netty4关于get和post参数的封装处理,io与业务分离
注:先简单介绍一下本人,2012年毕业,刚开始2年半从事游戏开发,做过主程带过几个team,现在从事互联网架构师方向
现在netty很热,很多rpc框架跟微服务框架的底层都选择它,那么如果用它作为一个简单的后端socket服务,该怎么优雅的处理get参数跟post参数呢?特别是需要做到io跟业务分离,以下我们来看看作者的处理方式。
说这个之前,我们得先了解一下netty的io模型:
提起IO模型首先想到的就是同步,异步,阻塞,非阻塞这几个概念。每个概念的含义,解释,概念间的区别这些都是好理解,这里深入*nix系统讲一下IO模型。
在*nix中将IO模型分为5类。
- Blocking I/O
- Nonblocking I/O
- I/O Multiplexing (select and poll)
- Signal Driven I/O (SIGIO)
- Asynchronous I/O (the POSIX aio_functions)
阻塞 I/O(blocking IO)
如图所示,系统调用recvfrom,内核kernel等待数据数据准备完成,在数据准备完成后将数据从内核态拷贝到用户态,recvfrom直到整个过程结束后才完成,在整个过程中经历2次阻塞。
非阻塞 I/O(nonblocking IO)
如图所示,系统调用recvfrom,内核kernel在数据没有准备完成时直接返回,系统会不断轮询,在kernel准备完成数据后将数据从内核态拷贝到用户态,在等待数据完成的过程中并不阻塞。
I/O 多路复用( IO multiplexing)
如图所示,IO multiplexing 使用select,poll,epoll等实现单个kernel的进程/线程处理多个IO请求,IO复用将等待数据准备和将数据拷贝给应用这两个阶段分开处理,让一个线程(而且是内核级别的线程)来处理所有的等待,一旦有相应的IO事件发生就通知继续完成IO操作,虽然仍然有阻塞和等待,但是等待总是发生在一个线程,这时使用多线程可以保证其他线程一旦唤醒就是处理数据。
信号驱动 I/O (Signal Driven I/O)
如图所示,系统调用recvfrom试图读取数据,并且直接返回,不管是否有数据可读,内核线程读完数据,给发信号通知应用线程,应用线程收到信息,等待内核线程将数据拷贝给应用线程。
异步 I/O(asynchronous IO)
如图所示,系统调用aio_read,内核kernel直接返回,系统不需要阻塞,继续做其他事情。kernel则进行等待数据准备完成,并将数据拷贝到用户态后,发送signal信号通知系统已经完成。
各个IO模型的对比
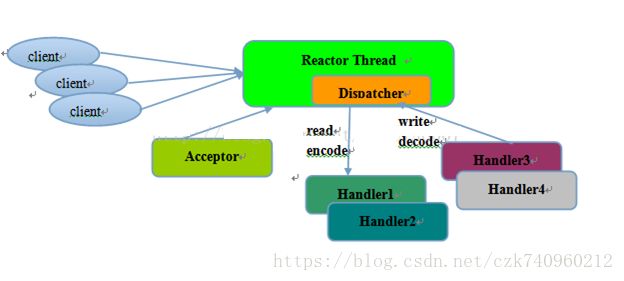
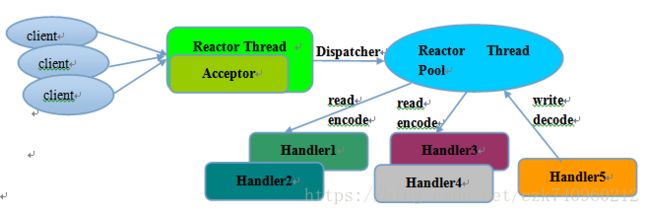
Netty是一个高性能、异步事件驱动的NIO框架,它提供了对TCP、UDP和文件传输的支持 Reactor模式,Reactor模式又分为单线程 Reactor模式,多线程 Reactor模式以及主从 Reactor模式。
单线程Reactor模型,可以参考nio,这里附上demo:
public void run() {
try {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
selector.select();
Set selected = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = selected.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
dispatch((SelectionKey) (it.next()));
selected.clear();
}
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */
}
}
本文采用的是多线程Reactor模型,在这个模式里,mainReactor只有一个,负责响应client的连接请求,并建立连接,它使用一个NIO Selector;subReactor可以有一个或者多个,每个subReactor都会在一个独立线程中执行,并且维护一个独立的NIO Selector。Netty里对应mainReactor的角色叫做“Boss”,而对应subReactor的角色叫做"Worker"。Boss负责分配请求,Worker负责执行,好像也很贴切!
