ScrollBy ScrollTo
Android View视图是没有边界的,Canvas是没有边界的
可以对Canvas对象进行了一定的操作
例如 :
translate(平移)、
clipRect(剪切)等
scrollTo(int x,int y):
scrollBy(int x,int y):
其实是对scrollTo的包装,移动的是相对位置
这里有个难点 :x y 的坐标怎么算
注意:mScrollX和mScrollY指的并不是坐标,而是偏移量。
计算方法:
:mScrollX = 原点(0) - x(坐标)
:mScrollY = 原点(0) - y(坐标)
这里的坐标是 相对父空间的 也就是 getX(), getY()
那么 如果移动scrollTo(100,100),mScrollX和mScrollY又是多少
根据源码显示
* Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the x position to scroll to
* @param y the y position to scroll to
*/
public void scrollTo(int x, int y) {
if (mScrollX != x || mScrollY != y) {
int oldX = mScrollX;
int oldY = mScrollY;
mScrollX = x;
mScrollY = y;
invalidateParentCaches();
onScrollChanged(mScrollX, mScrollY, oldX, oldY);
if (!awakenScrollBars()) {
postInvalidateOnAnimation();
}
}
}
/**
* Move the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the amount of pixels to scroll by horizontally
* @param y the amount of pixels to scroll by vertically
*/
public void scrollBy(int x, int y) {
scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y);
}mScrollX = 100,mScrollY = 100;
那么 view的位置在哪,相对于原来的位置是左移还是右移?
偏移量的公式:原点减去坐标
根据公式首先我们来确定原点在哪 ?
举例说明:
三种布局:打开手机布局边界
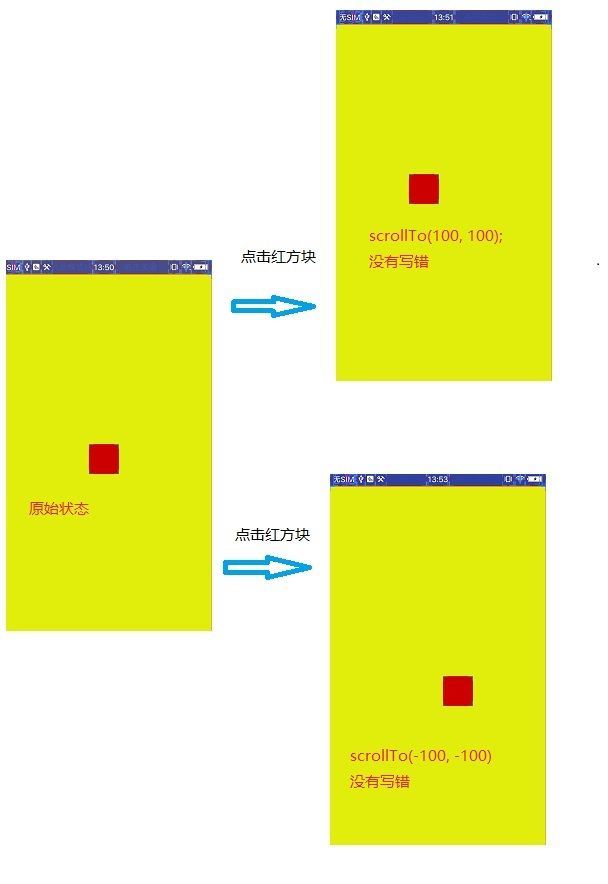
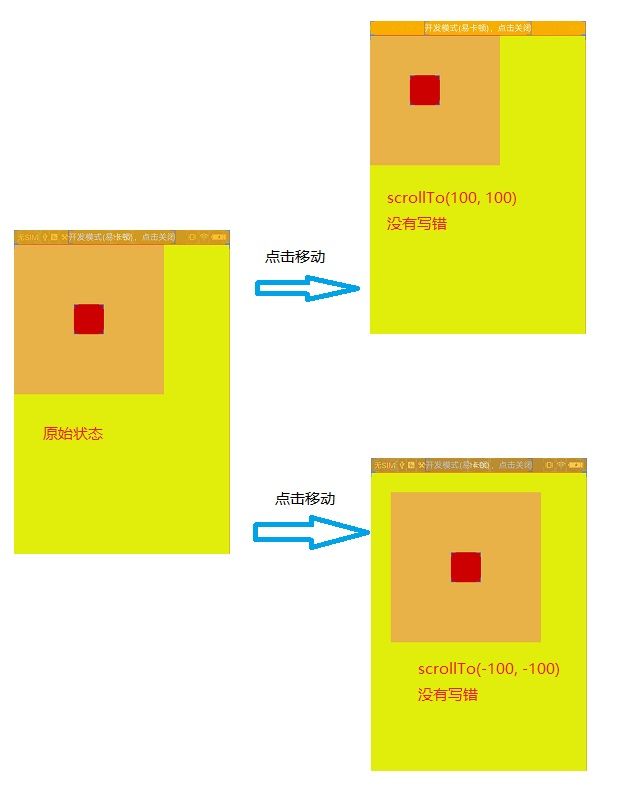
三种情况scrollTo(100, 100)和scrollTo(-100, -100); ;
情况一
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/linear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#e2ed0d"
>
<View
android:id="@+id/view"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
/>
RelativeLayout>
原始状态 点击移动(两种情况) 都是一样
08-15 13:38:26.359 24196-24196/com. I/cjw: view getX = 0.0
08-15 13:38:26.359 24196-24196/com. I/cjw: view getY = 0.0
08-15 13:38:26.359 24196-24196/com. I/cjw: view getLeft = 0
08-15 13:38:26.359 24196-24196/com. I/cjw: view getTop = 0情况二
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/linear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#e2ed0d"
>
<View
android:id="@+id/view"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
/>
RelativeLayout>原始状态 点击移动(两种情况) 都是一样
08-15 13:50:45.479 27246-27246/com. I/cjw: view getX = 465.0
08-15 13:50:45.479 27246-27246/com. I/cjw: view getY = 849.0
08-15 13:50:45.479 27246-27246/com. I/cjw: view getLeft = 465
08-15 13:50:45.479 27246-27246/com. I/cjw: view getTop = 849情况三
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/linear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#e2ed0d"
