Cocos2Dx之触控处理-欧阳左至
在上个章节中,我们已经看到了Win 32的消息泵驱动CCDirector在每个帧间隔时间到期后,调用mainLoop。但是对于触控事件,它同样是操作系统上报给应用的事件,我们没有看到它的踪迹。事实上,对于触控事件、键盘事件、应用相关的事件,比如关闭、转为背景应用等,都是放在Win 32的窗口回调函数当中处理的。
在AppDelegate::applicationDidFinishLaunching() 里面,我们会调用CCEGLView::sharedOpenGLView()来得到一个GLView。GLView在不同的平台上实现是不一样的,我们先看看Win 32上的实现。CCEGLView::sharedOpenGLView()先构造一个CCEGLView对象,并作一些简单的变量初始化,然后调用CCEGLView的Create()来真正创建一个窗口,用于游戏图像的绘制。
CCEGLView::Create()在前一个章节我们已经看到过。需要注意的是在初始化窗口类(WNDCLASS)的时候,将wc.lpfnWndProc赋值为_WindowProc。_WindowProc是一个C的封装函数,实际上调用的是CCEGLView::WindowProc。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
|
//file: cocos2dx\platform\win32\CCEGLView.cpp
LRESULT
CCEGLView::WindowProc(
UINT
message,
WPARAM
wParam,
LPARAM
lParam)
{
BOOL
bProcessed = FALSE;
switch
(message)
{
case
WM_LBUTTONDOWN:
if
(m_pDelegate && MK_LBUTTON == wParam)
{
...
if
(m_obViewPortRect.equals(CCRectZero) || m_obViewPortRect.containsPoint(tmp))
{
m_bCaptured =
true
;
SetCapture(m_hWnd);
...
handleTouchesBegin(1, &id, &pt.x, &pt.y);
}
}
break
;
case
WM_MOUSEMOVE:
if
(MK_LBUTTON == wParam && m_bCaptured)
{
...
handleTouchesMove(1, &id, &pt.x, &pt.y);
}
break
;
case
WM_LBUTTONUP:
if
(m_bCaptured)
{
...
handleTouchesEnd(1, &id, &pt.x, &pt.y);
ReleaseCapture();
m_bCaptured =
false
;
}
break
;
#if(_MSC_VER >= 1600)
case
WM_TOUCH:
{
...
PTOUCHINPUT pInputs =
new
TOUCHINPUT[cInputs];
if
(pInputs)
{
if
(s_pfGetTouchInputInfoFunction((HTOUCHINPUT)lParam, cInputs, pInputs,
sizeof
(TOUCHINPUT)))
{
for
(
UINT
i=0; i < cInputs; i++)
{
if
(m_obViewPortRect.equals(CCRectZero) || m_obViewPortRect.containsPoint(tmp))
{
if
(ti.dwFlags & TOUCHEVENTF_DOWN)
handleTouchesBegin(1,
reinterpret_cast
<
int
*>(&ti.dwID), &pt.x, &pt.y);
else
if
(ti.dwFlags & TOUCHEVENTF_MOVE)
handleTouchesMove(1,
reinterpret_cast
<
int
*>(&ti.dwID), &pt.x, &pt.y);
else
if
(ti.dwFlags & TOUCHEVENTF_UP)
handleTouchesEnd(1,
reinterpret_cast
<
int
*>(&ti.dwID), &pt.x, &pt.y);
}
}
bHandled = TRUE;
}
delete
[] pInputs;
}
if
(bHandled)
{
s_pfCloseTouchInputHandleFunction((HTOUCHINPUT)lParam);
}
}
break
;
#endif /* #if(_MSC_VER >= 1600) */
case
WM_SIZE:
switch
(wParam)
{
case
SIZE_RESTORED:
CCApplication::sharedApplication()->applicationWillEnterForeground();
break
;
case
SIZE_MINIMIZED:
CCApplication::sharedApplication()->applicationDidEnterBackground();
break
;
}
break
;
case
WM_KEYDOWN:
...
