Thymeleaf
1.理解:
(1)Thymeleaf是一款Java模板引擎,类似于JSP,Freemarker,能够处理html,xml,javaScript,Css甚至纯文本;
(2)自然模板,原型即页面
(3)语法优雅易懂,OGNL,SpringEL
(4)使用web标准,支持HTML5
2.Thymeleaf标准方言
(1)识别:
(2)方言内容:
(3)语法:
变量表达式:${........},用于存储变量,例name![]()
消息表达式:#{.......},也被称之为文本外部化,国际化后i18n,例city相当于key
选择表达式:*{........},与变量表达式的区别:他们是在当前选择的对象而不是整个上下文变量映射上执行
链接表达式:@{........},链接表达式可以是相对的,在这种情况下,应用程序上下文将不会作为URL的前缀,![]()
也可以是服务器相对(同样,没有应用程序上下文前缀),![]()
和协议相对(就像绝对URL,但浏览器使用在显示的页面中使用的相同的HTTP和Https协议),![]()
当然,Link表达式可以是绝对的,![]()
分段表达式:th:insert或th:replace
(4)字面量(文字):
文本:
数字(可以执行计算等):![]()
布尔:![]()
Null:![]()
算术操作:+,-,*,/,%(加减乘除取余)![]()
比较:<,>,<=,>=(lt,gt,le,ge)![]()
等价:==,!=(eq,ne)![]()
条件运算符:
无操作:_![]()
(5)设置属性值:
设置任意属性值:th:attr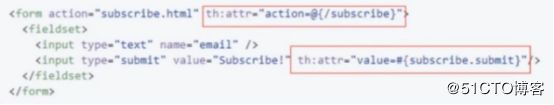
设置值到指定的属性:
固定值布尔属性:
(6)迭代器:
基本迭代器:th:each![]()
状态变量:index,count,size,current,even/odd,first/last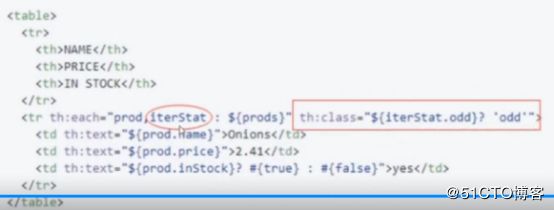
(7)条件语句:
th:if,th:unless

Switch:
3.Thymeleaf与Spring boot集成
(1)模板布局(我们在开发中可以看到页面中有许多的公用片段)
方式一:定义和引用片段:th:insert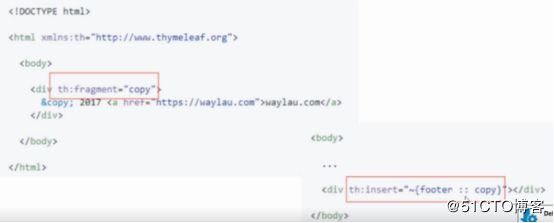
方式二:不使用th:fragment
th:insert,th:replace,th:include三者的区别
●th:insert它将简单的插入指定的片段作为正文的主标签
●th:replace用指定实际片段来替换其他主标签
●th:include类似于insert,不常用,了解即可
(2)属性优先级
(3)注释:
解析器级别注释(解析快中内容执行时会被删除)
(4)内联表达式:
[[.....]]或[(.....)]分别对应于th;text和th:utext![]()
![]()
禁用内联:
有时需要禁用这种机制,比如,想输出[[.......]]或[(...)]文本内容![]()
javaScript内联与Css均可以进行内联
(5)表达式的基本对象
基本对象:
#ctx:上下文对象
#locale:直接访问java.util.Locale相关联的当前的请求
Request/session等属性
Param:用于检索请求参数
Session:用于检索Session属性
Application:用于检索Application/servlet上下文属性
Web上下文对象:#Request,#Session,#ServletContext
(6)Thymeleaf与Spring boot集成
我们建立第一个Spring boot+Thymeleaf+mevan项目,测试项目是否正常运行:
项目创建成功后,我们导入IDE中,打开项目,我们编写一个helloController,项目结构如下:
测试项目是否能正常运行,我们添加Controller,让它输出一个字符串,代码如下:
package com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.web;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class helloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(HttpServletRequest request) {
String say="START TEST THYMELEAF,SAY HELLO WORD!!";
System.out.println("say: "+say);
return say;
}
}
接下来启动的项目,项目正常启动后,我们在浏览器,访问页面地址,观察结果,: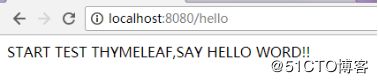
由此可以看出我们的项目正常运行,可以进入下一步的开发
4.实战Spring boot+thymeleaf,我们来实现一个简单的用户管理
(1)修改application.properties配置文件
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
#热部署静态文件,不需要缓存,实时观察文件修改效果
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
#使用html5标准
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5(2)API设计:
·GET /users:返回用于展示用户列表的list.html页面
·GET /users/{id}:返回用于展示用户的view.html页面,根据id获取的
·GET /users/form:返回用于新增或者修改用户的form.html页面
·POST /users:新增或者修改用户,成功后重定向到list.html页面
·GET /users/delete/{id}:根据id删除相应的用户,成功后重定向到list.html页面
·GET /users/modify/{id}:根据id获取相应的用户数据,并返回form页面来进行修改
(3)后台编码:
首先展示项目后台结构:
User实体(主要代码):
package com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.entity;
/**
* user实体
*
* @author QT
*/
public class User {
private Long id; // 用户的唯一标识
private String name; // 用户名
private String email; // 用户邮箱
public User() {
super();
}
public User(Long id, String name, String email) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
定义资源库(interface UserRepository)包含方法如下:
package com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.repository;
/**
* User Repository接口
* @author QT
*
*/
import java.util.List;
import com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.entity.User;
public interface UserRepository {
/**
* 修改或增加用户
*
* @param user
* @return
*/
public User saveOrUpdateUser(User user);
/**
* 根据Id删除用户
*
* @param id
*/
public void deleteUser(Long id);
/**
* 根据Id查询用户
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public User getUserById(Long id);
/**
* 获取用户列表
*
* @return
*/
public List listUser();
}
实现资源库,即实现增删改查的操作
