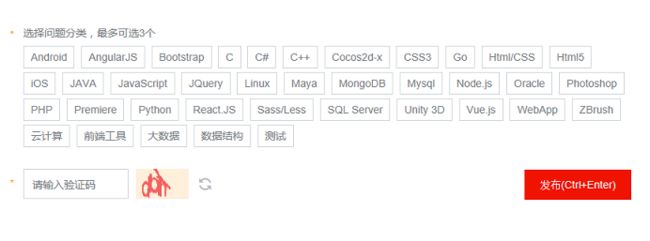
自定义流式布局
流式布局的使用已盛行it界许久了,可谓随处可见,随时可见,再不了解一下它,那就太out了。今天就让我们来看看 类似热门标签的流式布局吧~
以上都是从实际的应用中截取到的图片,事实证明流式布局真的很潮~
2.流式布局分析
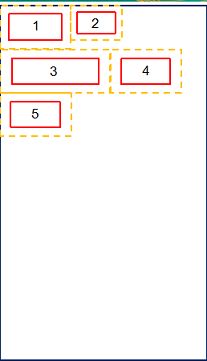
说到流式布局我们要先了解一下测量模式
①测量模式:
测量模式分三种即:
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:精确模式, eg:100dp,match_parent.
(注:为什么match_parent属于精确模式呢?这是因为我们手机屏幕的大小是确定的,即使你已经先制定了一个控件比如TextView的高为50dp,下面又设置了一个View的高为match_parent,那实际上
该View的高=屏幕的高(确定的)-TextView的高(也是确定的)
确定的值 减去 确定的值 结果还是确定的
)
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: 至多模式, view最多可以获得的宽高值,它需要计算所有包含的子view的宽高,最后计算出来的宽高总和值,eg:wrap_content.UNSPECIFIED:未指定模式,想设置多宽多高,就给你多宽多高,一般的控件不会指定这种模式,但也存在,eg:scrollview的宽高测量,就是使用的此种模式
②那么在我们的流式布局内,应该怎么设置布局的宽高呢? onMeasure():
1:如果布局指定的宽是match_parent或者精确的宽度值,那么直接就可以从父控件传入的测量规格中直接获取布局宽度,高度同理.
2:如果布局指定的宽高不是EXACTLY,而是AT_MOST,那么这时候,就需要计算每一个子view的宽高,来决定布局的宽高了。
宽度:摆放的所有子view占据宽度最多的一行,作为布局宽度。
高度:摆放的所有子view总共占据几行的高度总和。
③实现子View的布局方式: onLayout()
使用onLayout():设置ViewGroup内包含的所有子view的位置;
获取到每一行的每一个子view,计算出它的left,top,right,bottom,调用layout方法设置其在流式布局当中的位置。
宽度=子view最多的那行的宽度=那一行每一个子view的宽度+leftMargin+rightMargin;
高度=所有行的高度 = 每一行的高度+topMargin+bottomMargin;
使用 setMeasureDimension()—>设置流式布局的宽高。
那么下面我就按照分析的步骤来实现如下效果的流式布局
实现效果:
该流式布局特点:在布局内,随意摆放任意个view,每行所摆放的view个数,根据实施计算出来的宽度,一旦当前要摆放的view宽度和之前摆放的所有view宽度加在一起,超过了布局的宽度,那么就把该view换行摆放。且每个子view的背景颜色随机,点击时会变为白色。
3.流式布局的具体实现
①.自定义JMFlowLayout类继承ViewGroup类
public class JMFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
//构造器
public JMFlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public JMFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public JMFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
//需重写的onLayout()方法
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
}
}②在布局中使用我们自己定义的FlowLayout
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.chenjunmei.jmflowlayout.MainActivity">
<com.example.chenjunmei.jmflowlayout.JMFlowLayout
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="愿得一人心"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:textSize="30sp"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="向天再借五百年"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:textSize="30sp"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="蓝瘦香菇"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:textSize="30sp"
/>
com.example.chenjunmei.jmflowlayout.JMFlowLayout>
LinearLayout>
③测量,重写onMeasure()方法
代码中都已经详细说明:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//1获取宽度和高度的数值
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//2获取各自的设置模式
int withMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//声明相关变量
//声明当前视图的高宽
int width=0;
int height=0;
//声明每行的宽高
int lineWidth=0;
int lineHeight=0;
//3.1 获取子视图的总个数
int childCount=getChildCount();
//3.2 得到至多模式时的宽高
for (int i=0;i//注意!需要调用如下的方法之后,才可以获取子视图的宽高
measureChild(childView,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
//3.2.1获取子视图测量的宽高
int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
//注意!要想获取边距,必须重写当前类的方法generateLayoutParams()
//3.2.2获取子视图测量的margin值
MarginLayoutParams mp = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
