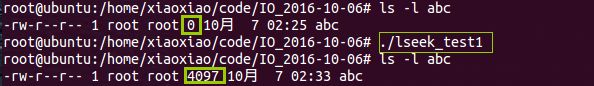
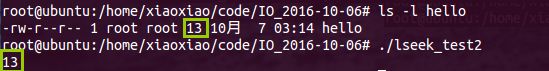
- C/C++中的 void*
wudi_demaxiya
C++c++c语言指针
在看《Unix/Linux系统编程》中关于POSIXThread部分的时候发现C语言中用void*传递了int类型变量,很疑惑,于是查了些资料并汇总了一下。介绍了C语言和C++中关于void*的用法,涉及到了C++中的reinterpret_cast如果哪里有错误欢迎指正!参考资料参考资料1.C/C++中的void*与其他指针类型转换1.1C中void*与其他指针类型转换C语言对指针类型的转换要求
- 【Linux网络编程】第九弹---深入解析TCP服务、IOService与Jsoncpp的应用与实现
小林熬夜学编程
Linux网络编程linux网络运维tcp/ipC语言c++服务器
✨个人主页:熬夜学编程的小林系列专栏:【C语言详解】【数据结构详解】【C++详解】【Linux系统编程】【Linux网络编程】目录1、TcpService.hpp1.1、TcpServer类基本结构1.2、构造析构函数1.3、Loop()1.3.1、内部类1.3.2、Execute()2、Service.hpp2.1、IOService类基本结构2.2、构造析构函数2.3、IOExcute()3、
- Linux系统编程之事件驱动
weixin_34342905
c/c++ui
通常,我们写服务器处理模型的程序时,有以下几种模型:(1)每收到一个请求,创建一个新的进程,来处理该请求;(2)每收到一个请求,创建一个新的线程,来处理该请求;(3)每收到一个请求,放入一个事件列表,让主进程通过非阻塞I/O方式来处理请求分析:第(1)中方法,由于创建新的进程的开销比较大,所以,会导致服务器性能比较差,但实现比较简单。第(2)种方式,由于要涉及到线程的同步,有可能会面临死锁等问题。
- [Linux系统编程]进程组和会话,守护进程
SlanderMC
linux运维服务器
一.进程组进程组,也称之为作业。BSD于1980年前后向Unix中增加的一个新特性。代表一个或多个进程的集合。每个进程都属于一个进程组。在waitpid.函数和kill函数的参数中都曾使用到。操作系统设计的进程组的概念,是为了简化对多个进程的管理。当父进程,创建子进程的时候,默认子进程与父进程属于同一进程组。进程组ID=第一个进程ID(组长进程)。可以使用kill-9-进程组ID(负数)来将整个进
- Linux系统编程(10)线程资源回收和互斥锁
流殇258
java开发语言
一、pthread_cancel函数pthread_cancel函数用于请求取消一个线程。当调用pthread_cancel时,它会向指定的线程发送一个取消请求。#includeintpthread_cancel(pthread_tthread);thread:要发送取消请求的线程标识符。成功时,返回0。失败时,返回一个错误号二、pthread_detach函数pthread_detach用于将线
- 重头开始嵌入式第二十七天(Linux系统编程 信号通信)
FLPGYH
Linux系统高级编程c语言linuxvim
目录进程间通信===》1.信号通信1.信号的五种类型:2.kill1、信号kill-l==>前32个有具体含义的信号3.信号注册函数原型:1.自定义信号处理:2、在所有的信号中有如下两个特列:2.共享内存信号量集1.key创建方式有三种:共享内存===》效率最高的进程间通信方式1、申请对象:2.映射对象:shmat()3.读写共享内存:类似堆区内存的直接读写:4.撤销映射:shmdt5.删除对象:
- 重头开始嵌入式第二十八天(Linux系统编程 网络通信 套接字)
FLPGYH
linuxvimc语言