case
WM_KEYUP:
...
break
;
case
WM_CHAR:
...
break
;
case
WM_PAINT:
...
break
;
case
WM_CLOSE:
CCDirector::sharedDirector()->end();
break
;
case
WM_DESTROY:
destroyGL();
PostQuitMessage(0);
break
;
}
}
|
通过Windows来编写Cocos2Dx游戏,可能大部分Windows电脑并没有提供触摸屏。Cocos2Dx通过鼠标事件进行了模拟。WM_LBUTTONDOWN被看做是触摸动作的开始,WM_MOUSEMOVE看做是触摸移动,WM_LBUTTONUP被看做是触摸动作的结束。对于单点触摸,这样的设计是合理的,但是鼠标不能模拟多点触摸。
触控事件携带的触控数据有一个非常重要的成员:触控点标示符。因为可能存在多点触控发生,每个触控点都需要一个标示符。它对应到CCEGLViewProtocol的触控处理函数,就是第二个参数ids[]。所有鼠标模拟的触控事件,它们的触控点标示符都是0。对于真正的触控事件,会从系统上报的消息数据中获取。需要注意的是,现在的Cocos2Dx版本是2.2.3,对于所有的多点触控事件,Cocos2Dx还是把它们分开单独处理的。
上面的窗口回调函数,还告诉了我们,什么时候调用AppDelegate的applicationWillEnterForeground()和applicationDidEnterBackground()函数,什么时候调用CCDirector的end()函数。
CCEGLView::WindowProc根据收到的不同的系统事件,分别调用handleTouchesBegin、handleTouchesMove和handleTouchesEnd来分发触控消息。注意,没有handleTouchesCancel。这几个函数来自于CCEGLView继承的父类CCEGLViewProtocol。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
void
CCEGLViewProtocol::handleTouchesBegin(
int
num,
int
ids[],
float
xs[],
float
ys[])
{
CCSet set;
for
(
int
i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
int
id = ids[i];
float
x = xs[i];
float
y = ys[i];
CCInteger* pIndex = (CCInteger*)s_TouchesIntergerDict.objectForKey(id);
int
nUnusedIndex = 0;
if
(pIndex == NULL)
{
nUnusedIndex = getUnUsedIndex();
CCTouch* pTouch = s_pTouches[nUnusedIndex] =
new
CCTouch();
pTouch->setTouchInfo(nUnusedIndex, (x - m_obViewPortRect.origin.x) / m_fScaleX, (y - m_obViewPortRect.origin.y) / m_fScaleY);
CCInteger* pInterObj =
new
CCInteger(nUnusedIndex);
s_TouchesIntergerDict.setObject(pInterObj, id);
set.addObject(pTouch);
pInterObj->release();
}
}
m_pDelegate->touchesBegan(&set, NULL);
}
|
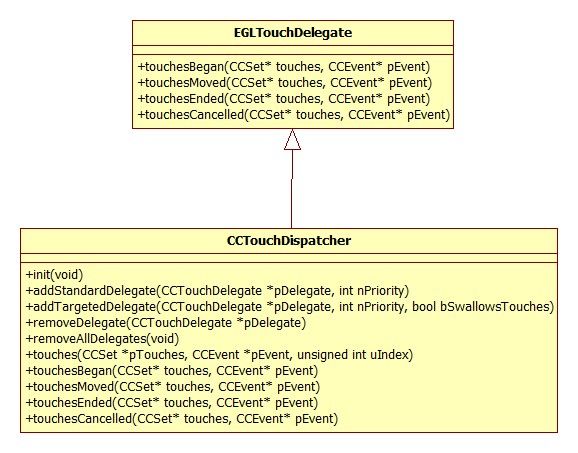
发送给CCEGLViewProtocol的触摸处理函数的触控点位置已经在CCEGLView::WindowProc转换为像素单位。CCEGLViewProtocol::handleTouchesBegin首先在全局变量s_TouchesIntergerDict中根据触控标示符查找一个索引,该索引指向了触控对象CCTouch在全局数组s_pTouches中的位置。s_TouchesIntergerDict是Cocos2Dx自己的一个键值容器。如果在s_TouchesIntergerDict查到的索引值不为空,意味着handleTouchesBegin处理的并不是一个新的触控,系统出错,错误处理相关的代码已经被删除了。否则,这是一个新的触控,我们需要处理。首先去获取一个尚未被使用的s_pTouches索引。然后构造兵初始化一个CCTouch对象,将对象在s_pTouches数组的索引存放到s_TouchesIntergerDict。最后将CCTouch对象添加到CCSet对象中。在完成所有数据的处理后,调用EGLTouchDelegate的touchesBegan函数。EGLTouchDelegate是在我们调用CCDirector的setOpenGLView(pEGLView)函数时设置的。CCDirector在初始化函数init()中,设置m_pTouchDispatcher = new CCTouchDispatcher()。setOpenGLView再将CCDirector自己的m_pTouchDispatcher,通过CCEGLView的setTouchDelegate注册到CCEGLView里面。因此,最后调用的是CCTouchDispatcher的touchesBegan函数。
CCTouchDispatcher继承自EGLTouchDelegate接口。
回过头来,我们继续看CCEGLViewProtocol的handleTouchesMove、handleTouchesEnd和handleTouchesCancel的实现。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
void
CCEGLViewProtocol::handleTouchesMove(
int
num,
int
ids[],