//3.2.3 具体的测量和计算过程
if (lineWidth+childWidth+mp.leftMargin+mp.rightMargin<=widthSize){
//说明不换行
//行宽要增加
lineWidth+=childWidth+mp.leftMargin+mp.rightMargin;
//比较后确定当前行高
lineHeight=Math.max(lineHeight,childHeight+mp.topMargin+mp.bottomMargin);
}else{
//说明要换行了
//比较一下,取较大值作为布局的宽
width=Math.max(lineWidth,width);
//布局的高要增加
height+=lineHeight;
//再重新赋值 :行宽和行高
lineWidth=childWidth+mp.leftMargin+mp.rightMargin;
lineHeight=childHeight+mp.topMargin+mp.bottomMargin;
}
//如果是最后一个元素,要特别注意一下,保证最后一个元素的正确性
if (i==childCount-1){
width=Math.max(lineWidth,width);
height+=lineHeight;
}
}
//打印查看各个值
//即当前布局的宽高
Log.e("TAG", "width = " + width + ",height = " + height);
//其实就是屏幕的宽高
Log.e("TAG", "widthSize = " + widthSize + ",heightSize = " + heightSize);
//3.0 相当于设值当前布局的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(withMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? widthSize : width, heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? heightSize:height);
}
//注意!要想获取边距,必须重写当前类的方法generateLayoutParams()
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
MarginLayoutParams mp = new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
return mp;
}
④绘制,重写onLayout()方法
先提供两个集合
//第一个-->集合元素:存放的是每一行的高度
private List<Integer> allHeights=new ArrayList<>();
//第二个是集合的集合,外层集合元素为:存放的是每一行的childView的集合
private List<List<View>> allViews=new ArrayList<>();下面给每一个子view布局,childView.layout(l,t,r,b)
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
//得到父视图的宽度
int width=this.getWidth();
//设置每行的行高,行宽
int lineWidth=0;
int lineHeight=0;
//创建每一行的子视图的集合
List lineList=new ArrayList<>();
//获取子视图的总个数
int childCount= getChildCount();
//装配集合数据
for (int i=0;i//获取子视图
View childView=getChildAt(i);
//获取子视图的宽高
int childWidth=childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight=childView.getMeasuredHeight();
//获取子视图的边距
MarginLayoutParams mp=(MarginLayoutParams)childView.getLayoutParams();
//注意:!!!这里还要加上lineWidth
if (childWidth+mp.leftMargin+mp.rightMargin+lineWidth<=width){
//不换行,则把当前的子view加到 "行的集合中"
lineList.add(childView);
lineWidth+=childWidth+mp.leftMargin+mp.rightMargin;
lineHeight=Math.max(lineHeight,childHeight+mp.topMargin+mp.bottomMargin);
}else{
//换行,则把 "每行的子view的集合" 添加到所有的集合中,把行高加到行高的集合中
allViews.add(lineList);
allHeights.add(lineHeight);
//换行以后需要执行的操作
//重新new一个行的集合
lineList=new ArrayList<>();
//把新的一行的子view加到行的集合中
lineList.add(childView);
lineWidth=childWidth+mp.leftMargin+mp.rightMargin;
lineHeight=childHeight+mp.topMargin+mp.bottomMargin;
}
if (i==childCount-1){ //最后一个元素
allViews.add(lineList);
allHeights.add(lineHeight);
}
}
//都表示行数,所以两者应该相等
Log.e("TAG", "allViews.size = " + allViews.size() + ",allHeights.size = " + allHeights.size());
//遍历集合元素,调用每一个view的layout方法
//提供需要累加的两个人变量
int x=0;
int y=0;
//第一层得到的是每一行的数据
for (int i=0;i lineViews=allViews.get(i);
//第二层得到的是每一个子view
for (int j=0;jget(j);
//得到边距
MarginLayoutParams mp= (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
//到l,t,r,b
int left=x+mp.leftMargin;
int top=y+mp.topMargin;
int right=left+childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int bottom=top+childView.getMeasuredHeight();
