【Linux】我的第一个驱动程序——scull字符设备驱动
最近,终于有时间开始学习写Linux的驱动了。
我的第一个驱动程序,其实基本上都是抄的,只是结合自己的理解把它们都拼起来。
参考资料:《Linux设备驱动程序(第三版)》(Linux Device Driver, LDD)
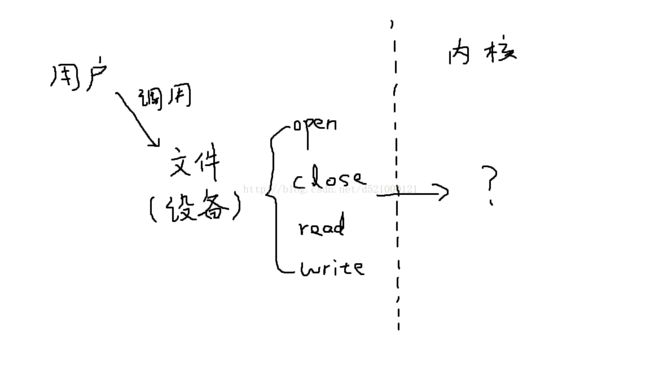
首先,对于Linux的设备,在系统中,它的表示也是一个文件,只不过比较特殊而已,如下图:
而驱动,就是对这样的特殊文件的功能进行定义,就像普通文件的open、close等等,那当用户对设备进行open、close的时候应该怎么处理?这就是内核的作用了。
对于一个驱动程序,在系统中就是一个模块,所以要让模块能进入到系统中工作,就要在安装模块的时候做点事情。
1、申请这个驱动对应的设备号
2、注册设备
对于字符设备,就是告诉系统,要添加编号为某某的设备,这里有一个重要的结构体就是cdev了。
有安装就有卸载。
所以最后第一部分程序是这样的:
#ifndef __KERNEL__
#define __KERNEL__
#endif
#ifndef __MODULE__
#define __MODULE__
#endif
#include "scull_driver.h" //local define
int scull_major = SCULL_MAJOR;
int scull_minor = SCULL_MINOR;
int scull_nr_devs = SCULL_NR_DEVS;
int scull_quantum = SCULL_QUANTUM;
int scull_qset = SCULL_QSET;
module_param(scull_major, int, S_IRUGO); /*模块参数,可以在安装模块时指定*/
module_param(scull_minor, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_nr_devs, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_quantum, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_qset, int, S_IRUGO);
pSCULL_DEV pdev = NULL;
static int scull_trim ( pSCULL_DEV pdev )
{
pSCULL_QSET next;
pSCULL_QSET dptr;
int qset = pdev->qset;
int i;
for ( dptr = pdev->data; dptr; dptr = next )
{
if ( dptr->data )
{
for ( i = 0; i < qset; i++ )
kfree ( dptr->data[i] );
kfree ( dptr->data );
dptr->data = NULL;
}
next = dptr->next;
kfree ( dptr );
}
pdev->size = 0;
pdev->quantum = scull_quantum;
pdev->qset = scull_qset;
pdev->data = NULL;
return 0;
}
static void cleanup_scull ( void )
{
int i;
dev_t devno = MKDEV ( scull_major, scull_minor );
if ( pdev )
{
for ( i = 0; i < scull_nr_devs; i++ )
{
cdev_del ( &pdev[i].cdev );
scull_trim ( &pdev[i] );
printk( KERN_NOTICE "scull%d removed!", i );
}
}
kfree ( pdev );
unregister_chrdev_region ( devno, scull_nr_devs );
}
static int scull_setup_cdev ( pSCULL_DEV pdev, int index )
{
int err, devno = MKDEV( scull_major, scull_minor + index );
cdev_init ( &pdev->cdev, &scull_fops );
pdev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
pdev->cdev.ops = &scull_fops;
err = cdev_add ( &pdev->cdev, devno, 1 );
if ( err )
{
printk ( KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding scull %d", err, index );
return err;
}
return 0;
}
static int __init init_sucll ( void )
{
dev_t devno;
int i;
int result = 0;
/*get major*/
if ( scull_major )
{
devno = MKDEV( scull_major, scull_minor );
result = register_chrdev_region ( devno, scull_nr_devs, "scull" );
}
else
{
result = alloc_chrdev_region ( &devno, scull_minor, scull_nr_devs, "scull");
scull_major = MAJOR ( devno );
}
if ( result < 0 )
{
printk ( KERN_WARNING "scull: can't get major %d\n", scull_major );
return result;
}
/*setup device*/
pdev = kmalloc ( sizeof ( SCULL_DEV ) * scull_nr_devs , GFP_KERNEL );
if ( !pdev )
{
printk ( KERN_WARNING "scull: kmalloc failed" );
