前言:这篇文章将对几个“非主流”的IO流进行简单的介绍
一 内存操作流
内存操作流的主要作用是完成内存的输入和输出。比如说在某些情况下需要生成一些临时信息,而将这些临时信息保存在文件中不仅要进行文件的读写而且在功能完成之后还需要删除这个临时文件,因此比较麻烦,这时或许就需要用到内存操作流了。
需要用到的API是:ByteArrayInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream,分别表示输入流和输出流,示例代码如下:
package javase.io;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String str = "HTTP://WWW.ZIFANGSKY.CN";
//内存操作输入流
ByteArrayInputStream bInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
//内存操作输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream bOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int temp = 0;
//一个个字节的读,并且将大写转换为小写
while((temp = bInputStream.read()) != -1)
bOutputStream.write(Character.toLowerCase(temp));
// bOutputStream.flush();
bInputStream.close();
bOutputStream.close();
System.out.println(bOutputStream.toString());
}
}
输出:
http://www.zifangsky.cn
二 管道流
管道流的主要作用是可以进行两个线程之间的通信,如果要进行管道的输出,则必须把输出流连接到输入流上,需要用到的方法是:connect(PipedInputStream pipedInputStream)
需要用到的API是:PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream,示例代码如下:
package javase.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
class SendData implements Runnable {
private PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = null;
// 获取管道输出流实例
public PipedOutputStream getPipedOutputStream() {
return pipedOutputStream;
}
// 在构造方法中实例化
public SendData() {
pipedOutputStream = new PipedOutputStream();
}
public void run() {
String str = "http://www.zifangsky.cn";
try {
pipedOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
pipedOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class ReceiveData implements Runnable {
private PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = null;
// 获取管道输入流实例
public PipedInputStream getPipedInputStream() {
return pipedInputStream;
}
public ReceiveData() {
pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream();
}
public void run() {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
pipedInputStream));
String temp = "";
try {
while ((temp = reader.readLine()) != null)
System.out.println(temp);
reader.close();
pipedInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class PipedDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SendData send = new SendData();
ReceiveData receive = new ReceiveData();
try {
//连接管道
send.getPipedOutputStream().connect(receive.getPipedInputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(send).start();
new Thread(receive).start();
}
}
注:上面的示例代码定义了两个线程对象,分别表示管道输出流和管道输入流,在操作的时候只需要使用PipedOutputStream类中提供的connect()connect(PipedInputStream pipedInputStream)方法就可以将两个管道流连接起来,线程启动后就会自动进行管道的输入和输出操作了
三 合并流
合并流的主要功能是将两个流的内容合并到一起
需要用到的API是:SequenceInputStream,实例代码如下:
package javase.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
public class SequenceDmeo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//输入流1
InputStream iStream1 = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\demo.txt");
//输入流2
InputStream iStream2 = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\demo2.txt");
//输出流
OutputStream oStream = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\demo3.txt");
//合并流
SequenceInputStream stream = new SequenceInputStream(iStream1, iStream2);
int temp = 0;
while((temp = stream.read()) != -1)
oStream.write(temp);
iStream1.close();iStream2.close();oStream.close();stream.close();
}
}
上面代码执行完毕的结果就是demo.txt文件和demo2.txt文件的内容都会合并到一个文件demo3.txt这个文件中去了
四 压缩流
在Java中可以通过压缩流将文件或文件夹压缩成ZIP,JAR或GZIP等格式,当然也可以进行反向解压缩。
有关压缩的常用几个API:
i)JAR:JarOutputStream和JarInputStream
ii)GZIP(比如说在Linux下常见的.gz格式):GZIPOutputStream和GZIPInputStream
iii)ZIP:ZipOutputStream,ZipInputStream,ZipFile,ZipEntity等
下面以ZIP格式来举例说明压缩与解压缩
(1)单个文件的ZIP压缩:
/**
* 压缩文件
*
* @param filePath
* 待压缩的文件路径
* @param zipPath
* 压缩之后的ZIP文件的路径
* */
public void compressFile(String filePath, String zipPath)
throws IOException {
// 源文件
File file1 = new File(filePath);
// 定义压缩后的文件
File zipFile = new File(zipPath);
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file1);
// 实例化压缩输出流并指定路径
ZipOutputStream zOutputStream = new ZipOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(zipFile));
zOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(file1.getName()));
zOutputStream.setComment("http://www.zifangsky.cn"); // 设置注释
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = inputStream.read()) != -1)
zOutputStream.write(temp);
inputStream.close();
zOutputStream.close();
}
测试:
ZipOutputStreamDemo demo = new ZipOutputStreamDemo(); String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\demo.txt"; String zipPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\demo.zip"; demo.compressFile(filePath, zipPath);