目录1.网络编程1.OSI(OpenSystemInterconnection)模型即开放式系统互联通信参考模型。TFTP(TrivialFileTransferProtocol)即简单文件传输协议。2.TCP/IP模型也叫网际互联模型共分为4层:也叫协议栈3、TCP/IP协议族:4.DNS(DomainNameSystem,域名系统)是互联网的一项重要服务。4、网络基础(ABCDE类)5.网络相
- 重头开始嵌入式第二十一天(Linux系统编程 文件相关函数)
FLPGYH
vimlinuxc语言
目录1.getpwuid2.getpwnam3.getgrgid4.symlink在Linux和类Unix系统中,创建软链接(符号链接)的常用指令是ln-s。5.remove6.rename7.link8.truncate9.perror10.strerror11.error1.makefile2.gdbstrtok1.getpwuidgetpwuid函数是C语言标准库中的一个函数,用于通过用户I
- linux系统编程:数据库
ヾ(´∀`。ヾ)307
数据库
1.数组、链表、变量-----》内存:程序运行结束、掉电数据丢失文件----------------------》硬盘:程序运行结束、掉电数据不丢失数据库:专业存储数据、大量数据-----》硬盘sqlite相关的命令.tables查看数据库中的表.headerson/off开启或者关闭表头.modecolumn列对齐.width列宽1列宽2设置每一列的列宽.schema表名查看表的结构sqlite
- 重头开始嵌入式第二十六天(Linux系统编程 进程间通信 IPC)
FLPGYH
vimlinuxc语言
目录IPC进程间通信1.管道通信管道的特性使用流程无名管道1.创建并打开管道:2.无名管道的读写:3.关闭管道:close();4.使用例子:有名管道1、创建:mkfifo2、打开有名管道open3、管道的读写:文件IO4、关闭管道:5、卸载管道:remove();IPC进程间通信进程间通信(Inter-ProcessCommunication,简称IPC)是指在不同进程之间进行数据交换、消息传递
- Linux 系统编程从入门到进阶 学习指南
后端
引言大家好,我是小康,今天我们来学习一下Linux系统编程相关的知识。Linux系统编程是连接高级语言和硬件的桥梁,它对深入理解计算机系统至关重要。无论你是打算构建高性能服务器还是开发嵌入式设备,掌握Linux系统编程是C和C++开发者的基本技能。本文旨在为初学者提供一个清晰的Linux系统编程入门指南,带你步入Linux系统编程的世界,从基本概念到实用技能,一步步建立起您的知识体系。基本概念什么
- Linux系统编程(四)进程
Patarw_Li
Linux系统编程linux运维服务器c语言
一、进程的产生(fork)fork(2)系统调用会复制调用进程来创建一个子进程,在父进程中fork返回子进程的pid,在子进程中返回0。#include#includepid_tfork(void);fork后子进程不继承未决信号和文件锁,资源利用量清0。由于进程文件描述符表也继承下来的,所以可以看到父子进程的输入输出指向都是一样的,这个特性可以用于实现基本的父子进程通信。init()是所有进程的
- 文件fd【Linux系统编程】
勤奋的懒羊羊~
Linux系统编程linux服务器
本文是基础IO的第一个部分,基础IO部分将主要讲解以下内容:文件fd文件系统软硬链接操作系统的内存管理以及动静态库。本节重点讲解文件fd,其余内容将在后面的博客更新。一、共识文件=内容+属性文件分为打开了的文件和没打开的文件。打开的文件:谁打开?进程(本质是研究进程和文件的关系)没打开的文件:磁盘里,很多,如何存储?------>快速增删查改。本节重点讨论打开的文件!文件被打开,必须先加载到内存,
- 【Linux系统编程】进程
橘猫0.o
#进程Linux系统编程linux运维服务器c语言数据结构笔记经验分享