result = -ENOMEM;
goto err;
}
for ( i = 0; i < scull_nr_devs; i++ )
{
pdev[i].data = NULL;
pdev[i].quantum = scull_quantum;
pdev[i].qset = scull_qset;
sema_init ( &pdev[i].sem, 1 );
result = scull_setup_cdev ( &pdev[i], i );
if ( result )
goto err;
printk( KERN_NOTICE "scull%d setup success!", i );
}
return 0;
/*err*/
err:
cleanup_scull ();
return result;
}
MODULE_AUTHOR ( "LJY" );
MODULE_LICENSE ( "GPL" );
module_init ( init_sucll );
module_exit ( cleanup_scull );然后就实现驱动的功能了
这里就先实现了四个
那我们要先告诉系统,为了实现这些功能,分别调用的是哪些函数,这就是file_operation结构的作用了。
struct file_operations scull_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = scull_llseek,
.read = scull_read,
.write = scull_write,
.ioctl = scull_ioctl,
.open = scull_open,
.release = scull_release,
};然后实现的是open、close、read、write
loff_t scull_llseek ( struct file *filp, loff_t pos, int count )
{
return 0;
}
ssize_t scull_read ( struct file *filp, char __user *to, size_t count, loff_t *pos )
{
pSCULL_DEV pdev = ( pSCULL_DEV ) filp->private_data;
struct scull_qset *dptr;
int quantum = pdev->quantum;
int qset = pdev->qset;
int itemsize = quantum * qset;
int item, s_pos, q_pos, rest;
int i;
ssize_t res = -ENOMEM;
if ( down_interruptible( &pdev->sem ) )
return -ERESTARTSYS;
if ( *pos > pdev->size )
goto err;
if ( *pos + count > pdev->size )
count = pdev->size - *pos;
item = ( long ) *pos / itemsize;
rest = ( long ) *pos % itemsize;
s_pos = rest / quantum;
q_pos = rest % quantum;
dptr = pdev->data;
for ( i = 0; i < item && dptr; i++ )
dptr = dptr->next;
if ( dptr == NULL || !dptr->data || !dptr->data[s_pos] )
{
printk ( KERN_WARNING "don't fill holes" );
res = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
if ( count > quantum - q_pos )
count = quantum - q_pos;
if ( copy_to_user ( to, dptr->data[s_pos] + q_pos, count) )
{
res = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
*pos += count;
res = count;
err:
up( &pdev->sem );
return res;
}
ssize_t scull_write ( struct file *filp, const char __user *from, size_t count, loff_t *pos )
{
pSCULL_DEV pdev = ( pSCULL_DEV ) filp->private_data;
struct scull_qset *dptr;
int quantum = pdev->quantum;
int qset = pdev->qset;
int itemsize = quantum * qset;
int item, s_pos, q_pos, rest;
int i;
ssize_t res = -ENOMEM;
printk ( KERN_DEBUG"function:scull_write\nwrite postion:%d, scull size: %d, write size: %d\n", *pos, pdev->size, count);
if ( down_interruptible( &pdev->sem ) )
return -ERESTARTSYS;
/*find the postion to write*/
item = ( long ) *pos / itemsize;
rest = ( long ) *pos % itemsize;
s_pos = rest / quantum;
q_pos = rest % quantum;
printk ( KERN_DEBUG"the real postion:\n item: %d, qset: %d, quantum: %d\n", item, s_pos, q_pos );
dptr = pdev->data;
if ( !dptr )
{
pdev->data = dptr = kmalloc ( sizeof ( struct scull_qset ), GFP_KERNEL );
if ( !dptr )
goto err;
