APK安装流程系列文章整体内容如下:
- APK安装流程详解0——前言
- APK安装流程详解1——有关"安装ing"的实体类概述
- APK安装流程详解2——PackageManager简介
- APK安装流程详解3——PackageManager与PackageManagerService
- APK安装流程详解4——安装中关于so库的那些事
- APK安装流程详解5——PackageInstallerService和Installer
- APK安装流程详解6——PackageManagerService启动前奏
- APK安装流程详解7——PackageManagerService的启动流程(上)
- APK安装流程详解8——PackageManagerService的启动流程(下)
- APK安装流程详解9——PackageParser解析APK(上)
- APK安装流程详解10——PackageParser解析APK(下)
- APK安装流程详解11——普通应用安装简介
- APK安装流程详解12——PackageManagerService中的新安装流程上(拷贝)
- APK安装流程详解13——PackageManagerService中的新安装流程下(装载)
- APK安装流程详解14——PMS中的新安装流程上(拷贝)补充
- APK安装流程详解15——PMS中的新安装流程下(装载)补充
- APK安装流程详解16——Android包管理总结(尚未完结请期待)
本片文章的主要内容如下:
- 1、PackageManagerService的启动概述
- 2、PackageManagerService的启动之SystemServer部分
- 3、PackageManagerService的启动之PackageManagerService部分
- 4、PackageManagerService#scanDirLI(File dir, final int parseFlags, int scanFlags, long currentTime)方法解析
一、PackageManagerService的启动概述
PackageManager在启动时会扫描所有的APK文件和jar包,然后把他们的信息读取出来,保存在内存中,这样系统运行时就能迅速找到各种应用和组件的信息。扫描中如果遇到没有优化过的文件还要进行优化工作(dex格式转换成oat格式(Android 5.0以前是odex)),优化后的文件放在/data/dalvik-cache/下面
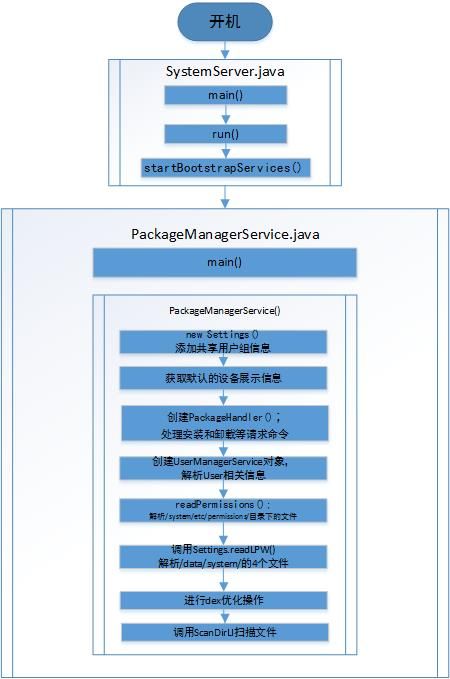
PackageManagerService的启动流程如下图:
我把PackageManagerService分为两个部分:
- 1、SystemServer部分
- 2、PackageManagerService部分
二、PackageManagerService的启动之SystemServer部分
在Android系统开机启动的时候会调用SystemServer的main方法
1、SystemServer#main(String[])方法
代码在SystemServer.java 176行
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
我们看到在SystemServer的main方法里面主要是做了两件事
- 第一步:new了一个SystemServer对象
- 第二步:调用这个SystemServer对象的run()方法
2、SystemServer无参构造函数
代码在SystemServer.java 167行
public SystemServer() {
// Check for factory test mode.
mFactoryTestMode = FactoryTest.getMode();
}
我们看到在SystemServer无参构造函数里面就是初始化mFactoryTestMode
3、SystemServer的run方法
代码在SystemServer.java 176行
private void run() {
// If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
// APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
// java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
// hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it shortly.
// 时间修复 ,如果设备的时钟是在1970年之前,则修复它
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
// "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
// using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
// AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
// and system apps are allowed to set them.
//
// NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
// core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
// 系统语言设置
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// Here we go!
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
// the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
// property so that it is in sync. We can't do this in
// libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
// had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
// running as root and we need to be the system user to set
// the property. http://b/11463182
// 设置系统属性
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
// Enable the sampling profiler.
// 启动采样分析器
if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer = new Timer();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
}
}, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
}
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
// 清空内存
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
// 由于system server一直在运行,所以它需要更多的内存
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
// 确保指纹识别初始化
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
// 设置用户权限设置,如果没有显示指定用户,则无法访问System Server
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
// 确保 binder 请求 进入系统后,一直在前台运行。
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
// 设置 优先级
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Initialize native services.
// 初始化 native 服务
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
// 检查上次的关机是否失败
performPendingShutdown();
// Initialize the system context.
// 初始化系统的Context
createSystemContext();
// Create the system service manager.