float
xs[],
float
ys[])
{
CCSet set;
for
(
int
i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
int
id = ids[i];
float
x = xs[i];
float
y = ys[i];
CCInteger* pIndex = (CCInteger*)s_TouchesIntergerDict.objectForKey(id);
CCTouch* pTouch = s_pTouches[pIndex->getValue()];
if
(pTouch)
{
pTouch->setTouchInfo(pIndex->getValue(), (x - m_obViewPortRect.origin.x) / m_fScaleX,(y - m_obViewPortRect.origin.y) / m_fScaleY);
set.addObject(pTouch);
}
}
m_pDelegate->touchesMoved(&set, NULL);
}
|
CCEGLViewProtocol的handleTouchesMove函数首先从全局字典s_TouchesIntergerDict中,根据触控点标示符找到CCTouch对象的索引。然后从全局的CCTouch数组s_pTouches中取出对应的CCTouch对象。handleTouchesMove执行之前,肯定执行过handleTouchesBegin,字典和数组里面一定存在一个拥有相同触控标示符的CCTouch对象。取出CCTouch后,将位置信息更新为当前的位置信息。然后添加到CCSet中,最后调用CCTouchDispatcher的touchesMoved函数。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
void
CCEGLViewProtocol::handleTouchesEnd(
int
num,
int
ids[],
float
xs[],
float
ys[])
{
CCSet set;
getSetOfTouchesEndOrCancel(set, num, ids, xs, ys);
m_pDelegate->touchesEnded(&set, NULL);
}
void
CCEGLViewProtocol::getSetOfTouchesEndOrCancel(CCSet& set,
int
num,
int
ids[],
float
xs[],
float
ys[])
{
for
(
int
i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
int
id = ids[i];
float
x = xs[i];
float
y = ys[i];
CCInteger* pIndex = (CCInteger*)s_TouchesIntergerDict.objectForKey(id);
CCTouch* pTouch = s_pTouches[pIndex->getValue()];
if
(pTouch)
{
pTouch->setTouchInfo(pIndex->getValue(), (x - m_obViewPortRect.origin.x) / m_fScaleX,(y - m_obViewPortRect.origin.y) / m_fScaleY);
set.addObject(pTouch);
pTouch->release();
s_pTouches[pIndex->getValue()] = NULL;
removeUsedIndexBit(pIndex->getValue());
s_TouchesIntergerDict.removeObjectForKey(id);
}
}
}
|
CCEGLViewProtocol的handleTouchesEnd函数,同样先从字典查找索引,然后根据索引获取指定触控标示符的CCTouch对象。然后更新位置信息,调用CCTouchDispatcher的touchesEnded函数。handleTouchesEnd意味着,触控操作已经结束,我们需要做一些资源释放的工作:调用CCTouch的release()释放其占用的内存;将数组s_pTouches的对应位置置空,最后从字典中清除。
可以观察到,CCTouchDispatcher的触控处理函数的第二个参数CCEvent并没有使用。
现在我们走到CCTouchDispatcher了,休息一下,回头看看Android是怎么工作的。
Cocos2dxRenderer继承自GLSurfaceView.Renderer,它里面定义了四个触控相关的函数。这些函数最后会在Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView中被调用。Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView继承自GLSurfaceView,而GLSurfaceView又继承自android.view.SurfaceView,后者继承自android.view.View。android.view.View有一个可被重载的函数onTouchEvent来处理触控事件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
//file: cocos2dx\platform\android\java\src\org\cocos2dx\lib\Cocos2dxRenderer.java
public
void
handleActionDown(
final
int
pID,
final
float
pX,
final
float
pY) {
Cocos2dxRenderer.nativeTouchesBegin(pID, pX, pY);
}
public
void
handleActionUp(
final
int
pID,
final
float
pX,
final
float
pY) {
Cocos2dxRenderer.nativeTouchesEnd(pID, pX, pY);