printk ( KERN_DEBUG"alloc data\n" );
dptr->data = NULL;
dptr->next = NULL;
}
for ( i = 0; i < item; i++ )
{
if ( !dptr->next )
{
dptr->next = kmalloc ( sizeof ( struct scull_qset ), GFP_KERNEL );
if ( !dptr->next )
goto err;
dptr->next->data = NULL;
dptr->next->next = NULL;
printk ( KERN_DEBUG"alloc one item\n" );
}
dptr = dptr->next;
}
if ( !dptr->data )
{
dptr->data = kmalloc ( qset * sizeof ( char * ), GFP_KERNEL );
if ( !dptr->data )
goto err;
memset ( dptr->data, 0, qset * sizeof ( char * ) );
printk ( KERN_DEBUG"alloc qset\n" );
}
if ( !dptr->data[s_pos] )
{
dptr->data[s_pos] = kmalloc ( quantum, GFP_KERNEL );
if ( !dptr->data[s_pos] )
goto err;
memset ( dptr->data[s_pos], 0, quantum );
printk ( KERN_DEBUG"alloc quantum\n" );
}
if ( count > quantum - q_pos )
count = quantum - q_pos;
if ( copy_from_user ( dptr->data[s_pos]+q_pos, from, count ) )
{
res = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
*pos += count;
res = count;
printk ( KERN_DEBUG"write %d\n", res );
if ( pdev->size < *pos )
pdev->size = *pos;
err:
up( &pdev->sem );
return res;
}
int scull_ioctl ( struct inode *in, struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long a )
{
return 0;
}
int scull_open ( struct inode *inode, struct file *filp )
{
pSCULL_DEV pdev;
pdev = container_of ( inode->i_cdev, SCULL_DEV, cdev );
filp->private_data = pdev;
if ( ( filp->f_flags & O_ACCMODE ) == O_WRONLY )
scull_trim(pdev);
printk ( KERN_NOTICE "scull%d opened", imajor( inode ) );
return 0;
}
int scull_release ( struct inode *inode, struct file *filp )
{
printk ( KERN_NOTICE "scull%d closeed", imajor( inode ) );
return 0;
}然后补上一个头文件
#ifndef _SCULL_DRIVER_H_
#define _SCULL_DRIVER_H_
#include //module
#include //init&exit
#include
#include //printk,container
#include //dev_t
#include //funciton&struct
#include
#include //cdev
#include //memory copy
#ifndef SCULL_PARAM
#define SCULL_PARAM
#define SCULL_MAJOR 0 //0:dynamic device major, others:fix device major
#define SCULL_MINOR 0
#define SCULL_NR_DEVS 1
#define SCULL_QUANTUM 4000
#define SCULL_QSET 1000
#endif
struct scull_qset
{
void **data;
struct scull_qset *next;
};
//typedef struct scull_qset SCULL_QSET;
typedef struct scull_qset *pSCULL_QSET;
struct scull_dev
{
pSCULL_QSET data;
int quantum;
int qset;
unsigned long size;
unsigned int access_key;
struct semaphore sem;
struct cdev cdev;
};
typedef struct scull_dev SCULL_DEV;
typedef SCULL_DEV *pSCULL_DEV;
#endif
安装的脚本也是按照书上的写的
#!/bin/sh
module="scull_driver"
device="scull"
mode="664"
/sbin/insmod ./$module.ko $* || exit 1
rm -f /dev/${device}0
major=$(awk "\$2==\"$device\" {print \$1}" /proc/devices)
mknod /dev/${device}0 c $major 0
echo $major
group="staff"
grep -q '^staff:' /etc/group || group="wheel"
chgrp $group /dev/${device}0
chmod $mode /dev/${device}0
最后再自己写点小测试程序。