>
<View
android:id="@+id/view"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
/>
RelativeLayout>原始状态 点击移动(两种情况) 都是一样
08-15 14:03:51.549 30241-30241/com. I/cjw: view getX = 300.0
08-15 14:03:51.549 30241-30241/com. I/cjw: view getY = 300.0
08-15 14:03:51.549 30241-30241/com. I/cjw: view getLeft = 300
08-15 14:03:51.549 30241-30241/com. I/cjw: view getTop = 300Activity 代码
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private View view;
private View linear;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main_activity);
view = findViewById(R.id.view);
linear = findViewById(R.id.linear);
view.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
print();
}
});
view.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
linear.scrollTo(100, 100);
//linear.scrollTo(-100, -100);
print();
}
});
}
private void print() {
Log.i("cjw", "view getX = " + view.getX());
Log.i("cjw", "view getY = " + view.getY());
Log.i("cjw", "view getLeft = " + view.getLeft());
Log.i("cjw", "view getTop = " + view.getTop());
}
}
是不是觉得原点在红块块的左上角 , NO NO NO··
原点是父空间的左上角(黄色区域) why ? ?
scrollTo 移动不是红块 是移动的父控件里面的布局
不信可以在里面再加个蓝色的方块
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/linear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#e2ed0d"
>
<View
android:id="@+id/view"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view2"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="100dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
/>
RelativeLayout> 蓝色的方块,会和红色的方块一起移动
好像懂了? 可这玩意有什么用了 。。。。
如侧滑,自己写viewPage ,侧滑菜单,scroller 都有用到。
我立体思维差,那就先记住几点规则
- 原点: 父控件的左上角 ,参照物,不管怎么移动,以左上角来移动其他坐标
- 偏移量: 原点减去getX getY (就是该子控件在父控件的位置。)
- scrollTo,scrollBy 都是移动的偏移量
- scrollBy 偏移量小于0 ->右边移动,偏移量大于0 ->左边移动 , 偏移量为0 不动
- scrollTo 偏移量小于0 ->右边移动,偏移量大于0 ->左边移动 , 偏移量为0 到原点 。
- scrollBy 相对与本身在的位置,scrollTo移动不参考本身的位置直接跳对应的偏移量。
例子 :
Activity代码
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private View view;
private View linear;
private boolean click = false;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main_activity);
view = findViewById(R.id.view);
linear = findViewById(R.id.linear);
view.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
print();
}
});
view.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (click) {
linear.scrollTo((int) view.getX(), (int) view.getY());
} else {
//linear.scrollTo(-100, -100);