// 创建SystemServiceManager
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Start services.
try {
// 这里会开启PackageManagerService,下面会详解
startBootstrapServices();
// 开启系统核心服务,里面会开启BatteryService和UsageStatsService和WebViewUpdateService
startCoreServices();
// 开启一系列Service
startOtherServices();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
}
// For debug builds, log event loop stalls to dropbox for analysis.
if (StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging()) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Enabled StrictMode for system server main thread.");
}
// Loop forever.
// 开启循环
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
这个方法内部我已经添加注释了,这里面主要是调用startBootstrapServices()方法,那我们就来看下这里面的具体实现
4、SystemServer的startBootstrapServices方法
代码在SystemServer.java 322行
/**
* Starts the small tangle of critical services that are needed to get
* the system off the ground. These services have complex mutual dependencies
* which is why we initialize them all in one place here. Unless your service
* is also entwined in these dependencies, it should be initialized in one of
* the other functions.
*/
private void startBootstrapServices() {
// Wait for installd to finish starting up so that it has a chance to
// create critical directories such as /data/user with the appropriate
// permissions. We need this to complete before we initialize other services.
// 等待intalld完成启动,这样就有创建适当权限的的关键目录。比如
// /data/user,所以我们要在初始化其他服务之前,进行这个操作。
// 第一块
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
// Activity manager runs the show.
// 第二块
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
// Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it.
// Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready
// to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify
// the permissions for those calls).
// 第三块
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
// Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager
// initialize power management features.
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
// Manages LEDs and display backlight so we need it to bring up the display.
// 第四块
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
// Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager
// starts up.
// 第五块
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
// We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager.
// 第六块——开启PackageManagerService
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
// Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt");
if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
} else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
}
// Start the package manager.
Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
// 判断是不是第一次开机启动
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
Slog.i(TAG, "User Service");
// 第七块
ServiceManager.addService(Context.USER_SERVICE, UserManagerService.getInstance());
// Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
// Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
// 第八块
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
// The sensor service needs access to package manager service, app ops
// service, and permissions service, therefore we start it after them.
// 第九块
startSensorService();
}
有必要先讲解下注释,翻译如下:
开启一小戳重要的系统服务,因为这些系统服务相互之前有这个强耦合性,这就是我们在一个地方初始化的原因。如果你的服务和这些系统没有非常强的依赖性,建议应该在其他方法里面进行初始化。
我将startBootstrapServices方法里面的主要内容分为9块,如下图:
- 第一块:开启Installer这个Service
- 第二块:开启ActivityManagerService(Activity管理)这个Service
- 第三块:开启PowerManagerService(电力管理)这个Service
- 第四块:开启LightsService(灯光管理)这个Service
- 第五块:开启DisplayManagerService(显示器管理)这个Service
- 第六块:开启PackageManagerService(包管理)这个Service
- 第七块:SystemManager添加UserManagerService(用户管理)
- 第八块:给mActivityManagerService设置为系统进程
- 第九块:开启SensorService(传感器管理)这个Service
这里我们重点看下PackageManagerService的启动流程,如下:
// Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
// 第一步
String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt");
if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
} else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
}
// Start the package manager.
Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
// 第二步
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
启动PackageManagerService,我将其又分为两步
- 第一步:获取mOnlyCore,mOnlyCore表示仅仅是核心,因为如果我们在加密设备的时候,仅仅能跑"核心"程序。
- 第二步:调用PackageManagerService的静态main方法,这里注意传入的mOnlyCore是true。
那我们就继续看下PackageManagerService的main方法具体实现
三、PackageManagerService的启动之PackageManagerService部分
我们先来看下PackageManagerService的main方法的实现
1、PackageManagerService的main方法
代码在PackageManagerService.java 322行
public static PackageManagerService main(Context context, Installer installer,
boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) {
// 第一步
PackageManagerService m = new PackageManagerService(context, installer,
factoryTest, onlyCore);
// 第二步
ServiceManager.addService("package", m);
return m;
}
通过上面代码我们知道main方法里面主要是做了两件事:
- 第一件事情:构造一个PackageManagerService对象
- 第二件事情:调用ServiceManager.addService()方法
2、PackageManagerService的构造函数
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1801行
PackageManagerService构造函数的主要功能是,扫描Android系统中几个目标文件夹中的APK,从而建立合适的数据结构以管理诸如Package信息、四大组件信息、权限信息等信息。抽象的看,PackageManagerService就像一个加工厂,它解析实际的物理文件(APK文件)以生成符合自己要求的产品。例如,PackageManagerService将解析APK包中的AndroidManifest.xml,并根据其中声明的Activity标签来创建与此对应的对象并加以保管。