}
public
void
handleActionCancel(
final
int
[] pIDs,
final
float
[] pXs,
final
float
[] pYs) {
Cocos2dxRenderer.nativeTouchesCancel(pIDs, pXs, pYs);
}
public
void
handleActionMove(
final
int
[] pIDs,
final
float
[] pXs,
final
float
[] pYs) {
Cocos2dxRenderer.nativeTouchesMove(pIDs, pXs, pYs);
}
|
分别是直接去调用了本地方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
//file: cocos2dx\platform\android\jni\TouchesJni.cpp
JNIEXPORT
void
JNICALL Java_org_cocos2dx_lib_Cocos2dxRenderer_nativeTouchesBegin(JNIEnv * env, jobject thiz, jint id, jfloat x, jfloat y) {
cocos2d::CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getOpenGLView()->handleTouchesBegin(1, &id, &x, &y);
}
JNIEXPORT
void
JNICALL Java_org_cocos2dx_lib_Cocos2dxRenderer_nativeTouchesEnd(JNIEnv * env, jobject thiz, jint id, jfloat x, jfloat y) {
cocos2d::CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getOpenGLView()->handleTouchesEnd(1, &id, &x, &y);
}
JNIEXPORT
void
JNICALL Java_org_cocos2dx_lib_Cocos2dxRenderer_nativeTouchesMove(JNIEnv * env, jobject thiz, jintArray ids, jfloatArray xs, jfloatArray ys) {
int
size = env->GetArrayLength(ids);
jint id[size];
jfloat x[size];
jfloat y[size];
env->GetIntArrayRegion(ids, 0, size, id);
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(xs, 0, size, x);
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(ys, 0, size, y);
cocos2d::CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getOpenGLView()->handleTouchesMove(size, id, x, y);
}
JNIEXPORT
void
JNICALL Java_org_cocos2dx_lib_Cocos2dxRenderer_nativeTouchesCancel(JNIEnv * env, jobject thiz, jintArray ids, jfloatArray xs, jfloatArray ys) {
int
size = env->GetArrayLength(ids);
jint id[size];
jfloat x[size];
jfloat y[size];
env->GetIntArrayRegion(ids, 0, size, id);
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(xs, 0, size, x);
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(ys, 0, size, y);
cocos2d::CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getOpenGLView()->handleTouchesCancel(size, id, x, y);
}
|
Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView重写了android.view.View的onTouchEvent函数。Android上面的多点触控就是直接发送的,没有像Win 32一样分开发送。代码非常直观,我们就不分析了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
//file: cocos2dx\platform\android\java\src\org\cocos2dx\lib\Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView.java
@Override
public
boolean
onTouchEvent(
final
MotionEvent pMotionEvent) {
final
int
pointerNumber = pMotionEvent.getPointerCount();
final
int
[] ids =
new
int
[pointerNumber];
final
float
[] xs =
new
float
[pointerNumber];
final
float
[] ys =
new
float
[pointerNumber];
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < pointerNumber; i++) {