本项目使用的项目构建工具是gradle,主要依赖如下:
//netty
compile 'io.netty:netty-all:4.1.5.Final'
//http请求
compile group: 'org.apache.httpcomponents', name: 'httpasyncclient-cache', version: '4.1.1'
compile group: 'org.apache.httpcomponents', name: 'httpclient', version: '4.5.1'
compile group: 'org.apache.httpcomponents', name: 'httpmime', version: '4.5.1'
//工具jar
compile 'commons-collections:commons-collections:3.2.2' static final boolean SSL = System.getProperty("ssl") != null;
static final int PORT = 8048;
/**
* CPU 核数乘2 ,理论上最优性能
*/
static final int GroupSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()*2;
public void bind(){
Thread thread=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
// Configure SSL.
final SslContext sslCtx;
if (SSL) {
SelfSignedCertificate ssc = new SelfSignedCertificate();
sslCtx = SslContextBuilder.forServer(ssc.certificate(), ssc.privateKey()).build();
} else {
sslCtx = null;
}
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(GroupSize);
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
b.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
b.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
b.childHandler(new HttpServerInitializer(sslCtx));
Channel ch = b.bind(PORT).sync().channel();
System.err.println("Open your web browser and navigate to " +
(SSL? "https" : "http") + "://127.0.0.1:" + PORT + '/');
ch.closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(-1);
}
}
});
thread.setName("HttpServer");
thread.start();
}
代码中bossGroup就是mainReactor,只有一个线程;而workerGroup就是subReactor,是cpu核数*2.
如果想要设置为主从Reactor模式,只需要把 bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(number);
number代表数量,2以上即可
现在来了,我们看看我们封装参数的重点!
为了保持解读的完整性,我们还是先看看HttpServerInitializer(基本配置信息):
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
if (sslCtx != null) {
pipeline.addLast(sslCtx.newHandler(ch.alloc()));
}
pipeline.addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpResponseEncoder());
// Remove the following line if you don't want automatic content compression.
pipeline.addLast(new HttpContentCompressor());
// body max size
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(2*1024*1024));
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerHandler());
}
接着重头戏来了,我们定义了一个HttpServerHandler的类,它继承了SimpleChannelInboundHandler对象,为了达到跟业务分离的对象,我们需要做一些准备:
/**
* post请求的参数
*/
private final Map post=new HashMap();
/**
* get请求的参数
*/
private Map get=new HashMap();
//业务标识号
private int cmdId;
/**
* 返回前端的响应类型
*/
private ResponseType type=ResponseType.text;
我们把所有post的请求都封装到Map
get参数封装主要如下:
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
HttpRequest request = this.request = (HttpRequest) msg;
URI uri = new URI(request.uri());
String httpUrl= uri.getQuery();
if(httpUrl!=null && httpUrl.startsWith("cmdId")){
get.clear();
String[] params = httpUrl.split("&");
for(String param:params){
String name=param.substring(0,param.indexOf("="));
String value=param.substring(param.indexOf("=")+1);
get.put(name, value);
System.out.println(name+" --> "+value);
}
if(httpUrl.contains("cmdId")){
cmdId=MapUtils.getInteger(get, "cmdId");
}
if(httpUrl.contains("responseType")){
int type=MapUtils.getInteger(get, "responseType");
this.type=ResponseType.values()[type];
}
}
//TODO 过滤非法请求
else{
writeResponse(ctx.channel());
ctx.channel().close();
return;
}
post.clear();
responseContent.setLength(0);
// new getMethod
for (Entry entry : request.headers()) {
logger.debug("HEADER: " + entry.getKey() + '=' + entry.getValue());
}
// new getMethod
Set cookies;
String value = request.headers().get(HttpHeaderNames.COOKIE);
if (value == null) {
cookies = Collections.emptySet();
} else {
cookies = ServerCookieDecoder.STRICT.decode(value);
}
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
logger.debug("COOKIE: " + cookie);
}
QueryStringDecoder decoderQuery = new QueryStringDecoder(request.uri());
Map> uriAttributes = decoderQuery.parameters();
for (Entry> attr: uriAttributes.entrySet()) {
for (String attrVal: attr.getValue()) {
logger.debug("URI: " + attr.getKey() + '=' + attrVal);
}
}
// if GET Method: should not try to create a HttpPostRequestDecoder
