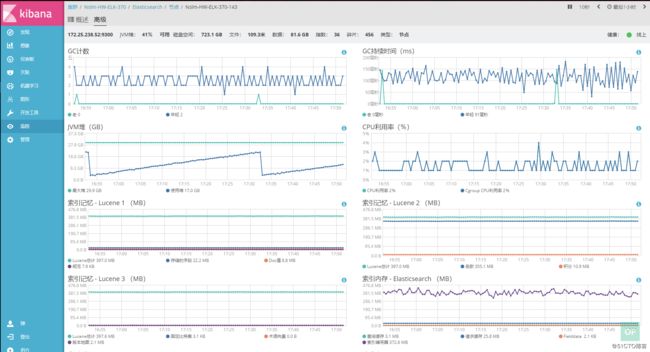
2.elasticserch监控图
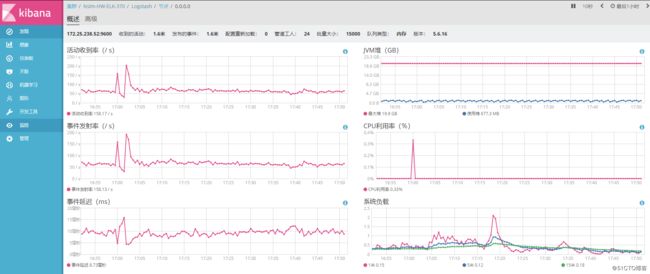
3.logstash监控图
1.配置介绍
Centos 6.4
logstash-5.6.4-1.noarch
elasticsearch-5.6.4-1.noarch
kibana-5.6.4-1.x86_64
2.yum源配置
1. 安装key
rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
2.添加/etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo
[elastic-5.x]
name=Elastic repository for 5.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/5.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md
3.安装logstash
1. yum install logstash-5.6.4-1.noarch
2. 目录介绍
logstash 跟目录 /usr/share/logstash/
配置文件目录在 /etc/logstash/
数据目录 /var/lib/logstash/
3. 安装logstash的x-pack扩展
cd /usr/share/logstash/bin/ && ./logstash-plugin install x-pack
4.修改配置文件/etc/logstash/logstash.yml
pipeline.batch.size: 5000 #在发送给过滤器+工作人员之前,从输入中检索多少事件
pipeline.batch.delay: 30 #不足125个时间批量发送等待时间,值以毫秒为单位
pipeline.workers: 24 #过滤器并行数量
pipeline.output.workers: 24 #输出程序的并行进程数量
path.config: /etc/logstash/conf.d #配置文件目录
http.host: "10.0.0.1" #监听地址
http.port: 9600 #监听端口
log.level: info #日志级别
path.logs: /var/log/logstash #日志目录
path.data: /var/lib/logstash #数据目录
#xpack.monitoring.enabled: false #是否关闭logstash x-pack监控
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.url: "http://10.16.26.31:9200" #监控数据写入地址
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: "logstash_system" #链接es的账户 此用户和密码是es安装x-pack之后默认生成
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: "changeme" #链接es的密码
5.如果logstahs的数据处理配置文件output是输入到es需要添加用户名密码,密码需要在kibana dev创建
output {
if [type] =~ "reslog|itemlog" {
elasticsearch {
user => "logstash_internal"
password => "changeme"
id => "nslm3-%{[type]}"
hosts => ["10.0.0.1:9200"]
index => "logstash-nslm3-%{[type]}-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template => "/etc/logstash/template/index_template.json"
template_name => "nslm3"
#template_overwrite => true
}
}
#stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}
3.安装elasticsearch
1.yum install elasticsearch-5.6.4-1.noarch
2.目录介绍
elasticsearch 跟目录 /usr/share/elasticsearch/
配置文件目录在 /etc/elasticsearch/
数据目录 /var/lib/elasticsearch/
3.x-pack扩展安装
cd /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/ && ./elasticsearch-plugin install x-pack
过程中需要输入y确认
4.修改配置文件/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: Elk #集群名
node.name: Elk-31 #节点名
path.data: /data/elasticsearch/data #数据目录
path.logs: /data/elasticsearch/logs #日志目录
bootstrap.memory_lock: false #关闭内存所
bootstrap.system_call_filter: false
network.host: 10.0.0.1
http.port: 9200
#多线程配置
thread_pool.index.size: 24 #线程池大小(建议2~3倍cpu数)
thread_pool.index.queue_size: 10000 #队列大小
thread_pool.search.size: 36 #搜索线程池大小
thread_pool.search.queue_size: 10000 #队列大小
thread_pool.get.size: 24 #启动线程数
thread_pool.get.queue_size: 10000 #队列长度
thread_pool.bulk.size: 24 #启动线程数
thread_pool.bulk.queue_size: 10000 #队列长度
thread_pool.refresh.core: 1 #最小1
thread_pool.refresh.max: 12 #最大12 cpu的一半
thread_pool.refresh.keep_alive: 2m #2天不活跃的进城自动关闭
cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries: 12 #节点重新启动后未分配的主节点的恢复使用来自本地磁盘的数据。多进程
cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_incoming_recoveries: 12 #传入到这个节点的并发恢复分片数
cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_outgoing_recoveries: 12 #传出到其他节点的并发恢复分片出
cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_recoveries: 12 #同时recovery并发数
indices.memory.index_buffer_size: 20% #每个index提供的缓冲大小
#集群配置
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.16.26.35", "10.16.26.34","10.16.26.31"] #自动发现节点
discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 120s
discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 6
discovery.zen.fd.ping_interval: 20s
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
gateway.recover_after_nodes: 2
3.安装kibana
1. yum install kibana-5.6.4-1.x86_64
2. 目录介绍
kibana 跟目录 /usr/share/kibana/
配置文件目录在 /etc/kibana/
数据目录 /var/lib/kibana/
3.x-pack扩展
cd /usr/share/kibana/bin/ && ./kibana-plugin install x-pack
4.修改配置文件/etc/kibana/kibana.yml
server.port: 5601 #监听端口
server.host: "10.0.0.1" #监听地址
server.name: "kibana-1" #节点名
elasticsearch.url: "http://10.0.0.1:9200" #读取es的东周
i18n.defaultLocale: "ch"
elasticsearch.username: "elastic" #连接es的用户 此用户和密码是es安装x-pack之后默认生成
elasticsearch.password: "changeme" #连接es的密码
#geoip地图地址库连接
tilemap.url: "http://webrd02.is.autonavi.com/appmaptile?lang=zh_cn&size=1&scale=1&style=7&x={x}&y={y}&z={z}"
tilemap.options.minZoom: "1"
tilemap.options.maxZoom: "10"
tilemap.options.attribution: "? [Elastic Maps Service](https://www.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service)"
4.重启es kibana
/etc/init.d/elasticsearch stop && /etc/init.d/elasticsearch start
/etc/init.d/kibana restart
5.登陆kibana
1.web登陆http://10.0.0.1:5601
2.输入默认账号密码elastic changeme

3.选择 Dev Tools
4.创建角色 logstash
#创建logstash role权限
POST _xpack/security/role/logstash_writer
{
"cluster": ["manage_index_templates", "monitor"],
"indices": [{
"names": [ "logstash-*","business-index-*"],
"privileges": ["write","delete","create_index"]
}]
}
#创建logstash_用户
POST /_xpack/security/user/logstash_internal
{
"password" : "changeme",
"roles" : [ "logstash_writer"],
"full_name" : "Internal Logstash User"
}
5.启动logstash
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash "--path.settings" "/etc/logstash"
6.观察日志/var/log/logstash/logstash-plain.log