PackageManagerService的工作流程相对简单,复杂的是其中用于保存各种信息的数据结构和它们之间的关系,以及影响最终结果的策略控制(比如前面代码中的onlyCore变量,用于判断是否只扫描系统目录)。
这里代码太多了,我粘贴以后就满了。所以我就不粘贴了,我把PackageManagerService的构造函数里面的主要内容分为8个步骤
- 1、new Setting()对象,添加用户组信息
- 2、获取默认的设备展示信息
- 3、创建PackageHandler()
- 4、创建UserManagerService对象,解析User相关信息
- 5、获取权限信息
- 6、调用Settings.readLPW(),解析/data/system/的4个文件
- 7、进行dex优化操作
- 8、调用scanDirLI扫描文件
我们就来详细分析下:
2.1、new Setting()对象,添加用户组信息
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1806行
// mSdkVersion是PackageManagerService的成员变量,定义的时候进行赋值,其值取自系统属性"ro.build.version.sdk",
// 即编译的SDK版本。如果没有定义,则APK就无法知道自己运行在Android那个版本上了。
if (mSdkVersion <= 0) {
Slog.w(TAG, "**** ro.build.version.sdk not set!");
}
mContext = context;
// 设置运行模式,工厂模式是一种测试模式
mFactoryTest = factoryTest;
// onlyCore为true表示只处理系统应用,通常为false
mOnlyCore = onlyCore;
// 如果此系统是eng版,则扫描Package后,不对package做dex优化
mLazyDexOpt = "eng".equals(SystemProperties.get("ro.build.type"));
// 初始化mMetrics,存储与显示屏幕相关的一些属性,例如屏幕的宽/高尺寸,分辨率等信息
mMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
//设置UID,添加SharedUserSetting对象到Settings中,UID相同的包可以运行在同一个进程中,或者可以相互读取资源。这里添加6种系统的UID:
// system、radio、log、nfc、bluetooth和shell
mSettings = new Settings(mPackages);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.system", Process.SYSTEM_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.phone", RADIO_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.log", LOG_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.nfc", NFC_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.bluetooth", BLUETOOTH_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.shell", SHELL_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
2.2、获取默认的设备展示信息
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1830行
//dexopt缓存的时间
long dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes;
if (mLazyDexOpt) {
// 30分钟
dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes = 30; // only last 30 minutes of apps for eng builds.
} else {
// 7天
dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes = 7 * 24 * 60; // apps used in the 7 days for users.
}
// 把以分钟为单位改成毫秒级别的单位
mDexOptLRUThresholdInMills = dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes * 60 * 1000;
// 该值和调试有关,一般不设置该属性
String separateProcesses = SystemProperties.get("debug.separate_processes");
if (separateProcesses != null && separateProcesses.length() > 0) {
if ("*".equals(separateProcesses)) {
mDefParseFlags = PackageParser.PARSE_IGNORE_PROCESSES;
mSeparateProcesses = null;
Slog.w(TAG, "Running with debug.separate_processes: * (ALL)");
} else {
mDefParseFlags = 0;
mSeparateProcesses = separateProcesses.split(",");
Slog.w(TAG, "Running with debug.separate_processes: "
+ separateProcesses);
}
} else {
mDefParseFlags = 0;
mSeparateProcesses = null;
}
// 创建一个Installer对象,该对象和Native进程installd交互,后面会一篇文章专门讲解它的作用,Installer为应用安装器
mInstaller = installer;
// 构造mPackageDexOptimizer 对象
mPackageDexOptimizer = new PackageDexOptimizer(this);
// 构造MoveCallbacks对象
mMoveCallbacks = new MoveCallbacks(FgThread.get().getLooper());
// 构造OnPermissionChangeListeners对象
mOnPermissionChangeListeners = new OnPermissionChangeListeners(
FgThread.get().getLooper());
// 用系统属性来设置DisplayMetrics对象
getDefaultDisplayMetrics(context, mMetrics);
2.3、new Setting()对象,添加用户组信息
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1864行
// SystemConfig用于获取系统的全局配置信息,初始化mGlobalGids、mSystemPermissions和mAvailableFeatures
SystemConfig systemConfig = SystemConfig.getInstance();
//取出全局的groupId 保存在PackageManagerService中
mGlobalGids = systemConfig.getGlobalGids();
// 取出系统权限保存到PackageManagerService的全局变量中
mSystemPermissions = systemConfig.getSystemPermissions();
// 取出可用的feature保存在PackageManagerService的全局变量中
mAvailableFeatures = systemConfig.getAvailableFeatures();
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
// 初始化mHandlerThread
mHandlerThread = new ServiceThread(TAG,
Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND, true /*allowIo*/);
mHandlerThread.start();
// 初始化mHandler
mHandler = new PackageHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
//将mHandler加入到Watchdog检测中,安装应用可能会有大量的I/O操作会比较耗时
// 因此这里的WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT设置为10min,一般为60s或者30s
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler, WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT);
// 为/data 目录下子目录生成文件对象
File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();
// 对应 /data/data 目录: 用于存放应用数据的目录
mAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "data");
// 对应 /data/data 目录:用于存放安装的应用
mAppInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app");
// 对应 /data/app-lib 目录:用于存放 应用的native库
mAppLib32InstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-lib");
mAsecInternalPath = new File(dataDir, "app-asec").getPath();
// 对应 /data/user 目录: 用于存放用户的数据文件
mUserAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "user");
// 对应 /data/app-private 目录:存放drm保护的应用
mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-private");
2.4、创建UserManagerService对象,解析User相关信息
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1886行
// 创建用户管理服务,管理多用户
sUserManager = new UserManagerService(context, this,mInstallLock, mPackages);
创建一个UserManager对象,目前没有什么作用,但前途不可限量。根据谷歌的设想,未来手机将支持多个User,每个User将安装自己的应用,该功能的目的是Android手机推向企业用户打下基础。
2.5、获取权限信息
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1889行
// Propagate permission configuration in to package manager.
