Javascript在客户端对于unicode编码的数据操作支持非常友好,但是对二进制数据的处理就不尽人意。Node.js为了能够处理二进制数据或非unicode编码的数据,便设计了Buffer类,该类实现了Uint8Array接口,并对其进行了优化,它的实例类似于整型数组,但是它的大小在创建后便不可调整。在介绍Buffer如何使用之前,先介绍几个知识点。
1、V8引擎的内存使用限制
V8引擎最大堆内存使用在32位系统上默认为512M,在64位系统上是1GB,虽然可以使用--max-old-space-size参数调整该值,但还是建议要用到大内存的时候使用Buffer或Stream,因为Buffer的内存分配不在V8的堆上。
2、单个Buffer实例大小限制
单个Buffer实例的大小最大数值为1GB-1(32位系统)或2GB-1(64位系统),所以在创建Buffer实例的时候不能超过该值,或者使用readFile()方法读取大文件,否则将抛出RangeError错误。
3、8KB池
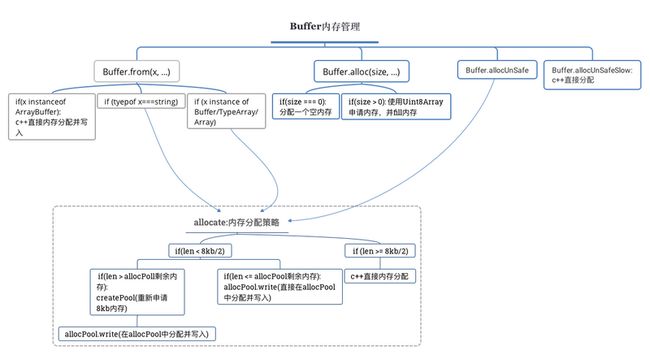
Nodejs在创建Buffer实例的时候,当用户申请的空间大于8KB,会直接调用内部的createUnsafeBuffer()方法创建一个Buffer,如果申请的空间大于0且小于4KB,新的Buffer则会建立在当前的8kb SLAB上,并更新剩余空间,如下图所示:
下面介绍Buffer API的简单使用:
1、创建Buffer实例
使用Buffer.from(), Buffer.alloc(), Buffer.allocUnsafe()等方法来创建一个Buffer实例,6.0版本以前直接使用构造函数创建的方法new Buffer()已被丢弃,不推荐使用,因为有可能会造成内存泄漏。
方法Buffer.alloc(size[, fill[, encoding]]),参数含义如下:
- size,指定buffer的长度,但不能超过buffer.kMaxLength,若不是数字则报错
- fill,指定初始化buffer的值,默认为0
- encoding,如果fill是字符串,则该参数指定fill的编码
使用如下所示:
const buf1 = Buffer.alloc(10); console.log(buf1);//const buf2 = Buffer.alloc(10,'hello'); console.log(buf2);// const buf3 = Buffer.alloc(10,'hello','base64'); console.log(buf3);//
方法Buffer.allocUnsafe(size),size参数指定buffer的大小,该方法返回一个没有初始化的buffer,因此可能还保留有敏感的数据,造成信息的泄漏,建议使用buffer.fill(0)函数初始化buffer,该方法与Buffer.alloc(size, fill)是不一样的,有可能使用8KB池。使用如下所示:
const buf4 = Buffer.allocUnsafe(10); console.log(buf4);//,可以看出是有数据的 buf4.fill(0); console.log(buf4);//
方法Buffer.allocUnsafeSlow(size),参数含义同上,该方法不会使用Buffer池,容易造成内存的浪费,使用如下所示:
const buf5 = Buffer.allocUnsafeSlow(10); console.log(buf5);//
方法Buffer.from(value,[...]),这里分为四种情况,如下所示:
第一,value为16进制数组,将数组转化为buffer,如果不是16进制,则会进行转换,如下:
const buf6 = Buffer.from([1,2,3,5,17]); console.log(buf6);//
第二,value为字符串,则转换字符串为buffer,该方法会使用buffer池,如下:
const buf7 = Buffer.from('hello world!');
console.log(buf7);//
第三,value为buffer实例,则将value拷贝至新的buffer中,这里只是值的拷贝,不会共享内存,如下:
const buf8 = Buffer.from('hello world');
const buf9 = Buffer.from(buf8);
console.log(buf8);//
console.log(buf9);//
buf9[0] = 0x66;
console.log(buf8);//
console.log(buf9);//
第四,value为arrayBuffer时,还有两个可选参数[, byteOffset[, length]],byteOffset指定从arrayBuffer开始复制的位置,length复制的长度。如下:
const arr = new Uint8Array(2); arr[0] = 128; arr[1] = 200; const buf10 = Buffer.from(arr,0,2); console.log(buf10);//
如果引用的是arr.buffer,则新创建的buffer buf10与arr共享内存,如下:
const arr = new Uint8Array(2); arr[0] = 128; arr[1] = 200; const buf10 = Buffer.from(arr.buffer); arr[0] = 254; console.log(buf10);//
2、buffer解码
使用buf.toString([encoding[, start[, end]]])方法将buffer转换成字符串,encoding指定字符编码,默认为'utf8',start开始位置,end结束位置(不包括),目前encoding只支持'ascii,utf8,utf16le,ucs2,base64,latin1,binary,hex',使用如下所示:
const buf12 = Buffer.from('我爱中国');
console.log(buf12.toString('base64'));//5oiR54ix5Lit5Zu9
console.log(buf12.toString('utf8'));//我爱中国
console.log(buf12.toString('hex'));//e68891e788b1e4b8ade59bbd
3、buffer拼接、复制、填充、分割
方法buf.fill(value[, offset[, end]][, encoding])使用指定的值填充buffer,参数offset指定填充的起始位置,end为结束位置,使用如下所示:
console.log(Buffer.allocUnsafe(5).fill('a').toString());//aaaaa
console.log(Buffer.allocUnsafe(5).fill(65).toString('utf8'));//AAAAA
方法Buffer.concat(list[, totalLength])将多个buffer合并在一起,并返回一个新的buffer实例,参数totalLength为指定的buffers的长度总和,如果不提供该值,函数内部会循环去获取每一个buffer的长度,然后进行拼接,因此为了速度,最好指定一个总长度,使用如下:
function bufferInjoin(buffArr){
var len = 0;
buffArr.forEach((buff,idx,arr)=>{
len+=buff.length;
});
var buffer = Buffer.concat(buffArr,len);
return buffer;
}
var buff = bufferInjoin([Buffer.from('hehe'),Buffer.allocUnsafe(5).fill('a')]);
console.log(buff);//
console.log(buff.length);//9
console.log(buff.toString());//heheaaaaa
方法buf.copy(target[, targetStart[, sourceStart[, sourceEnd]]])可以实现buf到target的复制,参数含义如下:
- target,复制目标
- targetStart,复制目标开始被覆盖的位置
- sourceStart,复制源开始复制的位置
- sourceEnd,复制源复制结束的位置
使用如下所示:
const buf1 = Buffer.from('hello world!');
const buf2 = Buffer.allocUnsafe(5).fill('x');
buf1.copy(buf2,0,0,5);
console.log(buf2.toString());//hello
方法buf.slice([start[, end]])可以分割buffer,返回一个新的buffer,但是仍然是引用原buffer,因此改变原buffer数据,该新buffer也会跟着改变,如果参数start,end为负数,则先要加上buffer的长度再进行计算,如下所示:
const buf1 = Buffer.from('hello world.');
const buf2 = buf1.slice(0);
console.log(buf2);//
buf2[0] = 88;
console.log(buf1);//
const buf3 = buf1.slice(-6,-1);
console.log(buf3.toString());//world
3、buffer读写
buffer写操作通过write开头的写api来完成,主要有以下这些:
- buf.write(string[, offset[, length]][, encoding]),向buffer写入字符串
- buf.writeDoubleBE(value, offset[, noAssert])写入64位浮点型数字,大端对齐
- buf.writeDoubleLE(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入64位浮点型数字,小端对齐
- buf.writeFloatBE(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入32位浮点型数字,大端对齐
- buf.writeFloatLE(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入32位浮点型数字,小端对齐
- buf.writeInt8(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入有符号8位整型数字
- buf.writeInt16BE(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入有符号16位整型数字,大端对齐
- buf.writeInt16LE(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入有符号16位整型数字,小端对齐
- buf.writeInt32BE(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入有符号32位整型数字,大端对齐
- buf.writeInt32LE(value, offset[, noAssert]),写入有符号32位整型数字,小端对齐
- buf.writeIntBE(value, offset, byteLength[, noAssert]),以下便不再累述
- buf.writeIntLE(value, offset, byteLength[, noAssert])
- buf.writeUInt8(value, offset[, noAssert])
- buf.writeUInt16BE(value, offset[, noAssert])
- buf.writeUInt16LE(value, offset[, noAssert])
- buf.writeUInt32BE(value, offset[, noAssert])
- buf.writeUInt32LE(value, offset[, noAssert])
- buf.writeUIntBE(value, offset, byteLength[, noAssert])
- buf.writeUIntLE(value, offset, byteLength[, noAssert])