ids[i] = pMotionEvent.getPointerId(i);
xs[i] = pMotionEvent.getX(i);
ys[i] = pMotionEvent.getY(i);
}
switch
(pMotionEvent.getAction() & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK) {
case
MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN:
final
int
indexPointerDown = pMotionEvent.getAction() >> MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_ID_SHIFT;
final
int
idPointerDown = pMotionEvent.getPointerId(indexPointerDown);
final
float
xPointerDown = pMotionEvent.getX(indexPointerDown);
final
float
yPointerDown = pMotionEvent.getY(indexPointerDown);
this
.queueEvent(
new
Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run() {
Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView.
this
.mCocos2dxRenderer.handleActionDown(idPointerDown, xPointerDown, yPointerDown);
}
});
break
;
case
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// there are only one finger on the screen
final
int
idDown = pMotionEvent.getPointerId(
0
);
final
float
xDown = xs[
0
];
final
float
yDown = ys[
0
];
this
.queueEvent(
new
Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run() {
Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView.
this
.mCocos2dxRenderer.handleActionDown(idDown, xDown, yDown);
}
});
break
;
case
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
this
.queueEvent(
new
Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run() {
Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView.
this
.mCocos2dxRenderer.handleActionMove(ids, xs, ys);
}
});
break
;
case
MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP:
final
int
indexPointUp = pMotionEvent.getAction() >> MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_ID_SHIFT;
final
int
idPointerUp = pMotionEvent.getPointerId(indexPointUp);
final
float
xPointerUp = pMotionEvent.getX(indexPointUp);
final
float
yPointerUp = pMotionEvent.getY(indexPointUp);
this
.queueEvent(
new
Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run() {
Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView.
this
.mCocos2dxRenderer.handleActionUp(idPointerUp, xPointerUp, yPointerUp);
}
});
break
;
case
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
// there are only one finger on the screen
final
int
idUp = pMotionEvent.getPointerId(
0
);
final
float
xUp = xs[
0
];
final
float
yUp = ys[
0
];
this
.queueEvent(
new
Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run() {
Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView.
this
.mCocos2dxRenderer.handleActionUp(idUp, xUp, yUp);
}
});
break
;
case
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
this
.queueEvent(
new
Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run() {
Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView.