// 获取系统中定义的permissions,这些permissions从/etc/permissions目录下面读取的。
ArrayMap permConfig
= systemConfig.getPermissions();
for (int i=0; i libConfig = systemConfig.getSharedLibraries();
for (int i=0; i 2.6、调用Settings.readLPW(),解析/data/system/的4个文件
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1912行
// 读取文件 package.xml内容,解析后插到mSettings的mPackages等变量中
mRestoredSettings = mSettings.readLPw(this, sUserManager.getUsers(false), mSdkVersion, mOnlyCore);
// 设置模块来代替framework-res.apk中缺省的ResolverActivity
String customResolverActivity = Resources.getSystem().getString(
R.string.config_customResolverActivity);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(customResolverActivity)) {
customResolverActivity = null;
} else {
mCustomResolverComponentName = ComponentName.unflattenFromString(
customResolverActivity);
}
// 记录开始扫描的时间
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_SYSTEM_SCAN_START,
startTime);
// Set flag to monitor and not change apk file paths when
// scanning install directories.
// 配置扫描的参数
final int scanFlags = SCAN_NO_PATHS | SCAN_DEFER_DEX | SCAN_BOOTING | SCAN_INITIAL;
// 保存一些已经进行dex优化过的apk,比如"framework-res.apk"、Java启动类库、framework所有核心库,这部分不需要再优化
final ArraySet alreadyDexOpted = new ArraySet();
/**
* Add everything in the in the boot class path to the
* list of process files because dexopt will have been run
* if necessary during zygote startup.
*/
// 获取Java 启动类库、framework所有核心库,在init.rc文件配置
final String bootClassPath = System.getenv("BOOTCLASSPATH");
final String systemServerClassPath = System.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
// 把它们加入到已经优化集合中去
if (bootClassPath != null) {
String[] bootClassPathElements = splitString(bootClassPath, ':');
for (String element : bootClassPathElements) {
alreadyDexOpted.add(element);
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "No BOOTCLASSPATH found!");
}
// 把环境变量SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH中定义的包加入到已优化集合alreadyDexOpted
if (systemServerClassPath != null) {
String[] systemServerClassPathElements = splitString(systemServerClassPath, ':');
for (String element : systemServerClassPathElements) {
alreadyDexOpted.add(element);
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "No SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH found!");
}
final List allInstructionSets = InstructionSets.getAllInstructionSets();
final String[] dexCodeInstructionSets =
getDexCodeInstructionSets(
allInstructionSets.toArray(new String[allInstructionSets.size()]));
2.7、进行dex优化操作
代码在PackageManagerService.java 1969行
/**
* Ensure all external libraries have had dexopt run on them.
*/
// 对比当前系统的指令集,检查mSharedLibraries中记录的jar包是否需要转化成odex格式
// mSharedLibraries 变量中的动态库是通过SystemConfig.getSharedLibraries()从/etc/permissions/platform.xml中读取出来的
if (mSharedLibraries.size() > 0) {
// NOTE: For now, we're compiling these system "shared libraries"
// (and framework jars) into all available architectures. It's possible
// to compile them only when we come across an app that uses them (there's
// already logic for that in scanPackageLI) but that adds some complexity.
for (String dexCodeInstructionSet : dexCodeInstructionSets) {
for (SharedLibraryEntry libEntry : mSharedLibraries.values()) {
final String lib = libEntry.path;
if (lib == null) {
continue;
}
try {
int dexoptNeeded = DexFile.getDexOptNeeded(lib, null, dexCodeInstructionSet, false);
if (dexoptNeeded != DexFile.NO_DEXOPT_NEEDED) {
alreadyDexOpted.add(lib);
// 调用install的dexopt命令,优化后的文件放在/data/dalvik-cache/下面
mInstaller.dexopt(lib, Process.SYSTEM_UID, true, dexCodeInstructionSet, dexoptNeeded, false);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Library not found: " + lib);
} catch (IOException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot dexopt " + lib + "; is it an APK or JAR? "
+ e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
File frameworkDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "framework");
// Gross hack for now: we know this file doesn't contain any
// code, so don't dexopt it to avoid the resulting log spew.