进程文章目录进程1.进程概念2.创建进程函数fork3.进程实际运用场景4.vfork函数创建进程5.进程退出6.父进程等待子进程退出僵尸进程wait函数waitpid函数孤儿进程7.exec族函数execl函数:execlp函数:execvp函数:8.linux下修改环境变量配置绝对路径9.exec族函数配合fork函数使用10.system函数11.popen函数1.进程概念1.1什么是程序,
- Linux系统编程(七)--线程控制
-出发-
Linux系统编程linux
文章目录1线程属性1.1pthread_attr_t1.2不同属性的作用2互斥量的共享属性2.1属性的初始化与回收2.2共享属性3互斥量的鲁棒属性3.1相关函数3.2互斥量状态一致性4递归型互斥量4.1相关函数4.2递归类型的互斥量5其它同步对象的属性5.1读写锁的属性5.2条件变量的属性5.3barrier属性6可重入函数(二)7errno变量与多线程8只被执行一次的函数8.1问题提出8.2pt
- Linux系统编程05--信号2
闲鱼蜡蕉的摸鱼时光
Linux学习linux
文章目录五、信号-2进程处理信号的行为PCB信号集信号集处理函数sigprocmask信号屏蔽字函数sigpending获取当前信号集的未决信号集信号捕捉设定用户自定义信号(利用SIGUSR1和SIGUSR2实现父子进程同步输出)C标准库信号处理函数可重入函数信号引起的竞态和异步I/O时序竞态(进程竞争CPU资源)避免异步I/O的类型volatileSIGCHLD信号SIGCHLD信号产生条件向信
- Linux系统编程之信号(上)
十年磨一剑,霜刃未曾试
linux算法运维
1、预备工作生活当中有很多的信号,例如:上课铃声、发令枪等。从这些中我们可以提炼出三个点,1、我们必须要认识信号2、我们收到信号会做出相应的动作3、我们听到信号会在适合的时候去完成。在技术当中也是这样子,进程收到信号也会满足这三个条件。例如:当我们在Linux中写了一个死循环程序,这时需要按下ctrl-c才可以暂停程序。所有的信号我们可以通过kill-l来查看2、信号的发送信号发送有四种方式1、通
- 【Linux系统编程二十八】基于条件变量的阻塞队列(生产消费模型)
小陶来咯
Linux系统编程linuxjvmc++
【Linux系统编程二十八】基于条件变量的阻塞队列(生产消费模型)一.同步问题二.条件变量1.实现原理2.等待的前提3.使用接口①.【定义条件变量】②.【初始化条件变量】③.【让线程去条件变量下等待】④.【为什么第二个参数是锁?】条件变量和锁的关系是什么?⑤.【唤醒等待队列的线程】三.生产消费模型321原则3种关系2种角色1个交易场所四.基于阻塞队列的生产消费模型。1.细节一:真正的生产和消费过程
- 【Linux系统编程三十】线程池实现
小陶来咯
Linux系统编程linux运维c++
线程池实现一.线程池的本质二.类内创建线程三.代码实现一.线程池的本质线程池里面存储的都是一批已经创建好的线程,当线程池里有数据时,这批线程就会被唤醒去竞争数据,当线程池里没有数据时,这批线程就去休眠等待。线程池的本质就是一个生产消费模型,当有生产者线程往线程池里发送任务时,线程池里的消费者线程就会竞争任务。比如主线程往线程池里投递一个任务,线程池里的若干线程就会被立刻唤醒,然后去竞争抢任务执行。
- 【Linux系统编程二十九】基于信号量的环形队列生产消费模型
小陶来咯
Linux系统编程linux服务器c++
【Linux系统编程二十九】基于信号量的环形队列生产消费模型一.信号量1.P操作2.V操作二.环形队列三.单生产单消费场景1.信号量维持生产消费之间互斥同步四.多生产多消费场景1.加锁维持生产生产,消费消费互斥五.总结一.信号量当共享资源被当成整体使用时,则共享资源的数量要么是1,要么是0。当被访问使用时,共享资源的数量就为0,当没有被使用时,数量就为1。共享资源是可以被分成多份来使用的,只不过不
- 【Linux系统编程】如何创建进程(什么是fork函数?进程创建的原理是什么?)
sunny-ll
Linux系统编程linux运维服务器c++算法数据结构
目录一、前言二、进程创建的初次了解(创建进程的原理)三、什么是fork函数?初识fork函数fork函数的四个为什么?⭐为什么fork()要给子进程返回0,给父进程返回子进程pid?⭐一个函数是如何做到返回两次的?如何理解?⭐fork()函数究竟在干什么?干了什么?⭐一个变量怎么会有不同的内容呢?四、总结五、共勉一、前言在之前的博客中,已经详细的讲解了什么是进程包括了进程的概念,进程与操作系统的关
- Linux系统编程——管道
Strive_LiJiaLe
Linux系统编程linuxc++运维
文章目录一、管道1.管道的特质2.管道的用法——pipe函数3.管道的读写行为4..管道的优劣二.实战练习:实现ls|wc-l指令三、fifo实现非血缘关系进程间通信一、管道1.管道的特质实现原理:内核借助环形队列机制,使用内核缓冲区实现。特质:1.伪文件2.管道中的数据只能一次读取。3.数据在管道中,只能单向流动。局限性:1.自己写,不能自己读。2.数据不可以反复读。3.半双工通信。4.血缘关系
- 嵌入式Linux系统编程学习之十七计时器与信号
PoroKing
嵌入式Linux系统编程学习linux
文章目录一、睡眠函数二、时钟处理一、睡眠函数 Linux下有2个睡眠函数,原型分别为:#includeunsignedintsleep(unsignedintseconds);voidusleep(unsignedlongusec); 函数sleep让进程睡眠seconds秒,函数usleep让进程睡眠usec微秒。 sleep睡眠函数内部是用信号机制进行处理的,用到的函数有:#includ
- 23国赛网络建设与运维正式赛题12.开发环境搭建和13.系统运维
南港清风i
23国赛正式赛题答案解析网络运维
开发环境搭建任务描述:实现linux系统编程开发环境搭建。在linux4上搭建开发环境。(1)利用系统iso文件,搭建c语言、c++语言、rust语言开发环境。安装C语言编译环境(GCC):yuminstallgcc安装C++语言编译环境(g++):yuminstallgcc-c++安装rust语言编译环境:#rust语言yum-yinstallrust*#验证C语言编译器gcc--version
- 七牛云测开实习一面凉经整理
软工菜鸡
面经java数据库linux七牛云面经软件测试大厂
七牛云测开实习一面凉经_牛客网23.8月可能七牛云测开实习一面凉经1.自我介绍2.为什么想做测试3.实习经历4.HashMap底层实现(1.7和1.8的区别)Java大厂面试——常见集合篇ListHashMap红黑树_javalist是连续内存吗-CSDN博客5.创建线程的方式23Java面试专题八股文面试全套真题(含大厂高频面试真题)多线程_linux系统编程多线程编程网络io编程八股文面经-C
- 【Linux系统编程应用层开发目录】介绍Linux应用层开发的知识点和文章
wkd_007
#✨LinuxC语言linuxLinux系统编程Linux应用层开发
博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/wkd_007专栏地址:LinuxC语言博客内容:嵌入式开发、Linux、C语言、C++、数据结构、音视频本文内容:介绍Linux应用层开发的知识点和文章金句分享:你不能选择最好的,但最好的会来选择你——泰戈尔目录一、Linux编程|文件操作二、Linux编程|常见操作三、Linux编程|进程相关四、Linux编程|网络编程五、预留六、预留我希
- 【C++基础】C++内存处理机制面试题(以面促学 )
X.Dragon
C++基础c++
欢迎来到C++基础专栏♀️作者介绍:前PLA队员目前是一名普通本科大三的软件工程专业学生IP坐标:湖北武汉目前技术栈:C/C++、Linux系统编程、计算机网络、数据结构、Mysql、Python(目前在学)博客介绍:通过分享学习过程,加深知识点的掌握,也希望通过平台能认识更多同僚,如果觉得文章有帮助,请您动动发财手点点赞,本人水平有限,有不足之处欢迎大家扶正~最后送大家一句话共勉:知不足而奋进
- Linux系统编程(二)文件IO/系统调用IO
Patarw_Li
Linux系统编程linux学习c语言
一、IO简介I/O是一切实现的基础:标准IO(stdio);系统调用IO(sysio,文件IO);不同系统上的系统调用IO的使用方式可能不一样,为了隐藏不同系统上的细节,提出了标准IO给程序员调用,标准IO的实现是依赖于系统调用IO的,但是标准IO的可移植性更好。文件IO都是不带缓冲的IO,而标准IO是带缓冲的IO。二、系统调用IO部分系统调用IO如下(文件描述符fd贯穿始终):open()、cl
- Linux系统编程(三)文件系统
Patarw_Li
Linux系统编程linux学习c语言
一、目录和文件1.1文件属性(stat)stat()可以通过文件名获取文件的属性。fstat()可以通过打开的文件描述符获取文件的属性。lstat()和stat()功能相同,有一点区别就是当pathname是一个符号链接文件的时候,lstat()返回的是符号链接文件本身的属性,而不是链接文件指向的文件的属性。而stat()则是返回符号链接所指向文件的属性。#include#include#incl
- 一文详细讲解 io_uring
Linux内核站
linux网络服务器内核io_uring
前言Linux内核5.1支持了新的异步IO框架iouring,由BlockIO大神也即Fio作者JensAxboe开发,意在提供一套公用的网络和磁盘异步IO,不过io_uring目前在磁盘方面要比网络方面更加成熟。背景简介熟悉Linux系统编程的同学都清楚,Linux并没有提供完善的异步IO(网络IO、磁盘IO)机制。在网络编程中,我们通常使用epollIO多路复用来处理网络IO,然而epoll也
- java工厂模式
3213213333332132
java抽象工厂
工厂模式有
1、工厂方法
2、抽象工厂方法。
下面我的实现是抽象工厂方法,
给所有具体的产品类定一个通用的接口。
package 工厂模式;
/**
* 航天飞行接口
*
* @Description
* @author FuJianyong
* 2015-7-14下午02:42:05
*/
public interface SpaceF
- nginx频率限制+python测试
ronin47
nginx 频率 python
部分内容参考:http://www.abc3210.com/2013/web_04/82.shtml
首先说一下遇到这个问题是因为网站被攻击,阿里云报警,想到要限制一下访问频率,而不是限制ip(限制ip的方案稍后给出)。nginx连接资源被吃空返回状态码是502,添加本方案限制后返回599,与正常状态码区别开。步骤如下:
- java线程和线程池的使用
dyy_gusi
ThreadPoolthreadRunnabletimer
java线程和线程池
一、创建多线程的方式
java多线程很常见,如何使用多线程,如何创建线程,java中有两种方式,第一种是让自己的类实现Runnable接口,第二种是让自己的类继承Thread类。其实Thread类自己也是实现了Runnable接口。具体使用实例如下:
1、通过实现Runnable接口方式 1 2
- Linux
171815164
linux
ubuntu kernel
http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.1.2-unstable/
安卓sdk代理
mirrors.neusoft.edu.cn 80
输入法和jdk
sudo apt-get install fcitx
su
- Tomcat JDBC Connection Pool
g21121
Connection
Tomcat7 抛弃了以往的DBCP 采用了新的Tomcat Jdbc Pool 作为数据库连接组件,事实上DBCP已经被Hibernate 所抛弃,因为他存在很多问题,诸如:更新缓慢,bug较多,编译问题,代码复杂等等。
Tomcat Jdbc P
- 敲代码的一点想法
永夜-极光
java随笔感想
入门学习java编程已经半年了,一路敲代码下来,现在也才1w+行代码量,也就菜鸟水准吧,但是在整个学习过程中,我一直在想,为什么很多培训老师,网上的文章都是要我们背一些代码?比如学习Arraylist的时候,教师就让我们先参考源代码写一遍,然
- jvm指令集
程序员是怎么炼成的
jvm 指令集
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/hudashi/article/details/7062675#comments
将值推送至栈顶时 const ldc push load指令
const系列
该系列命令主要负责把简单的数值类型送到栈顶。(从常量池或者局部变量push到栈顶时均使用)
0x02 &nbs
- Oracle字符集的查看查询和Oracle字符集的设置修改
aijuans
oracle
本文主要讨论以下几个部分:如何查看查询oracle字符集、 修改设置字符集以及常见的oracle utf8字符集和oracle exp 字符集问题。
一、什么是Oracle字符集
Oracle字符集是一个字节数据的解释的符号集合,有大小之分,有相互的包容关系。ORACLE 支持国家语言的体系结构允许你使用本地化语言来存储,处理,检索数据。它使数据库工具,错误消息,排序次序,日期,时间,货
- png在Ie6下透明度处理方法
antonyup_2006
css浏览器FirebugIE
由于之前到深圳现场支撑上线,当时为了解决个控件下载,我机器上的IE8老报个错,不得以把ie8卸载掉,换个Ie6,问题解决了,今天出差回来,用ie6登入另一个正在开发的系统,遇到了Png图片的问题,当然升级到ie8(ie8自带的开发人员工具调试前端页面JS之类的还是比较方便的,和FireBug一样,呵呵),这个问题就解决了,但稍微做了下这个问题的处理。
我们知道PNG是图像文件存储格式,查询资
- 表查询常用命令高级查询方法(二)
百合不是茶
oracle分页查询分组查询联合查询
----------------------------------------------------分组查询 group by having --平均工资和最高工资 select avg(sal)平均工资,max(sal) from emp ; --每个部门的平均工资和最高工资
- uploadify3.1版本参数使用详解
bijian1013
JavaScriptuploadify3.1
使用:
绑定的界面元素<input id='gallery'type='file'/>$("#gallery").uploadify({设置参数,参数如下});
设置的属性:
id: jQuery(this).attr('id'),//绑定的input的ID