if (request.method().equals(HttpMethod.GET)) {
// TODO get方法终止地方
// GET Method: should not try to create a HttpPostRequestDecoder
// So stop here
doWork(ctx);
return;
}
try {
decoder = new HttpPostRequestDecoder(factory, request);
} catch (ErrorDataDecoderException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
responseContent.append(e1.getMessage());
writeResponse(ctx.channel());
ctx.channel().close();
return;
}
readingChunks = HttpUtil.isTransferEncodingChunked(request);
if (readingChunks) {
readingChunks = true;
}
}
// check if the decoder was constructed before
// if not it handles the form get
if (decoder != null) {
if (msg instanceof HttpContent) {
// New chunk is received
HttpContent chunk = (HttpContent) msg;
try {
decoder.offer(chunk);
} catch (ErrorDataDecoderException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
responseContent.append(e1.getMessage());
writeResponse(ctx.channel());
ctx.channel().close();
return;
}
// example of reading chunk by chunk (minimize memory usage due to
// Factory)
readHttpDataChunkByChunk(ctx);
// example of reading only if at the end
if (chunk instanceof LastHttpContent) {
//TODO post方法最后调用
doWork(ctx);
readingChunks = false;
reset();
//关闭
ctx.disconnect();
ctx.close();
}
}
} else {
//TODO 决定是否get方法之后立马关闭连接
writeResponse(ctx.channel());
ctx.disconnect();
ctx.close();
}
}
get参数主要是HttpRequest的URI对象,通过url解析得到
post参数主要封装如下:
/**
* Example of reading request by chunk and getting values from chunk to chunk
*/
private void readHttpDataChunkByChunk(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
try {
while (decoder.hasNext()) {
InterfaceHttpData data = decoder.next();
if (data != null) {
// check if current HttpData is a FileUpload and previously set as partial
if (partialContent == data) {
logger.info(" 100% (FinalSize: " + partialContent.length() + ")");
partialContent = null;
}
try {
// new value
writeHttpData(data,ctx);
} finally {
data.release();
}
}
}
// Check partial decoding for a FileUpload
InterfaceHttpData data = decoder.currentPartialHttpData();
if (data != null) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
if (partialContent == null) {
partialContent = (HttpData) data;
if (partialContent instanceof FileUpload) {
builder.append("Start FileUpload: ")
.append(((FileUpload) partialContent).getFilename()).append(" ");
} else {
builder.append("Start Attribute: ")
.append(partialContent.getName()).append(" ");
}
builder.append("(DefinedSize: ").append(partialContent.definedLength()).append(")");
}
if (partialContent.definedLength() > 0) {
builder.append(" ").append(partialContent.length() * 100 / partialContent.definedLength())
.append("% ");
logger.info(builder.toString());
} else {
builder.append(" ").append(partialContent.length()).append(" ");
logger.info(builder.toString());
}
}
} catch (EndOfDataDecoderException e1) {
// end
}
}
private void writeHttpData(InterfaceHttpData data,ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
if (data.getHttpDataType() == HttpDataType.Attribute) {
Attribute attribute = (Attribute) data;
try {
//TODO 参数封装
post.put(attribute.getName(), attribute.getValue());
} catch (IOException e1) {
// Error while reading data from File, only print name and error
e1.printStackTrace();
responseContent.append("\r\nBODY Attribute: " + attribute.getHttpDataType().name() + ": "
+ attribute.getName() + " Error while reading value: " + e1.getMessage() + "\r\n");
return;
}
} else {
if (data.getHttpDataType() == HttpDataType.FileUpload) {
FileUpload fileUpload = (FileUpload) data;
if (fileUpload.isCompleted()) {
try {
fileUpload.getString(fileUpload.getCharset());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
fileUpload.isInMemory();// tells if the file is in Memory
//TODO to do something
// or on File
// fileUpload.renameTo(dest); // enable to move into another
// File dest
// decoder.removeFileUploadFromClean(fileUpload); //remove
// the File of to delete file
} else {
responseContent.append("\tFile to be continued but should not!\r\n");
}
}
}
}
解析的是HttpObject对象,HttpContent chunk = (HttpContent) msg
那么在哪里最终调用业务请求呢?