// 把framwork-res.apk加入到已优化的列表中
alreadyDexOpted.add(frameworkDir.getPath() + "/framework-res.apk");
// Gross hack for now: we know this file is only part of
// the boot class path for art, so don't dexopt it to
// avoid the resulting log spew.
// 把 core-libart.jar加入到已优化的列表中
alreadyDexOpted.add(frameworkDir.getPath() + "/core-libart.jar");
/**
* There are a number of commands implemented in Java, which
* we currently need to do the dexopt on so that they can be
* run from a non-root shell.
*/
// 对framework目录下面的文件执行dex到odex优化
String[] frameworkFiles = frameworkDir.list();
if (frameworkFiles != null) {
// TODO: We could compile these only for the most preferred ABI. We should
// first double check that the dex files for these commands are not referenced
// by other system apps.
for (String dexCodeInstructionSet : dexCodeInstructionSets) {
for (int i=0; i pkgSettingIter = mSettings.mPackages.values().iterator();
while (pkgSettingIter.hasNext()) {
PackageSetting ps = pkgSettingIter.next();
if (isSystemApp(ps)) {
mExistingSystemPackages.add(ps.name);
}
}
}
2.8、调用scanDirLI扫描文件
下面到PackageManagerService初始化过程的重头戏,PackageManagerService在开机后需要将系统中所有的package信息统计管理起来,首先扫描文件夹
代码在PackageManagerService.java 2066行
// ************** 第一块 **************
// Collect vendor overlay packages.
// (Do this before scanning any apps.)
// For security and version matching reason, only consider
// overlay packages if they reside in VENDOR_OVERLAY_DIR.
// 扫描 /vendor/overlay目录,收集目录中文件的信息
File vendorOverlayDir = new File(VENDOR_OVERLAY_DIR);
scanDirLI(vendorOverlayDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanFlags | SCAN_TRUSTED_OVERLAY, 0);
// Find base frameworks (resource packages without code).
// 扫描/system/framework目录,收集目录中文件的信息
scanDirLI(frameworkDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED,
scanFlags | SCAN_NO_DEX, 0);
// Collected privileged system packages.
// 扫描 /system/priv-app 目录,收集目录中文件的信息,这个是Android 4.4出现的
final File privilegedAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "priv-app");
scanDirLI(privilegedAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED, scanFlags, 0);
// Collect ordinary system packages.
// 扫描 /system/app 目录, 收集目录中文件信息
final File systemAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "app");
scanDirLI(systemAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanFlags, 0);
// Collect all vendor packages.
// 扫描 /vendor/app目录, 收集目录中文件信息
File vendorAppDir = new File("/vendor/app");
try {
vendorAppDir = vendorAppDir.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
// failed to look up canonical path, continue with original one
}
scanDirLI(vendorAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanFlags, 0);
// Collect all OEM packages.
// 扫描 /oem/app 目录, 收集目录中文件信息
final File oemAppDir = new File(Environment.getOemDirectory(), "app");
scanDirLI(oemAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanFlags, 0);
if (DEBUG_UPGRADE) Log.v(TAG, "Running installd update commands");
// 调用installd执行movefiles命令,执行/system/etc/updatecmds下的命令脚本
mInstaller.moveFiles();
// Prune any system packages that no longer exist.
// 这类List表示的是有可能有升级包的系统应用
final List possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps = new ArrayList();
if (!mOnlyCore) {
Iterator psit = mSettings.mPackages.values().iterator();
// 遍历mSettings.mPackages中保存的应用
while (psit.hasNext()) {
PackageSetting ps = psit.next();
/*
* If this is not a system app, it can't be a
* disable system app.
*/
// 忽略掉非系统应用
if ((ps.pkgFlags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) == 0) {
continue;
}
/*
* If the package is scanned, it's not erased.
*/
// 下面的mPackages是PackageManangerService的成员变量,
// 保存的是上面调用scanDirLI方法扫描目录得到的应用信息,不要和mSettings.mPackages弄混了
final PackageParser.Package scannedPkg = mPackages.get(ps.name);
if (scannedPkg != null) {
/*
* If the system app is both scanned and in the
* disabled packages list, then it must have been
* added via OTA. Remove it from the currently
* scanned package so the previously user-installed
* application can be scanned.