langFile: 'http://ww
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(17)使用ORACLE系统包
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*使用ORACLE系统包
*/
--1.DBMS_OUTPUT
--ENABLE:用于激活过程PUT,PUT_LINE,NEW_LINE,GET_LINE和GET_LINES的调用
--语法:DBMS_OUTPUT.enable(buffer_size in integer default 20000);
--DISABLE:用于禁止对过程PUT,PUT_LINE,NEW
- 【JVM一】JVM垃圾回收日志
bit1129
垃圾回收
将JVM垃圾回收的日志记录下来,对于分析垃圾回收的运行状态,进而调整内存分配(年轻代,老年代,永久代的内存分配)等是很有意义的。JVM与垃圾回收日志相关的参数包括:
-XX:+PrintGC
-XX:+PrintGCDetails
-XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps
-XX:+PrintGCDateStamps
-Xloggc
-XX:+PrintGC
通
- Toast使用
白糖_
toast
Android中的Toast是一种简易的消息提示框,toast提示框不能被用户点击,toast会根据用户设置的显示时间后自动消失。
创建Toast
两个方法创建Toast
makeText(Context context, int resId, int duration)
参数:context是toast显示在
- angular.identity
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS API
angular.identiy 描述: 返回它第一参数的函数. 此函数多用于函数是编程. 使用方法: angular.identity(value); 参数详解: Param Type Details value
*
to be returned. 返回值: 传入的value 实例代码:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
- java-两整数相除,求循环节
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CircleDigitsInDivision {
/**
* 题目:求循环节,若整除则返回NULL,否则返回char*指向循环节。先写思路。函数原型:char*get_circle_digits(unsigned k,unsigned j)
- Java 日期 周 年
Chen.H
javaC++cC#
/**
* java日期操作(月末、周末等的日期操作)
*
* @author
*
*/
public class DateUtil {
/** */
/**
* 取得某天相加(减)後的那一天
*
* @param date
* @param num
*
- [高考与专业]欢迎广大高中毕业生加入自动控制与计算机应用专业
comsci
计算机
不知道现在的高校还设置这个宽口径专业没有,自动控制与计算机应用专业,我就是这个专业毕业的,这个专业的课程非常多,既要学习自动控制方面的课程,也要学习计算机专业的课程,对数学也要求比较高.....如果有这个专业,欢迎大家报考...毕业出来之后,就业的途径非常广.....
以后
- 分层查询(Hierarchical Queries)
daizj
oracle递归查询层次查询
Hierarchical Queries
If a table contains hierarchical data, then you can select rows in a hierarchical order using the hierarchical query clause:
hierarchical_query_clause::=
start with condi
- 数据迁移
daysinsun
数据迁移
最近公司在重构一个医疗系统,原来的系统是两个.Net系统,现需要重构到java中。数据库分别为SQL Server和Mysql,现需要将数据库统一为Hana数据库,发现了几个问题,但最后通过努力都解决了。
1、原本通过Hana的数据迁移工具把数据是可以迁移过去的,在MySQl里面的字段为TEXT类型的到Hana里面就存储不了了,最后不得不更改为clob。
2、在数据插入的时候有些字段特别长
- C语言学习二进制的表示示例
dcj3sjt126com
cbasic
进制的表示示例
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 0x32C;
printf("i = %d\n", i);
/*
printf的用法
%d表示以十进制输出
%x或%X表示以十六进制的输出
%o表示以八进制输出
*/
return 0;
}
- NsTimer 和 UITableViewCell 之间的控制
dcj3sjt126com
ios
情况是这样的:
一个UITableView, 每个Cell的内容是我自定义的 viewA viewA上面有很多的动画, 我需要添加NSTimer来做动画, 由于TableView的复用机制, 我添加的动画会不断开启, 没有停止, 动画会执行越来越多.