(2)文件夹的级联压缩
在上面的例子中举例说明了单个文件的压缩,但是我们通常可能需要将一个文件夹进行压缩,并且该文件夹中还有文件夹,比如说像这样:
这时候我们可以通过递归调用的方式来进行压缩。如果是普通文件则将文件内容压缩输出到ZipOutputStream流中,如果是文件夹则进行递归调用。完整示例代码如下:
/**
* 压缩文件或目录
*
* @param directoryPath
* 待压缩文件或目录的路径
* @param zipPath
* 压缩之后的ZIP文件的路径
* */
public void compressFolder(String directoryPath, String zipPath)
throws IOException {
// 源文件夹
File dir = new File(directoryPath);
// 定义压缩后的文件
File zipFile = new File(zipPath);
// 实例化压缩输出流并指定路径
ZipOutputStream zOutputStream = new ZipOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(zipFile));
zOutputStream.setComment("http://www.zifangsky.cn"); // 设置注释
compress(dir, dir.getName(), zOutputStream);
zOutputStream.close();
}
/**
* 循环递归压缩文件
*
* @param file
* 待压缩文件或目录
* @param path
* 压缩后的文件在压缩包中的起始路径
* @param zOutputStream
* ZIP压缩输出流
*
* */
public void compress(File file, String path, ZipOutputStream zOutputStream)
throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = null;
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File lists[] = file.listFiles();
int length = lists.length;
// 循环遍历每个文件
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
String temp_path = path + "\\" + lists[i].getName(); // 相对路径
// 如果是目录则继续递归压缩
if (lists[i].isDirectory())
compress(lists[i], temp_path, zOutputStream);
else {
// 如果是文件则将文件内容压缩输出到ZipOutputStream流中
inputStream = new FileInputStream(lists[i]);
zOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(temp_path));
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = inputStream.read()) != -1)
zOutputStream.write(temp);
inputStream.close();
}
}
} else {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
zOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(path));
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = inputStream.read()) != -1)
zOutputStream.write(temp);
inputStream.close();
}
}
在上面的例子的基础上继续进行测试:
String directoryPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\test"; String zipPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\dir.zip"; demo.compressFolder(directoryPath,zipPath);
测试效果如下:
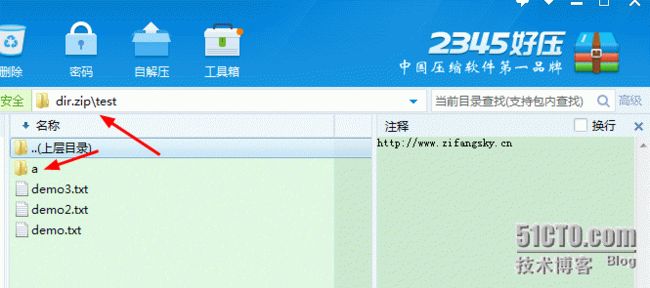
(3)对压缩文件进行级联解压缩
这里以上面例子中的dir.zip文件为测试目标进行解压缩,代码不难而且关键地方我已经写了注释,因此这里就不多说了,完整代码如下:
package javase.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipFile;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
public class ZipInputStreamDemo {
/**
* 压缩文件循环递归解压缩
*
* @param zipPath
* 压缩文件路径
* @param filePath
* 解压之后的文件的保存路径
* */
public void decompress(String zipPath, String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(zipPath); // 压缩文件
File outFile = null; // 解压后的文件
ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file);
ZipInputStream zInputStream = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(
file));
ZipEntry zipEntry = null; // 定义一个ZipEntry对象,用于接收压缩文件中的每一个实体
InputStream inputStream = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
// 获取压缩文件中的每个实体文件
while ((zipEntry = zInputStream.getNextEntry()) != null) {
outFile = new File(filePath + "\\" + zipEntry.getName()); // 实例化
if (!outFile.getParentFile().exists()) {
outFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); // 如果文件夹不存在则级联创建文件夹
}
if (!outFile.exists())
outFile.createNewFile(); // 如果文件不存在则创建新文件
inputStream = zipFile.getInputStream(zipEntry);
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = inputStream.read()) != -1)
outputStream.write(temp);
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
zInputStream.close();
zipFile.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ZipInputStreamDemo demo = new ZipInputStreamDemo();
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\decompress";
String zipPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\dir.zip";
demo.decompress(zipPath, filePath);
}
}
效果如下:
五 回退流
回退流,顾名思义,可以把读取出来的某些数据重新退回到输入流的缓冲区中
需要用到的API是:PushbackInputStream,示例代码如下:
package javase.io;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PushbackInputStream;
public class PushInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "http://www.zifangsky.cn";
// 内存输入流
ByteArrayInputStream bArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(
str.getBytes());
// 回退流
PushbackInputStream push = new PushbackInputStream(bArrayInputStream);
System.out.println("读取的数据为:");
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = push.read()) != -1) {
if (temp == '.') {
push.unread(temp); // 回退到缓冲区
push.read(); // 重新读取,不要直接丢弃
System.out.print("(退回" + (char) temp + ")");
} else
System.out.print((char) temp);
}
push.close();
bArrayInputStream.close();
}
}
输出:
读取的数据为: http://www(退回.)zifangsky(退回.)cn