//linear.scrollTo(0, 0);
//linear.scrollBy(-100, -100);
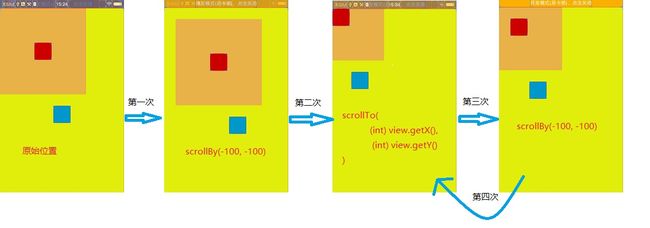
linear.scrollBy(-(int) view.getX(), -(int) view.getY()); //这个流程图没有画
}
click = !click;
print();
}
});
}
private void print() {
Log.i("cjw", "view getX = " + view.getX());
Log.i("cjw", "view getY = " + view.getY());
Log.i("cjw", "view getLeft = " + view.getLeft());
Log.i("cjw", "view getTop = " + view.getTop());
}
}
xml代码
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/linear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#e2ed0d"
>
<View
android:id="@+id/view"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="100dp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_dark"
/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view2"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
/>
RelativeLayout>这种情况 本身自带了个偏移量(margin=”100dp”)
实际上
原始位置就是 scrollTo(-margin, -margin);
第一次点击 是 scrollTo(-margin + (-100), -margin + (-100));
第二次点击 是 scrollTo(-margin + (getX()), -margin + (getY()));
第三次点击 是 scrollTo(-margin + (-100)), -margin + (-100));
mScrollX:表示离视图起始位置的x水平方向的偏移量
mScrollY:表示离视图起始位置的y垂直方向的偏移量
分别通过getScrollX() 和getScrollY()方法获得。
注意:mScrollX和mScrollY指的并不是坐标,而是偏移量
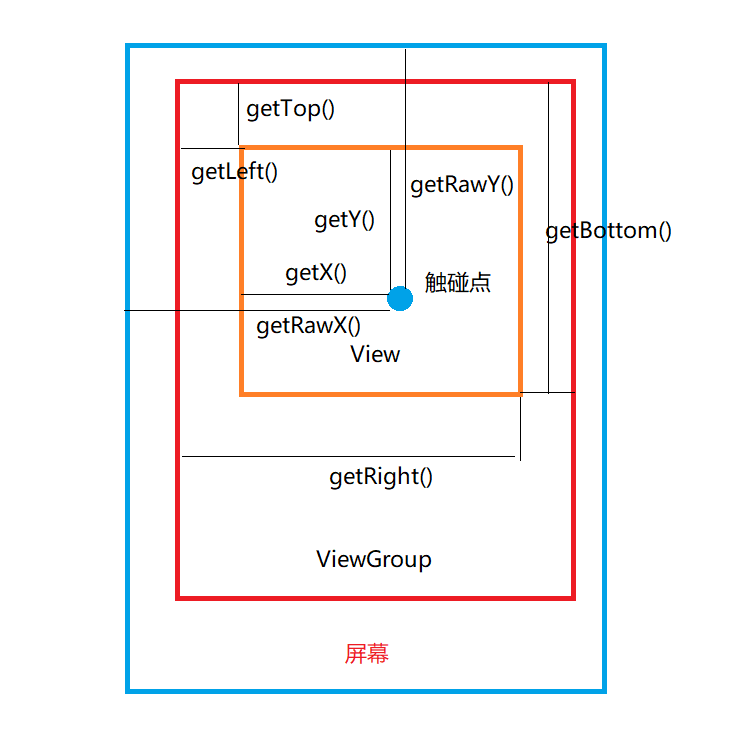
getRawX、getRawY与getX、getY的区别
在编写android的自定义控件,或者判断用户手势操作时
往往需要使用MotionEvent中
getRawX()、getRawY()与getX()、getY()取得触摸点在X轴与Y轴上的距离
这四个方法都返回一个float类型的参数,单位为像素(Pixel)
getRawX()、getRawY()返回的是触摸点相对于屏幕的位置
getX()、getY()返回的则是触摸点相对于父控件View的位置
怎么样移动View?
通过更改view的left,top,right,bottom来移动view
layout(l,r,t,b);
offsetLeftAndRight(offset);//同时对left和right进行偏移
offsetTopAndBottom(offset);//同时对top和bottom进行偏移left:表示当前view的左边距父view原点的距离
top:表示当前view的顶部距父view原点的距离
通过更改scrollX和scrollY来移动view,即scrollTo和scrollBy方法
如果是在ViewGroup中使用,则可以让当前view的所有子view同时移动,如果是对单个view使用,则可以让view的内容移动
让View平滑移动
1. Scroller实现
//第一步 初始化Scroller
Scroller scroller =new Scroller(getContext());
//第二步 开启模拟过程
//int startX; 滑动动作的起始点x坐标
//int startY; 滑动动作的起始点y坐标
//int dx; x轴偏移量向左为负,向右为正(即负值向右移,正值向左移)是x轴不是startX的偏移量
//int dy; y轴偏移量向左为负,向右为正(即负值向右移,正值向左移) 是y轴不是startY的偏移量
scroller.startScroll(startX, startY, dx, dy,500);
invalidate();
//第三步 在模拟过程中获取view真实移动时的值,并调用scrollTo去真正移动view
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
if(scroller.computeScrollOffset()){
scrollTo(scroller.getCurrX(), scroller.getCurrY());
invalidate();
}
}
- 自定义动画实现
用自定义动画实现View平滑移动
使用强大的ViewDragHelper