Kafka源码深度解析-序列11 -Server核心组件之1-KafkaController选举过程/Failover与Resignation
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU3NjU3NjYxMA==&tempkey=MTAwMV9kVTZyRytrVFBhdE1GNEhjTXhqU3dYS3dhU0ZEM013eHNoT2RvX2pmRXBvclV3WGJQZjE3WlpoM3VfZUFpQU5lRFZCVWxyTTVKQ19JMHBIal8tUjdPNDYzRFdBdXRBSDlRMUFPLVIwVzJtdGVySzB5Vi1vRVdzbnZfZlBLZGlSRVFDVDVxRXVvXy05WVI0dEpmd2YtVGxOWmF3U05WRFlLTGNFSjN3fn4%3D&chksm=7d108f6e4a67067869dce1d62c221751eb923428893abede4f92c52c436519fa6afd262182fb#rd
在上1篇我们提到整个Kafka集群有一个“中央控制器“-Controller,这个Controller从所有brokers中选举出来,当Controller挂了之后,其它brokers再次竞选出新的Controller,本篇将详细介绍这个过程。
Kafka集群的几大核心组件
在正式进入源码分析之前,我们先看一下整个Kafka集群的几大核心组件。让我们从整个服务器的main函数开始:
//Kafka
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
try {
val serverProps = getPropsFromArgs(args)
val kafkaServerStartable = KafkaServerStartable.fromProps(serverProps)
// attach shutdown handler to catch control-c
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
override def run() = {
kafkaServerStartable.shutdown //注册一个JVM关闭的钩子
}
})
kafkaServerStartable.startup //启动程序
kafkaServerStartable.awaitShutdown
}
catch {
case e: Throwable =>
fatal(e)
System.exit(1)
}
System.exit(0)
}
//KafkaServerStartable
class KafkaServerStartable(val serverConfig: KafkaConfig) extends Logging {
private val server = new KafkaServer(serverConfig)
def startup() {
try {
server.startup()
}
catch {
case e: Throwable =>
fatal("Fatal error during KafkaServerStartable startup. Prepare to shutdown", e)
// KafkaServer already calls shutdown() internally, so this is purely for logging & the exit code
System.exit(1)
}
}
...
}
//KafkaServer
def startup() {
try {
info("starting")
if(isShuttingDown.get)
throw new IllegalStateException("Kafka server is still shutting down, cannot re-start!")
if(startupComplete.get)
return
val canStartup = isStartingUp.compareAndSet(false, true)
if (canStartup) {
metrics = new Metrics(metricConfig, reporters, kafkaMetricsTime, true)
brokerState.newState(Starting)
//核心组件0
kafkaScheduler.startup()
zkUtils = initZk()
logManager = createLogManager(zkUtils.zkClient, brokerState)
logManager.startup()
config.brokerId = getBrokerId
this.logIdent = "[Kafka Server " + config.brokerId + "], "
//核心组件1
socketServer = new SocketServer(config, metrics, kafkaMetricsTime)
socketServer.startup()
//核心组件2
replicaManager = new ReplicaManager(config, metrics, time, kafkaMetricsTime, zkUtils, kafkaScheduler, logManager,
isShuttingDown)
replicaManager.startup()
//核心组件3
kafkaController = new KafkaController(config, zkUtils, brokerState, kafkaMetricsTime, metrics, threadNamePrefix)
kafkaController.startup()
//核心组件4
consumerCoordinator = GroupCoordinator.create(config, zkUtils, replicaManager)
consumerCoordinator.startup()
/* Get the authorizer and initialize it if one is specified.*/
authorizer = Option(config.authorizerClassName).filter(_.nonEmpty).map { authorizerClassName =>
val authZ = CoreUtils.createObject[Authorizer](authorizerClassName)
authZ.configure(config.originals())
authZ
}
//核心组件5
apis = new KafkaApis(socketServer.requestChannel, replicaManager, consumerCoordinator,
kafkaController, zkUtils, config.brokerId, config, metadataCache, metrics, authorizer)
requestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.brokerId, socketServer.requestChannel, apis, config.numIoThreads)