childView.layout(left,top,right,bottom);
//重新覆下一个子视图的左上顶点
x+=childView.getMeasuredWidth()+mp.leftMargin+mp.rightMargin;
}
//该层循环出来则表示 换行 了
//换行后,x要复位为0,y要重新赋值
x=0;
y+=allHeights.get(i);
}
} –>到此,开始设置的3个TextView开始显示出来,并实现了自动换行:
效果如下图:
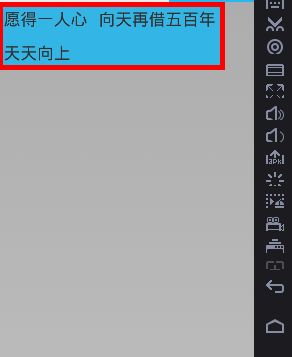
④再Mactivity中使用,并再做先关处理
a.用集合数据替换xml中的textView
private String[] datas = new String[]{
"新手计划", "乐享活系列90天计划", "钱包",
"30天理财计划(加息2%)",
"林业局投资商业经营与大捞一笔",
"中学老师购买车辆", "屌丝下海经商计划",
"新西游影视拍", "Java培训老师自己周转", "HelloWorld", "C++-C-ObjectC-java", "Android vs ios", "算法与数据结构", "JNI与NDK", "team working"};b.动态加载数据到flowLayout中
for (int i=0;i
final TextView tv=new TextView(getContext());
tv.setText(datas[i]);
// 相当于布局文件中的:
// android:layout_width="wrap_content"
// android:layout_height="wrap_content"
// 必须要写
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams mp= new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
tv.setLayoutParams(mp);
// -->太挤了,且字体太小
//设置边距
mp.leftMargin= JMUiUtils.dp2px(5);
mp.rightMargin=JMUiUtils.dp2px(5);
mp.topMargin=JMUiUtils.dp2px(5);
mp.bottomMargin=JMUiUtils.dp2px(5);
tv.setTextSize(JMUiUtils.dp2px(16));
} c.设置文本背景(有两种方式:代码中已经表明)
及点击时背景变白效果
Random random=new Random();
//设置背景颜色
int red=random.nextInt(180);
int green=random.nextInt(180);
int blue=random.nextInt(180);
//方式一:使用GradentDrawable类,相当于 <=> shape 中的 标签
// //指定颜色和圆角半径
// tv.setBackground(JMDrawableUtils.getDrawable(Color.rgb(red,green,blue),JMUiUtils.dp2px(5)));
//方式二:使用StateListDrawable类,相当于 <=> 我们经常使用的selector 标签
//给当前的颜色选择器添加选中图片指向状态,未选中图片指向状态
tv.setBackground(JMDrawableUtils.getSelector(JMDrawableUtils.getDrawable(Color.rgb(red, green, blue), JMUiUtils.dp2px(5)), JMDrawableUtils.getDrawable(Color.WHITE, JMUiUtils.dp2px(5))));
//使用方式二背景颜色可以改变,但是发现点击时,背景没有变为白色
//这是因为 TextView 默认是不可点的
//解决 TextView默认不可点的方法有如下两种:
//①设置为可点击的
// tv.setClickable(true);
//②当设置点击事件时,textview就默认为可点的啦
tv.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getContext(), tv.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
//背景框把字体包的太紧了
//提供内边距
int padding=JMUiUtils.dp2px(5);
tv.setPadding(padding,padding,padding,padding);
//添加视图到我们的自定义JMFlowLayout中
flowLayout.addView(tv);涉及到的工具类JMDrawableUtils :
public class JMDrawableUtils {
//提供一个指定颜色和圆角半径的Drawable对象
public static GradientDrawable getDrawable(int rgb, float radius) {
GradientDrawable gradientDrawable = new GradientDrawable();
gradientDrawable.setColor(rgb); //填充颜色
gradientDrawable.setGradientType(GradientDrawable.RECTANGLE); //shape矩形
gradientDrawable.setCornerRadius(radius); //四周圆角半径
gradientDrawable.setStroke(JMUiUtils.dp2px(1), rgb); //边框厚度与颜色
return gradientDrawable;
}
public static StateListDrawable getSelector(Drawable normalDrawable, Drawable pressDrawable) {
StateListDrawable stateListDrawable = new StateListDrawable();
//给当前的颜色选择器添加选中图片指向状态,未选中图片指向状态
stateListDrawable.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_enabled, android.R.attr.state_pressed}, pressDrawable);
stateListDrawable.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_enabled}, normalDrawable);
//设置默认状态
stateListDrawable.addState(new int[]{}, normalDrawable);
return stateListDrawable;
}
}