this
.mCocos2dxRenderer.handleActionCancel(ids, xs, ys);
}
});
break
;
}
return
true
;
}
|
继续CCTouchDispatcher分析。
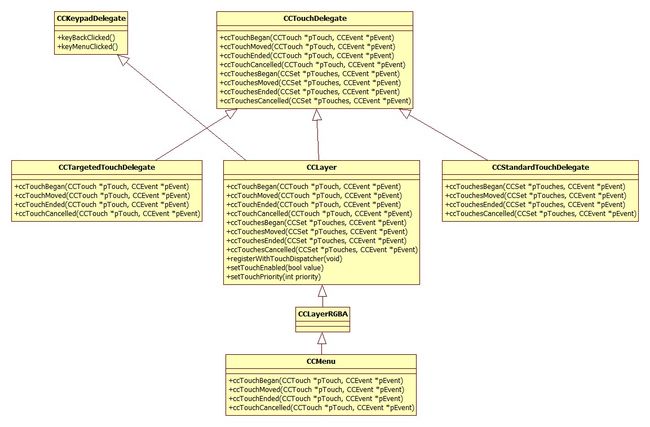
CCTouchDispatcher负责分发CCEGLView报来的触控消息。谁对触控消息感兴趣,就需要创建一个委托,然后注册到CCTouchDispatcher当中。CCTouchDelegate定义了委托应该实现的接口。创建我们的委托,需要做的就是继承并实现CCTouchDelegate的几个触控接口。由于CCTouchDispatcher的实例是被CCDirector持有的,我们需要通过CCDirector::getTouchDispatcher()来获取CCTouchDispatcher的实例,然后调用CCTouchDispatcher的注册函数:addStandardDelegate或者addTargetedDelegate。CCLayer是一个很好的例子。
CCLayer继承自CCTouchDelegate,自己拥有了处理触控事件的能力。为了真正能够接受到触控消息,我们还需要将CCLayer注册到CCTouchDispatcher当中。CCLayer默认是不做进行注册的。如果我们想自己创建CCLayer能够接收到触控消息,需要调用CCLayer::setTouchEnabled(bool enabled),参数指定我们是开启还是关闭触控。如果传入参数为true,调用CCLayer自己的registerWithTouchDispatcher函数,否则调用CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getTouchDispatcher()->removeDelegate(this)将自己从CCTouchDispatcher取消掉。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
void
CCLayer::registerWithTouchDispatcher()
{
CCTouchDispatcher* pDispatcher = CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getTouchDispatcher();
if
( m_eTouchMode == kCCTouchesAllAtOnce ) {
pDispatcher->addStandardDelegate(
this
, 0);
}
else
{
pDispatcher->addTargetedDelegate(
this
, m_nTouchPriority,
true
);
}
}
typedef
enum
{
kCCTouchesAllAtOnce,
kCCTouchesOneByOne,
} ccTouchesMode;
|
m_eTouchMode类型是一个枚举ccTouchesMode,kCCTouchesAllAtOnce意思将触控消息分发给所有的已经注册的委托者。kCCTouchesOneByOne意思是将触控消息按照委托者的优先级依次分发,排在前面的委托者可以决定是否继续分发消息。对应到CCTouchDispatcher提供的注册函数,kCCTouchesAllAtOnce是标准委托,注册函数为addStandardDelegate;kCCTouchesOneByOne是带目标的委托,注册函数为addTargetedDelegate。
这里看到的只是CCLayer的提供的实现,我们完全可以自己创建自己的委托者,然后直接调用CCTouchDispatcher提供的注册函数。
前面我们从操作系统理到了CCTouchDispatcher,然后又从开发者的角度理到了CCTouchDispatcher。是时候看CCTouchDispatcher这一个负责触控事件分发的核心类了。
CCTouchDispatcher继承自EGLTouchDelegate,自己定义的委托者继承自CCTouchDelegate。前者是从GL View的角度来看待触控处理 设计,后者是从Cocos2Dx的角度来看,符合Cocos2Dx使用很多的Protocol风格。虽然两者非常相似,可以合并。但这种角度上的分离仁者见仁智者见智了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
void
CCTouchDispatcher::addStandardDelegate(CCTouchDelegate *pDelegate,
int
nPriority)
{
CCTouchHandler *pHandler = CCStandardTouchHandler::handlerWithDelegate(pDelegate, nPriority);
if
(! m_bLocked)
{
forceAddHandler(pHandler, m_pStandardHandlers);
}
else
{
if
(ccCArrayContainsValue(m_pHandlersToRemove, pDelegate))
{
ccCArrayRemoveValue(m_pHandlersToRemove, pDelegate);
return
;
}
m_pHandlersToAdd->addObject(pHandler);
m_bToAdd =
true
;
}
|