Time 类在 Ruby 中用于表示日期和时间。它是基于操作系统提供的系统日期和时间之上。该类可能无法表示 1970 年之前或者 2038 年之后的日期。
本教程将让您熟悉日期和时间的所有重要的概念。
创建当前的日期和时间
下面是获取当前的日期和时间的简单实例:
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w time1 = Time.new puts "Current Time : " + time1.inspect # Time.now 是一个同义词 time2 = Time.now puts "Current Time : " + time2.inspect
这将产生以下结果:
Current Time : Mon Jun 02 12:02:39 -0700 2008 Current Time : Mon Jun 02 12:02:39 -0700 2008
获取 Date & Time 组件
我们可以使用 Time 对象来获取各种日期和时间的组件。请看下面的实例:
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w time = Time.new # Time 的组件 puts "Current Time : " + time.inspect puts time.year # => 日期的年份 puts time.month # => 日期的月份(1 到 12) puts time.day # => 一个月中的第几天(1 到 31) puts time.wday # => 一周中的星期几(0 是星期日) puts time.yday # => 365:一年中的第几天 puts time.hour # => 23:24 小时制 puts time.min # => 59 puts time.sec # => 59 puts time.usec # => 999999:微秒 puts time.zone # => "UTC":时区名称
这将产生以下结果:
Current Time : Mon Jun 02 12:03:08 -0700 2008 2008 6 2 1 154 12 3 8 247476 UTC
Time.utc、Time.gm 和 Time.local 函数
这些函数可用于格式化标准格式的日期,如下所示:
# July 8, 2008 Time.local(2008, 7, 8) # July 8, 2008, 09:10am,本地时间 Time.local(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10) # July 8, 2008, 09:10 UTC Time.utc(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10) # July 8, 2008, 09:10:11 GMT (与 UTC 相同) Time.gm(2008, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11)
下面的实例在数组中获取所有的组件:
[sec,min,hour,day,month,year,wday,yday,isdst,zone]
尝试下面的实例:
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w time = Time.new values = time.to_a p values
这将产生以下结果:
[26, 10, 12, 2, 6, 2008, 1, 154, false, "MST"]
该数组可被传到 Time.utc 或 Time.local 函数来获取日期的不同格式,如下所示:
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w time = Time.new values = time.to_a puts Time.utc(*values)
这将产生以下结果:
Mon Jun 02 12:15:36 UTC 2008
下面是获取时间的方式,从纪元以来的秒数(平台相关):
# 返回从纪元以来的秒数 time = Time.now.to_i # 把秒数转换为 Time 对象 Time.at(time) # 返回从纪元以来的秒数,包含微妙 time = Time.now.to_f
时区和夏令时
您可以使用 Time 对象来获取与时区和夏令时有关的所有信息,如下所示:
time = Time.new # 这里是解释 time.zone # => "UTC":返回时区 time.utc_offset # => 0:UTC 是相对于 UTC 的 0 秒偏移 time.zone # => "PST"(或其他时区) time.isdst # => false:如果 UTC 没有 DST(夏令时) time.utc? # => true:如果在 UTC 时区 time.localtime # 转换为本地时区 time.gmtime # 转换回 UTC time.getlocal # 返回本地区中的一个新的 Time 对象 time.getutc # 返回 UTC 中的一个新的 Time 对象
格式化时间和日期
有多种方式格式化日期和时间。下面的实例演示了其中一部分:
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w
time = Time.new
puts time.to_s
puts time.ctime
puts time.localtime
puts time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
这将产生以下结果:
Mon Jun 02 12:35:19 -0700 2008 Mon Jun 2 12:35:19 2008 Mon Jun 02 12:35:19 -0700 2008 2008-06-02 12:35:19
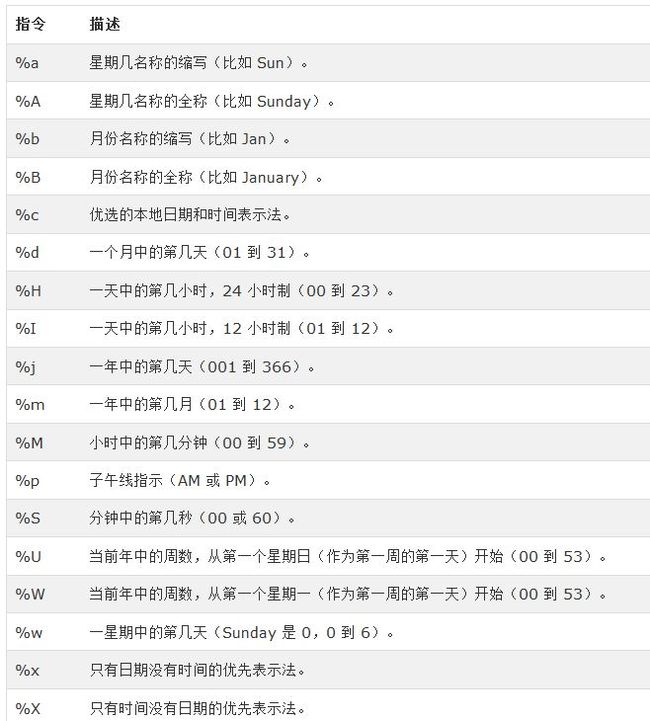
时间格式化指令
下表所列出的指令与方法 Time.strftime 一起使用。
时间算法
您可以用时间做一些简单的算术,如下所示:
now = Time.now # 当前时间 puts now past = now - 10 # 10 秒之前。Time - number => Time puts past future = now + 10 # 从现在开始 10 秒之后。Time + number => Time puts future diff = future - now # => 10 Time - Time => 秒数 puts diff
这将产生以下结果:
Thu Aug 01 20:57:05 -0700 2013 Thu Aug 01 20:56:55 -0700 2013 Thu Aug 01 20:57:15 -0700 2013 10.0