brokerState.newState(RunningAsBroker)
Mx4jLoader.maybeLoad()
/* start dynamic config manager */
dynamicConfigHandlers = Map[String, ConfigHandler](ConfigType.Topic -> new TopicConfigHandler(logManager),
ConfigType.Client -> new ClientIdConfigHandler(apis.quotaManagers))
// Apply all existing client configs to the ClientIdConfigHandler to bootstrap the overrides
// TODO: Move this logic to DynamicConfigManager
AdminUtils.fetchAllEntityConfigs(zkUtils, ConfigType.Client).foreach {
case (clientId, properties) => dynamicConfigHandlers(ConfigType.Client).processConfigChanges(clientId, properties)
}
// Create the config manager. start listening to notifications
dynamicConfigManager = new DynamicConfigManager(zkUtils, dynamicConfigHandlers)
dynamicConfigManager.startup()
/* tell everyone we are alive */
val listeners = config.advertisedListeners.map {case(protocol, endpoint) =>
if (endpoint.port == 0)
(protocol, EndPoint(endpoint.host, socketServer.boundPort(protocol), endpoint.protocolType))
else
(protocol, endpoint)
}
kafkaHealthcheck = new KafkaHealthcheck(config.brokerId, listeners, zkUtils)
kafkaHealthcheck.startup()
/* register broker metrics */
registerStats()
shutdownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1)
startupComplete.set(true)
isStartingUp.set(false)
AppInfoParser.registerAppInfo(jmxPrefix, config.brokerId.toString)
info("started")
}
}
catch {
case e: Throwable =>
fatal("Fatal error during KafkaServer startup. Prepare to shutdown", e)
isStartingUp.set(false)
shutdown()
throw e
}
}
除了代码,我们也看一下服务器的启动/关闭的shell脚本:
bin/kafka-server-start.sh
通过 nohup 守护进程,具体脚本细节就不在此列出了。
//bin/kafak-server-stop.sh 可以看到,进程的关闭很简单,就是通过kill命令,发送SIGTERM信号。JVM收到信号,执行上面的钩子函数
ps ax | grep -i 'kafka\.Kafka' | grep java | grep -v grep | awk '{print $1}' | xargs kill -SIGTERM
通过看Server的启动函数,我们可以看到有以下几大核心组件:
1。SocketServer + KafkaApis 前者接收所有网络请求,后者处理请求
2。KafkaController 负责Controller选举
3。ConsumerCoordinator 前面在分析consumer的时候已经讲过,用于consumer group的负载均衡
4。ReplicaManager 机器的管理
5。KafkaSchedule
本篇着重分析KafkaController,其它核心组件,后面会一一讲述。
选举的基本原理
整个选举过程是通过zk上的一个临时节点来实现的:/controller节点,其data结构为:核心信息就是记录当前的controller的brokerId。
"version" -> 1, "brokerid" -> brokerId, "timestamp" -> timestamp
当controller挂了,其它所有broker监听到此临时节点消失,然后争相创建此临时节点,谁创建成功,谁就成为新的Controller。
除了/controller节点,还有一个辅助的/controller_epoch,记录当前Controller的轮值数。
KafkaController与ZookeeperLeaderElector
整个选举过程是通过这2个核心类实现的,其中ZookeeperLeaderElector是KafkaController的一个成员变量:
//KafkaController的一个成员变量
private val controllerElector = new ZookeeperLeaderElector(controllerContext, ZkUtils.ControllerPath, onControllerFailover,
onControllerResignation, config.brokerId)
下图展示了选举的整个交互过程:
(1)KafkaController和ZookeeperLeaderElector内部各有1个Listener,一个监听session重连,1个监听/controller节点变化。
(2)当session重连,或者/controller节点被删除,则调用elect()函数,发起重新选举。在重新选举之前,先判断自己是否旧的Controller,如果是,则先调用onResignation退位。
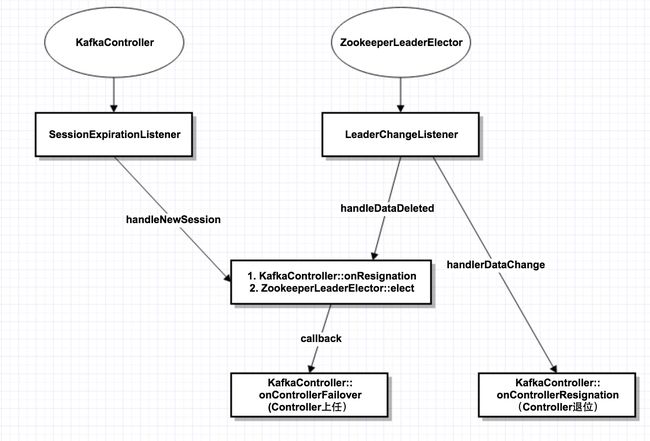
下面从KakfaController的startup函数看起:
def startup() = {
inLock(controllerContext.controllerLock) {
info("Controller starting up")
registerSessionExpirationListener() //第1种监听:SessionExpirationListener
isRunning = true
controllerElector.startup //第2种监听:LeaderChangeListener
info("Controller startup complete")
}
}
class SessionExpirationListener() extends IZkStateListener with Logging {
...