*/
// 如果某个扫描过的系统应用是带升级包的系统应用,把它从mPackages中移除,
// “disable” 列表是package.xml中标签标示的应用
if (mSettings.isDisabledSystemPackageLPr(ps.name)) {
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Expecting better updated system app for "
+ ps.name + "; removing system app. Last known codePath="
+ ps.codePathString + ", installStatus=" + ps.installStatus
+ ", versionCode=" + ps.versionCode + "; scanned versionCode="
+ scannedPkg.mVersionCode);
// 从扫描列表mPackages中移除
removePackageLI(ps, true);
// 放入mExpectingBetter列表,后面会进行处理的。
mExpectingBetter.put(ps.name, ps.codePath);
}
// 忽略在扫描列表mPackages中的文件
continue;
}
// 运行到这里说明ps表示的应用不在扫描列表mPackages中,也就是在系统中不存在
if (!mSettings.isDisabledSystemPackageLPr(ps.name)) {
// 如果这个文件不属于标识的应用,说明这个应用是残留在packages.xml中的,
// 可能还有数据目录,因此要删除
psit.remove();
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "System package " + ps.name
+ " no longer exists; wiping its data");
// 删除数据目录,内部也是通过installd来执行的
removeDataDirsLI(null, ps.name);
} else {
// 如果这个应用不在系统中,但是被标记了,
// 则加入到possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps列表
final PackageSetting disabledPs = mSettings.getDisabledSystemPkgLPr(ps.name);
if (disabledPs.codePath == null || !disabledPs.codePath.exists()) {
possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps.add(ps.name);
}
}
}
}
//look for any incomplete package installations
// 扫描并删除未安装成功的apk包
ArrayList deletePkgsList = mSettings.getListOfIncompleteInstallPackagesLPr();
//clean up list
for(int i = 0; i < deletePkgsList.size(); i++) {
//clean up here
cleanupInstallFailedPackage(deletePkgsList.get(i));
}
//delete tmp files
// 删除临时文件
deleteTempPackageFiles();
// Remove any shared userIDs that have no associated packages
// 删除掉Settings中的没有关联任何应用的SharedUserSetting对象
mSettings.pruneSharedUsersLPw();
// ************** 第二块 **************
// 开始处理非系统应用
if (!mOnlyCore) {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_DATA_SCAN_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
//扫描 /data/app 目录,保存到mPackages中
scanDirLI(mAppInstallDir, 0, scanFlags | SCAN_REQUIRE_KNOWN, 0);
// 扫描 /data/app-private目录,收集目录中文件信息
scanDirLI(mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir, PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK,
scanFlags | SCAN_REQUIRE_KNOWN, 0);
/**
* Remove disable package settings for any updated system
* apps that were removed via an OTA. If they're not a
* previously-updated app, remove them completely.
* Otherwise, just revoke their system-level permissions.
*/
// 放在possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps中的应用是在packge.xml中被标记成了待升级的系统应用
// 但是文件却不存在了,因此这里检查用户目录下升级文件是否还存在,然后进行处理
for (String deletedAppName : possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps) {
PackageParser.Package deletedPkg = mPackages.get(deletedAppName);
// 从mSettings.mDisabledSysPackages变量中移除去此应用
mSettings.removeDisabledSystemPackageLPw(deletedAppName);
String msg;
if (deletedPkg == null) {
// 用户目录中也没有升级包,则肯定是残留的应用信息,则把它的数据目录删除掉
msg = "Updated system package " + deletedAppName
+ " no longer exists; wiping its data";
// 删除应用数据目录
removeDataDirsLI(null, deletedAppName);
} else {
// 如果 在用户空间找到了文件,则说明系统目录下的文件可能被删除了
// 因此,把应用的系统属性去掉,以普通应用的方式运行
msg = "Updated system app + " + deletedAppName
+ " no longer present; removing system privileges for "
+ deletedAppName;
deletedPkg.applicationInfo.flags &= ~ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM;
PackageSetting deletedPs = mSettings.mPackages.get(deletedAppName);
deletedPs.pkgFlags &= ~ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM;
}
// 报告系统发生了不一致的情况
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, msg);
}
/**
* Make sure all system apps that we expected to appear on
* the userdata partition actually showed up. If they never
* appeared, crawl back and revive the system version.
*/
// 现在来处理mExpectingBetter列表,这个列表的应用是带有升级包的系统的应用,
// 前面把他们从mPackages列表中清除了并放到mExpectingBetter列表
// 最后也对他们进行扫描处理,但不会放到mPackages中
for (int i = 0; i < mExpectingBetter.size(); i++) {
final String packageName = mExpectingBetter.keyAt(i);
if (!mPackages.containsKey(packageName)) {
final File scanFile = mExpectingBetter.valueAt(i);
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Expected better " + packageName
+ " but never showed up; reverting to system");
final int reparseFlags;
// 确保应用位于下面4个系统应用目录,如果不在,不需要处理
if (FileUtils.contains(privilegedAppDir, scanFile)) {
reparseFlags = PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED;
} else if (FileUtils.contains(systemAppDir, scanFile)) {
reparseFlags = PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARS } else if (FileUtils.contains(vendorAppDir, scanFile)) {
reparseFlags = PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR;
} else if (FileUtils.contains(oemAppDir, scanFile)) {
reparseFlags = PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR;
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, "Ignoring unexpected fallback path " + scanFile);
// 如果应用不在上面这些目录,继续循环,不要处理
continue;
}
// 现在把这个apk标示为系统应用,从mSettings.mDisabledSysPackages中删除,
//因为在scanDirLI->scanPackageLI中会执行mSettings.disableSystemPackageLPw
// 所以此时包名的标签是只有,执行到这步之后变成标签,
// 在下面的scanPackageLI中又会添加一个标签的
mSettings.enableSystemPackageLPw(packageName);
try {
// 重新扫描一下这个文件,会添加一个标签
scanPackageLI(scanFile, reparseFlags, scanFlags, 0, null);
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to parse original system package: "
+ e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
// 清空目录
mExpectingBetter.clear();
// Now that we know all of the shared libraries, update all clients to have
// the correct library paths.