解决办法:
在配置cell的时候开始动画, 然后在cell结束显示的时候停止动画
查找cell结束显示的代理
- MySql中case when then 的使用
fanxiaolong
casewhenthenend
select "主键", "项目编号", "项目名称","项目创建时间", "项目状态","部门名称","创建人"
union
(select
pp.id as "主键",
pp.project_number as &
- Ehcache(01)——简介、基本操作
234390216
cacheehcache简介CacheManagercrud
Ehcache简介
目录
1 CacheManager
1.1 构造方法构建
1.2 静态方法构建
2 Cache
2.1&
- 最容易懂的javascript闭包学习入门
jackyrong
JavaScript
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2009/08/learning_javascript_closures.html
闭包(closure)是Javascript语言的一个难点,也是它的特色,很多高级应用都要依靠闭包实现。
下面就是我的学习笔记,对于Javascript初学者应该是很有用的。
一、变量的作用域
要理解闭包,首先必须理解Javascript特殊
- 提升网站转化率的四步优化方案
php教程分享
数据结构PHP数据挖掘Google活动
网站开发完成后,我们在进行网站优化最关键的问题就是如何提高整体的转化率,这也是营销策略里最最重要的方面之一,并且也是网站综合运营实例的结果。文中分享了四大优化策略:调查、研究、优化、评估,这四大策略可以很好地帮助用户设计出高效的优化方案。
PHP开发的网站优化一个网站最关键和棘手的是,如何提高整体的转化率,这是任何营销策略里最重要的方面之一,而提升网站转化率是网站综合运营实力的结果。今天,我就分
- web开发里什么是HTML5的WebSocket?
naruto1990
Webhtml5浏览器socket
当前火起来的HTML5语言里面,很多学者们都还没有完全了解这语言的效果情况,我最喜欢的Web开发技术就是正迅速变得流行的 WebSocket API。WebSocket 提供了一个受欢迎的技术,以替代我们过去几年一直在用的Ajax技术。这个新的API提供了一个方法,从客户端使用简单的语法有效地推动消息到服务器。让我们看一看6个HTML5教程介绍里 的 WebSocket API:它可用于客户端、服
- Socket初步编程——简单实现群聊
Everyday都不同
socket网络编程初步认识
初次接触到socket网络编程,也参考了网络上众前辈的文章。尝试自己也写了一下,记录下过程吧:
服务端:(接收客户端消息并把它们打印出来)
public class SocketServer {
private List<Socket> socketList = new ArrayList<Socket>();
public s
- 面试:Hashtable与HashMap的区别(结合线程)
toknowme
昨天去了某钱公司面试,面试过程中被问道
Hashtable与HashMap的区别?当时就是回答了一点,Hashtable是线程安全的,HashMap是线程不安全的,说白了,就是Hashtable是的同步的,HashMap不是同步的,需要额外的处理一下。
今天就动手写了一个例子,直接看代码吧
package com.learn.lesson001;
import java
- MVC设计模式的总结
xp9802
设计模式mvc框架IOC
随着Web应用的商业逻辑包含逐渐复杂的公式分析计算、决策支持等,使客户机越
来越不堪重负,因此将系统的商业分离出来。单独形成一部分,这样三层结构产生了。
其中‘层’是逻辑上的划分。
三层体系结构是将整个系统划分为如图2.1所示的结构[3]
(1)表现层(Presentation layer):包含表示代码、用户交互GUI、数据验证。
该层用于向客户端用户提供GUI交互,它允许用户