@throws(classOf[Exception])
def handleNewSession() {
info("ZK expired; shut down all controller components and try to re-elect")
inLock(controllerContext.controllerLock) {
onControllerResignation() //先退位
controllerElector.elect //发起重新选举
}
}
...
}
class LeaderChangeListener extends IZkDataListener with Logging {
@throws(classOf[Exception])
def handleDataChange(dataPath: String, data: Object) {
inLock(controllerContext.controllerLock) {
val amILeaderBeforeDataChange = amILeader
leaderId = KafkaController.parseControllerId(data.toString)
if (amILeaderBeforeDataChange && !amILeader)
onResigningAsLeader() //自己以前是controller,现在不是,退位
}
}
@throws(classOf[Exception])
def handleDataDeleted(dataPath: String) {
inLock(controllerContext.controllerLock) {
debug("%s leader change listener fired for path %s to handle data deleted: trying to elect as a leader"
.format(brokerId, dataPath))
if(amILeader)
onResigningAsLeader() //关键点:controller死了,有可能不是因为自己死了。而是和zookeeper的session断了。但是自己还在。此时,自己先退休,再重新发起选举。
elect //发起重现选举
}
}
}
2个关键回调:Failover(上任)与Resignation(退位)
在上面的选举过程中,存在2个关键的callback:也就是新Controller上任要做的事情和旧Controller退位要做的事情。
“上任“这个比较容易理解,也就是新的broker选举为controller;那为什么会有“退位“呢?
这是因为zk是用心跳来判断controller是否存活,可能controller存活,但zk认为它挂了,这个时候选举出了新的controller。那旧的controller发现自己是旧的,就得主动退位。
下面看一下“新官上任“和“旧官退位“时,分别做了什么:
def onControllerFailover() {
if(isRunning) {
readControllerEpochFromZookeeper()
//递增controller epoch
incrementControllerEpoch(zkUtils.zkClient)
//关键点:接管所有对broker/partition节点的监听
registerReassignedPartitionsListener()
registerIsrChangeNotificationListener()
registerPreferredReplicaElectionListener()
partitionStateMachine.registerListeners()
replicaStateMachine.registerListeners()
initializeControllerContext()
replicaStateMachine.startup()
partitionStateMachine.startup()
// register the partition change listeners for all existing topics on failover
controllerContext.allTopics.foreach(topic => partitionStateMachine.registerPartitionChangeListener(topic))
info("Broker %d is ready to serve as the new controller with epoch %d".format(config.brokerId, epoch))
brokerState.newState(RunningAsController)
maybeTriggerPartitionReassignment()
maybeTriggerPreferredReplicaElection()
/* send partition leadership info to all live brokers */
sendUpdateMetadataRequest(controllerContext.liveOrShuttingDownBrokerIds.toSeq)
if (config.autoLeaderRebalanceEnable) {
info("starting the partition rebalance scheduler")
autoRebalanceScheduler.startup()
autoRebalanceScheduler.schedule("partition-rebalance-thread", checkAndTriggerPartitionRebalance,
5, config.leaderImbalanceCheckIntervalSeconds.toLong, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
}
deleteTopicManager.start()
}
else
info("Controller has been shut down, aborting startup/failover")
}
def onControllerResignation() {
//关键点:放弃对所有broker/partition的监听
deregisterIsrChangeNotificationListener()
deregisterReassignedPartitionsListener()
deregisterPreferredReplicaElectionListener()
// shutdown delete topic manager
if (deleteTopicManager != null)
deleteTopicManager.shutdown()
// shutdown leader rebalance scheduler
if (config.autoLeaderRebalanceEnable)
autoRebalanceScheduler.shutdown()
inLock(controllerContext.controllerLock) {
// de-register partition ISR listener for on-going partition reassignment task
deregisterReassignedPartitionsIsrChangeListeners()
// shutdown partition state machine
partitionStateMachine.shutdown()
// shutdown replica state machine
replicaStateMachine.shutdown()
// shutdown controller channel manager
if(controllerContext.controllerChannelManager != null) {
controllerContext.controllerChannelManager.shutdown()
controllerContext.controllerChannelManager = null
}
// reset controller context
controllerContext.epoch=0
controllerContext.epochZkVersion=0
brokerState.newState(RunningAsBroker)
}
}