buffer读操作由read开头的api完成,主要有以下这些:
- buf.readDoubleBE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readDoubleLE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readFloatBE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readFloatLE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readInt8(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readInt16BE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readInt16LE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readInt32BE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readInt32LE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readIntBE(offset, byteLength[, noAssert])
- buf.readIntLE(offset, byteLength[, noAssert])
- buf.readUInt8(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readUInt16BE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readUInt16LE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readUInt32BE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readUInt32LE(offset[, noAssert])
- buf.readUIntBE(offset, byteLength[, noAssert])
- buf.readUIntLE(offset, byteLength[, noAssert])
使用如下所示,以32无符号整型为例:
const buf = Buffer.allocUnsafe(8); buf.writeUInt32BE(0x12345678,0) console.log(buf); const data = buf.readUInt32BE(0); console.log(data.toString(16));
最后利用buffer读API完成一个获取PNG格式图片尺寸的小工具,在开始编码之前,先简单介绍下PNG文件组成,如下所示:
| PNG文件标志 | PNG数据块 | …… | PNG数据块 |
|---|
这里我们只要用到PNG文件标识和PNG数据块的第一个块IHDR文件头数据块。文件标识是固定的8个字节,为89 50 4E 47 0D 0A 1A 0A,IHDR数据块的长度为13个字节,格式如下:
| 域的名称 | 字节数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Width | 4 bytes | 宽度 |
| Height | 4 bytes | 高度 |
| Bit depth | 1 bytes | 图像深度 |
| ColorType | 1 bytes | 颜色类型 |
| Compression method | 1 bytes | 压缩方法 |
| Filter method | 1 bytes | 滤波器方法 |
| Interlace method | 1 bytes | 隔行扫描方法 |
开始编码,如下所示:
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const argvs = process.argv.slice(2);
if(argvs.length<=0){
console.error('请输入图片:png.js img1 img2 ...');
process.exit(-1);
}
argvs.forEach((img,idx,arr)=>{
var stat = fs.statSync(img);
fs.open(img,'r',(err,fd)=>{
if(err) throw err;
var buff = Buffer.alloc(stat.size);
fs.read(fd,buff,0,stat.size,0,(err, bytesRead, buffer)=>{
if(err) throw err;
fs.close(fd,()=>{});
getImgDimension(buff,(err,dimension)=>{
if(err) throw err;
console.log(`${img}的尺寸为:${dimension.width}x${dimension.height}`);
});
});
});
});
function getImgDimension(buff,cb){
if((buff.toString('utf8',1,8) === 'PNG\r\n\x1a\n') && (buff.toString('utf8',12,16) === 'IHDR')){
return cb(null,{
width:buff.readUInt32BE(16),
height:buff.readUInt32BE(20)
}),!0;
}else{
return cb(new Error('不是PNG图片'),{}),!1;
}
}
执行结果如下:
E:\developmentdocument\nodejsdemo>node png.js 20160824083157.png 下载.png
20160824083157.png的尺寸为:195x195
下载.png的尺寸为:720x600
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。