使用gperftools对程序进行性能分析
gperftools是google出品的一个性能分析工具,相关介绍可见:
https://github.com/gperftools/gperftools/wiki
gperftools性能分析通过抽样方法完成,默认是1秒100个样本,即一个样本是10毫秒,因此程序运行时间要长一些。
1、安装gperftools
1.1、安装automake
sudo apt-get install automake
1.2、编译安装libunwind
从https://github.com/libunwind/libunwind/releases下载最新版本的libunwind源码包
解压到/usr/local/src目录
cd 解压源码目录
./autogen.sh
./configure
make -j6
make install
1.3、编译安装gperftools
从https://github.com/gperftools/gperftools/releases下载最新版本的gperftools源码包
解压到/usr/local/src目录
cd 解压源码目录
./autogen.sh
./configure
make -j6
make install
1.4、安装图像分析生成工具
sudo apt-get install graphviz
2、使用
2.1、运行一段时间就会正常退出的程序的性能分析
这种情况,我们可以直接在代码中插入性能分析函数。示例代码如下:
#include
#include
void f()
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<1024*1024; ++i)
{
char *p = (char*)malloc(1024*1024*120);
free(p);
}
}
int main()
{
ProfilerStart("test.prof");//开启性能分析
f();
ProfilerStop();//停止性能分析
return 0;
}
编译运行,注意编译时需要连接tcmalloc和profiler库。运行后会生成test.prof文件,然后用pprof就可以生成text的分析报告,具体如下:
root@ubuntu:/home/zte/test/perf# gcc not_run_alway.c -ltcmalloc -lprofiler
root@ubuntu:/home/zte/test/perf# ./a.out
PROFILE: interrupts/evictions/bytes = 14/0/776
root@ubuntu:/home/zte/test/perf# pprof --text a.out test.prof
Using local file a.out.
Using local file test.prof.
Total: 14 samples
3 21.4% 21.4% 3 21.4% SpinLock::Unlock (inline)
3 21.4% 42.9% 3 21.4% __GI_madvise
2 14.3% 57.1% 2 14.3% SpinLock::Lock (inline)
1 7.1% 64.3% 1 7.1% TCMalloc_PageMap2::get (inline)
1 7.1% 71.4% 4 28.6% do_malloc_pages
1 7.1% 78.6% 2 14.3% tcmalloc::PageHeap::Delete
1 7.1% 85.7% 2 14.3% tcmalloc::PageHeap::New
1 7.1% 92.9% 4 28.6% tcmalloc::PageHeap::ReleaseAtLeastNPages
1 7.1% 100.0% 1 7.1% tcmalloc::PageHeap::RemoveFromFreeList
0 0.0% 100.0% 2 14.3% SpinLockHolder (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 21.4% TCMalloc_SystemRelease
0 0.0% 100.0% 14 100.0% __libc_start_main
0 0.0% 100.0% 14 100.0% _start
0 0.0% 100.0% 4 28.6% do_allocate_full (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 10 71.4% do_free_pages
0 0.0% 100.0% 4 28.6% do_malloc (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 14 100.0% f
0 0.0% 100.0% 14 100.0% main
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 7.1% tcmalloc::PageHeap::Carve
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 21.4% tcmalloc::PageHeap::DecommitSpan
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 7.1% tcmalloc::PageHeap::GetDescriptor (inline)
0 0.0% 100.0% 4 28.6% tcmalloc::PageHeap::IncrementalScavenge
0 0.0% 100.0% 1 7.1% tcmalloc::PageHeap::MergeIntoFreeList
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 21.4% tcmalloc::PageHeap::ReleaseLastNormalSpan
0 0.0% 100.0% 4 28.6% tcmalloc::allocate_full_malloc_oom
0 0.0% 100.0% 3 21.4% ~SpinLockHolder (inline)输出数据解析:
每行包含6列数据,依次为:
1 分析样本数量(不包含其他函数调用)
2 分析样本百分比(不包含其他函数调用)
3 目前为止的分析样本百分比(不包含其他函数调用)
4 分析样本数量(包含其他函数调用)
5 分析样本百分比(包含其他函数调用)
6 函数名
样本数量相当于消耗的CPU时间。
整个函数消耗的CPU时间相当于包括函数内部其他函数调用所消耗的CPU时间
运行命令生成函数调用树形式的pdf分析报告:
pprof --pdf a.out test.prof >test.pdf 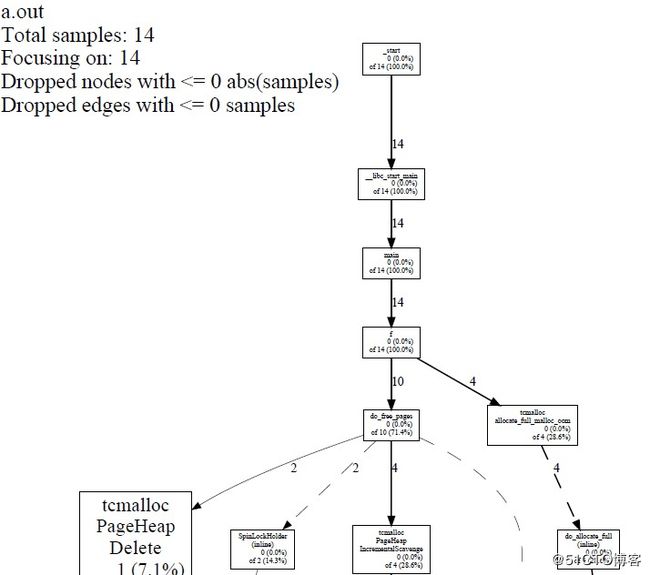
树上的每个节点代表一个函数,节点数据格式:
1、函数名 或者 类名+方法名
2、不包含内部函数调用的样本数 (百分比)
3、of 包含内部函数调用的样本数 (百分比) #如果没有内部调用函数则这一项数据不显示
2.2 一直运行的程序的性能分析
一直运行的程序由于不能正常退出,所以不能采用上面的方法。我们可以用信号量来开启/关闭性能分析,具体代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
void gprofStartAndStop(int signum) {
static int isStarted = 0;
if (signum != SIGUSR1) return;
//通过isStarted标记未来控制第一次收到信号量开启性能分析,第二次收到关闭性能分析。
if (!isStarted){
isStarted = 1;
ProfilerStart("test.prof");
printf("ProfilerStart success\n");
}else{
ProfilerStop();
printf("ProfilerStop success\n");
}
}
void f()
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<1024*1024; ++i)
{
char *p = (char*)malloc(1024*1024);
free(p);
}
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGUSR1, gprofStartAndStop);
while(1){
printf("call f\n");
f();
sleep(1);//为了防止死循环,导致信号处理函数得不到调度
}
return 0;
} 编译运行如下:
root@ubuntu:/home/zte/test/perf# gcc run_always.c -ltcmalloc -lprofiler
root@ubuntu:/home/zte/test/perf# ./a.out 通过kill命令发送信号给进程来开启/关闭性能分析:
用top命令查看进程的PID
kill -s SIGUSR1 PID //第一次运行命令启动性能分析
kill -s SIGUSR1 PID //再次运行命令关闭性能分析,产生test.prof
后续分析报告生成同2.1,不再赘述。