// 更新所有应用的动态库路径
updateAllSharedLibrariesLPw();
for (SharedUserSetting setting : mSettings.getAllSharedUsersLPw()) {
// NOTE: We ignore potential failures here during a system scan (like
// the rest of the commands above) because there's precious little we
// can do about it. A settings error is reported, though.
adjustCpuAbisForSharedUserLPw(setting.packages, null /* scanned package */,
false /* force dexopt */, false /* defer dexopt */,
false /* boot complete */);
}
// Now that we know all the packages we are keeping,
// read and update their last usage times.
mPackageUsage.readLP();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_SCAN_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
Slog.i(TAG, "Time to scan packages: "
+ ((SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime)/1000f)
+ " seconds");
// If the platform SDK has changed since the last time we booted,
// we need to re-grant app permission to catch any new ones that
// appear. This is really a hack, and means that apps can in some
// cases get permissions that the user didn't initially explicitly
// allow... it would be nice to have some better way to handle
// this situation.
// 如果平台的SDK版本和上次启动时候发生了变化,可能permission的定义也发生了变化,因此需要重新赋予应用权限
int updateFlags = UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;
if (ver.sdkVersion != mSdkVersion) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Platform changed from " + ver.sdkVersion + " to "
+ mSdkVersion + "; regranting permissions for internal storage");
updateFlags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_PKG | UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_ALL;
}
updatePermissionsLPw(null, null, StorageManager.UUID_PRIVATE_INTERNAL, updateFlags);
ver.sdkVersion = mSdkVersion;
// If this is the first boot or an update from pre-M, and it is a normal
// boot, then we need to initialize the default preferred apps across
// all defined users.
// 如果是第一次启动或者是Android M升级后的第一次启动,需要执行一些初始化工作
if (!onlyCore && (mPromoteSystemApps || !mRestoredSettings)) {
for (UserInfo user : sUserManager.getUsers(true)) {
mSettings.applyDefaultPreferredAppsLPw(this, user.id);
applyFactoryDefaultBrowserLPw(user.id);
primeDomainVerificationsLPw(user.id);
}
}
// ************** 第三块 **************
// If this is first boot after an OTA, and a normal boot, then
// we need to clear code cache directories.
// 如果是执行OTA后的第一次启动,需要清除cache
if (mIsUpgrade && !onlyCore) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Build fingerprint changed; clearing code caches");
for (int i = 0; i < mSettings.mPackages.size(); i++) {
final PackageSetting ps = mSettings.mPackages.valueAt(i);
if (Objects.equals(StorageManager.UUID_PRIVATE_INTERNAL, ps.volumeUuid)) {
deleteCodeCacheDirsLI(ps.volumeUuid, ps.name);
}
}
ver.fingerprint = Build.FINGERPRINT;
}
checkDefaultBrowser();
// clear only after permissions and other defaults have been updated
mExistingSystemPackages.clear();
mPromoteSystemApps = false;
// All the changes are done during package scanning.
ver.databaseVersion = Settings.CURRENT_DATABASE_VERSION;
// can downgrade to reader
// 把Settings的内容保存到packages.xml中去
mSettings.writeLPr();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_READY,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
mRequiredVerifierPackage = getRequiredVerifierLPr();
mRequiredInstallerPackage = getRequiredInstallerLPr();
mInstallerService = new PackageInstallerService(context, this);
mIntentFilterVerifierComponent = getIntentFilterVerifierComponentNameLPr();
mIntentFilterVerifier = new IntentVerifierProxy(mContext,
mIntentFilterVerifierComponent);
} // synchronized (mPackages)
} // synchronized (mInstallLock)
// ************** 第四块 **************
// Now after opening every single application zip, make sure they
// are all flushed. Not really needed, but keeps things nice and
// tidy.
//启动一次内存垃圾回收
Runtime.getRuntime().gc();
// Expose private service for system components to use.