package com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.repository.impl;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.entity.User;
import com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.repository.UserRepository;
@Repository
public class UserRepositoryImpl implements UserRepository {
// 用于计数的计数器,为了设置唯一Id
private static AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
private final ConcurrentMap userMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
@Override
public User saveOrUpdateUser(User user) {
Long id = user.getId();
if (id == null) { // 新增用户
id = counter.incrementAndGet();
user.setId(id);
}
this.userMap.put(id, user);
return user;
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
this.userMap.remove(id);
}
@Override
public User getUserById(Long id) {
return this.userMap.get(id);
}
@Override
public List listUser() {
return new ArrayList( this.userMap.values());
}
}
接下来编写Controller层,实现与前台的数据交互
package com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.web;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.entity.User;
import com.dhtt.spring.boot.blog.thymeleaf.action.repository.UserRepository;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class userController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
/**
* 查询所有用户
*
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping
public ModelAndView list(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("userList", userRepository.listUser());
model.addAttribute("title", "用户管理");
return new ModelAndView("users/list", "userModel", model);
}
/**
* 根据Id查询用户
*
* @param id
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("{id}")
public ModelAndView view(@PathVariable("id") Long id, Model model) {
User user = userRepository.getUserById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
model.addAttribute("title", "用户查询");
return new ModelAndView("users/view", "userModel", model);
}
/**
* 创建用户
*
* @param id
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/form")
public ModelAndView createForm(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User());
model.addAttribute("title", "创建用户");
return new ModelAndView("users/form", "userModel", model);
}
/**
* 新增或修改用户
*
* @param user
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
public ModelAndView saveOrUpdateUser(User user) {
user = userRepository.saveOrUpdateUser(user);
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/users", "userModel", user);
}
/**
* 获取删除用户
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public ModelAndView deleteUser(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
userRepository.deleteUser(id);
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/users"); // 重定向到list页面
}
/**
* 获取修改用户界面
*
* @param id
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/modify/{id}")
public ModelAndView modify(@PathVariable("id") Long id, Model model) {
User user = userRepository.getUserById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
model.addAttribute("title", "修改用户");
return new ModelAndView("users/form", "userModel", model);
}
}
后台写完以后,我们对前台进行编写:
(4)前台编码:
首先编写页面的头和尾,即为公共的html
展示前台项目结构:
公共代码片段—header.html:
Thymeleaf 用户管理
Thymeleaf in action
首页
公共代码片段—footer.html:
Thymeleaf 用户管理
公共页面编写完毕,进行功能页面编写:
功能页面—list.html
Thymeleaf 用户管理
ID
Email
Name
没有用户信息!!
功能页面—form.html
Thymeleaf 用户管理
功能页面—view.html
Thymeleaf 用户管理
ID:
NAME:
EMAIL:
我们启动项目进行功能测试,截图展示: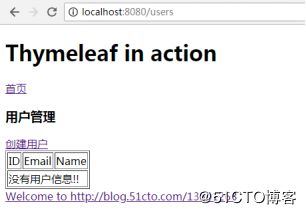
点击创建用户:
点击提交,添加成功重定向到list.html页面:
点击名称,展示详细信息: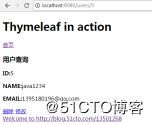
点击修改,跳转到form.html页面,并填写修改信息:
点击提交重定向到list.html,页面,可以发现信息已经修改成功: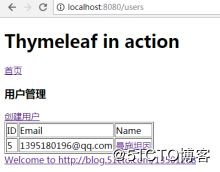
接下来查看详细信息
点击删除,重定向到list.html页面:
观察结果,我们发现数据信息删除成功,项目展示完毕,thymeleaf+spring+mevan学习完毕