眼尖的童鞋,已经发现
// if GET Method: should not try to create a HttpPostRequestDecoder
if (request.method().equals(HttpMethod.GET)) {
// TODO get方法终止地方
// GET Method: should not try to create a HttpPostRequestDecoder
// So stop here
doWork(ctx);
return;
}
处理如下:
/**
* 业务工作处理
* @param ctx 通道
*/
private void doWork(ChannelHandlerContext ctx){
try{
// TODO 正式处理
HttpResponse res=WeiboOperation.get().request(cmdId, post, get);
if(type==ResponseType.html){
responseContent.append(res.getData());
}
if(type==ResponseType.text){
responseContent.append(JSON.toJSONString(res));
}
writeResponse(ctx.channel());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
统一处理业务的地方是WeiboOperation,我们来看看WeiboOperation的做了啥:
/**
* 内部请求
* @param cmdId 业务指令
* @param post post参数
* @param get get参数
* @return 返回
*/
public HttpResponse request(int cmdId, Map post,Map get) {
HttpResponse res=new HttpResponse();
log.info("get_param: "+JSON.toJSONString(get));
log.info("post_param: "+JSON.toJSONString(post));
switch(cmdId){
case ModuleID.WEIBO_ADD_SUBSCRIBE:{
res.setRet(1);
res.setData(cmdId+" -> "+"ok!");
//Doing...
break;
}
case ModuleID.WEIBO_ADD_USERS:{
res.setRet(1);
res.setData(cmdId+" -> "+"ok!");
//Doing...
break;
}
case ModuleID.WEIBO_DEL_SUBSCRIBE:{
res.setRet(1);
res.setData(cmdId+" -> "+"ok!");
//Doing...
break;
}
default:{
res.setMsg("NOT definded!");
break;
}
}
return res;
}
到了这里我们就看到了答案了,在这里我们完成不需要关系io是怎么操作的,只需要根据cmdid的业务请求码去找到最终的处理了地方,ModuleID定义了一些请求业务
/**
* @describe 业务管理
* @author zhikai.chen
* @date 2016年3月1日 下午1:53:31
*/
public interface ModuleID {
@Text("微博模块")
public static final int WEIBO = 100;
@Text("微博 -> 添加订阅关键字")
public static final int WEIBO_ADD_SUBSCRIBE = 10001;
@Text("微博 -> 删除订阅关键字")
public static final int WEIBO_DEL_SUBSCRIBE = 10002;
@Text("微博 -> 添加订阅用户")
public static final int WEIBO_ADD_USERS = 10003;
/************************************************* 下推标识号 ********************************************************/
}
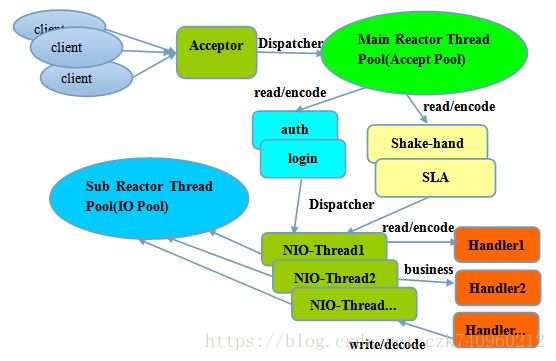
到此,本教程基本完成了,这里附上流程图: