详解Java集合
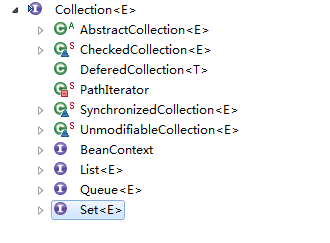
Java集合有两类,一类为Collection,一类为Map,两者继承关系如下所示:
对于collection,它分为有序和无序,可重复和不可重复等,所以包含了Collection接口可以分为三类接口:List、Queue、Set
依次说明如下:
List接口:申明了list的公有方法,包括:
add,addAll,clear,contains(Object), containsAll,equals,hashCode,get(int),set(int,E)
indexOf,lastIndexOf,isEmpty,iterator,listIterator,listIterator(int),remove(int),remove(Obj)
removeAll,retainAll,size,toArray,toArray(T[]),subList(int, int)。
toArray将list中的元素放入数组,然后返回。
Iterator和ListIterator的不同:
Iterator是按顺序遍历,只能从前到后,而ListIterator可以从后向前;
对于提供的方法,Iterator:hasNext(),next(),remove()
后者提供了hasPrevious(),previous(), nextIndex(),previousIndex(),remove(),set(E e),add(E e),hasNext(),next()
List的实现类:
AbstractList实现了list提供的部分方法。add方法是调用add(int,E),而后者在该类中是直接抛出异常,set、remove(int)也是抛出异常。
有一个removeRange方法,该方法在clear中有调用。
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
ListIterator it = listIterator(fromIndex);
for (int i=0, n=toIndex-fromIndex; i 继承AbstractList的最常见的是ArrayList,需要知道的是:
默认初始容量为 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
所有的元素存放在private transient Object[] elementData;
自动扩容为1.5倍的容量,
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}再看Vector,和ArrayList很类似,但是他是一个线程安全的实现。
与ArrayList的不同:
首先它线程安全;
它有protected int capacityIncrement;在扩容的时候,如果该值大于0,则按该值扩容,否则在原来的基础上扩大到2倍。
AbstractSequentialList是一个继承AbstractList的抽象类,linkedList会继承它,重写了add、get、set、remove等方法,在方法中都是用了listIterator来实现的。
LinkedList:这是私有静态内部类
private static class Node {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
} 这是一个双向链表,可以前插和后插,默认后插,获取头尾的复杂度为O(1),还提供了pop和push操作,在将链表作为栈的情况下可以使用。
/**
* Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, inserts the element at the front of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @since 1.6
*/
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
/**
* Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, removes and returns the first element of this list.
*
*
This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}.
*
* @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top
* of the stack represented by this list)
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}