LocalServices.addService(PackageManagerInternal.class, new PackageManagerInternalImpl());
}
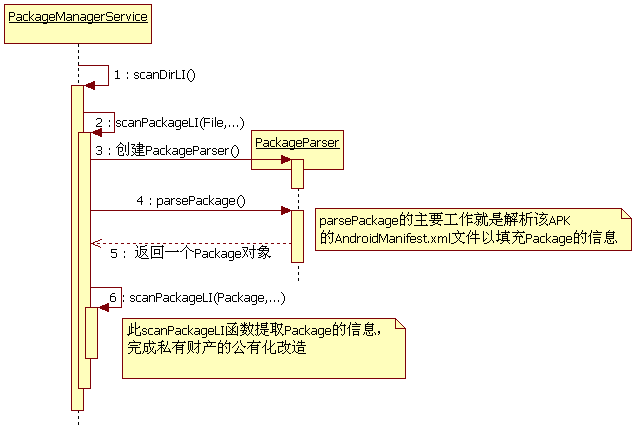
整体时序图如下:
我将本方法的内部分为3个部分
- 1、扫描系统文件夹
- 2、扫描第三方应用目录
- 3、OTA换粗处理
- 4|、清理内存收尾
这里重点说下第一个,扫描系统文件夹
2.8.1、扫描系统文件夹
这一部分是PackageManagerService初始化的重量级部分,从code中可以看到这里扫描的文件夹有:
- "/vendor/overlay"
- "framework"
- "system/priv-app"
- "system/app"
- "/vendor/app"
- "oem/app"
扫描文件夹的操作会一步一步最终调用到scanPackageDirtyLI()方法,这个方法中PackageManagerService将package中的组件管理起来从而实现系统应用的安装过程,如图:
从上图中我们主要知道两点,第一,PackageParser将package进行彻底的解析,第二,PackageManagerService将上面解析得到的数据统计到自身变量中用于管理。
四、PackageManagerService#scanDirLI(File dir, final int parseFlags, int scanFlags, long currentTime)方法解析
代码在PackageManagerService.java 5624行
private void scanDirLI(File dir, int parseFlags, int scanFlags, long currentTime) {
//拿到文件的所有目录
final File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(files)) {
Log.d(TAG, "No files in app dir " + dir);
return;
}
if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) {
Log.d(TAG, "Scanning app dir " + dir + " scanFlags=" + scanFlags
+ " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(parseFlags));
}
for (File file : files) {
// 过滤掉非apk文件
final boolean isPackage = (isApkFile(file) || file.isDirectory())
&& !PackageInstallerService.isStageName(file.getName());
if (!isPackage) {
// Ignore entries which are not packages
continue;
}
try {
//如果是 APK则进行扫描
scanPackageLI(file, parseFlags | PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK,
scanFlags, currentTime, null);
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
// 如果扫描APK过程中发生异常
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to parse " + file + ": " + e.getMessage());
// Delete invalid userdata apps
// 如果解析失败,并且是非系统APP
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) == 0 &&
e.error == PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK) {
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Deleting invalid package at " + file);
// 删除APP
if (file.isDirectory()) {
mInstaller.rmPackageDir(file.getAbsolutePath());
} else {
file.delete();
}
}
}
}
}
其实这个方法的逻辑非常简单,首先拿到指定目录下面的所有文件,并过滤掉非apk文件,然后调用scanPackageLI方法进行解析,注意这里的scanPackageLI方法的第一个参数是File吗,它还有一个重载的方法,这个重载的方法第一个参数是PackageParser.Package。我们看下scanPackageLI做了什么吧,代码里面首先创建了PackageParser.Package对象,并调用了parsePackage方法,这里同样要注意的一点就是这个parsePackage方法,这里也要注意parsePackage方法的第一个参数是File类型,我们看下parsePackage方法里面做了什么,parsePackage的逻辑其实也很简单,就是通过AssertManager拿到apk文件的Resource文件,然后拿到Androidmanifest.xml文件,并进行解析,并将结果以PackageParser.Package的形式返回给PackageManagerService,PackageManagerService为了方便以后的访问,需要将这个Package对象保存起来,于是调用了第一个scanPackageLI方法。
这里说下PackageManagerService扫描文件目录的目的:
PackageManagerService在扫描APK的目录时会使用PackageParser类对APK的androidManifest.xml文件进行解析,保存到Package类型的变量中,然后通过PackageManagerService的scanPackageDirtyLI()将解析后组件数据统计到PackageManagerService本地变量中,用于管理查询调用,当系统中任意某个apk的package发生改变时,如卸载,升级等操作都会更新package的统计数据到PackageManagerService,PackageManagerService正式基于拥有系统中所有Package的信息才能胜任Package管理者的角色。
PS:注意不同目录下扫描规则不同,PackageParser在解析apk包的时候对于不同安装目录下的apk解析规则是不同的,其中很多重要的解析,这也正式adb push 和adb install 不同方式的安装应用可能有不同效果的原因所在。
这个方法里面的核心方法是scanPackageLI,那我们就来跟踪下scanPackageLI方法的执行
scanPackageLI是有一对重载方法,一个方法的首参数为File,另一个方法的首参数为PackageParser.Package。上面调用的方法为首参数为File的方法。
上一篇文章 APK安装流程详解6——PackageManagerService启动前奏
下一篇文章 APK安装流程详解8——PackageManagerService的启动流程(下)