Spark检查点机制
Spark中对于数据的保存除了持久化操作之外,还提供了一种检查点的机制,检查点(本质是通过将RDD写入Disk做检查点)是为了通过lineage(血统)做容错的辅助,lineage过长会造成容错成本过高,这样就不如在中间阶段做检查点容错,如果之后有节点出现问题而丢失分区,从做检查点的RDD开始重做Lineage,就会减少开销。检查点通过将数据写入到HDFS文件系统实现了RDD的检查点功能。
cache和checkpoint的区别:
缓存(cache)把 RDD 计算出来然后放在内存中,但是RDD 的依赖链(相当于数据库中的redo 日志),也不能丢掉,当某个点某个 executor 宕了,上面cache 的RDD就会丢掉,需要通过依赖链重放计算出来。不同的是,checkpoint是把 RDD 保存在 HDFS中, 是多副本可靠存储,所以依赖链就可以丢掉了,就斩断了依赖链, 是通过复制实现的高容错。
如果存在以下场景,则比较适合使用检查点机制:
1) DAG中的Lineage过长,如果重算,则开销太大(如在PageRank中)。
2) 在宽依赖上做Checkpoint获得的收益更大。
为当前RDD设置检查点。该函数将会创建一个二进制的文件,并存储到checkpoint目录中,该目录是用SparkContext.setCheckpointDir()设置的。在checkpoint的过程中,该RDD的所有依赖于父RDD中的信息将全部被移出。对RDD进行checkpoint操作并不会马上被执行,必须执行Action操作才能触发。
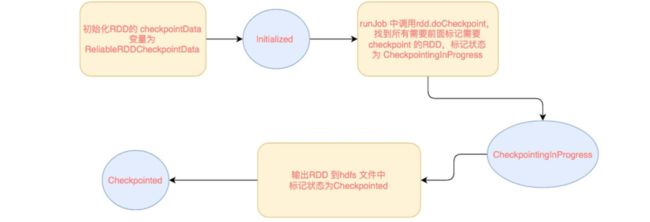
checkpoint写流程
RDD checkpoint 过程中会经过以下几个状态:
[ Initialized → marked for checkpointing → checkpointing in progress → checkpointed ]
转换流程如下:
RDD 需要经过 [ Initialized --> marked for checkpointing --> checkpointing in progress --> checkpointed ] 这几个阶段才能被 checkpoint。
Initialized: 首先 driver program 需要使用 rdd.checkpoint() 去设定哪些 rdd 需要 checkpoint,设定后,该 rdd 就接受 RDDCheckpointData 管理。用户还要设定 checkpoint 的存储路径,一般在 HDFS 上。
marked for checkpointing:初始化后,RDDCheckpointData 会将 rdd 标记为 MarkedForCheckpoint,这时候标记为 Initialized 状态。
checkpointing in progress:每个 job 运行结束后会调用 finalRdd.doCheckpoint(),finalRdd 会顺着 computing chain 回溯扫描,碰到要 checkpoint 的 RDD 就将其标记为 CheckpointingInProgress,然后将写磁盘(比如写 HDFS)需要的配置文件(如 core-site.xml 等)broadcast 到其他 worker 节点上的 blockManager。完成以后,启动一个 job 来完成 checkpoint(使用 rdd.context.runJob(rdd, CheckpointRDD.writeToFile(path.toString, broadcastedConf)))。
checkpointed:job 完成 checkpoint 后,将该 rdd 的 dependency 全部清掉, 怎么清除依赖的呢, 就是把RDD 变量的强引用设置为 null,垃圾回收了,会触发 ContextCleaner 里面的监听,清除实际 BlockManager 缓存中的数据。并设定该 rdd 状态为 checkpointed。然后,为该 rdd 强加一个依赖,设置该 rdd 的 parent rdd 为 CheckpointRDD,该 CheckpointRDD 负责以后读取在文件系统上的 checkpoint 文件,生成该 rdd 的 partition。
checkpoint读流程
在 runJob() 的时候会先调用 finalRDD 的 partitions() 来确定最后会有多个 task。rdd.partitions() 会去检查(通过 RDDCheckpointData 去检查,因为它负责管理被 checkpoint 过的 rdd)该 rdd 是会否被 checkpoint 过了,如果该 rdd 已经被 checkpoint 过了,直接返回该 rdd 的 partitions 也就是 Array[Partition]。
当调用 rdd.iterator() 去计算该 rdd 的 partition 的时候,会调用 computeOrReadCheckpoint(split: Partition) 去查看该 rdd 是否被 checkpoint 过了,如果是,就调用该 rdd 的 parent rdd 的 iterator() 也就是 CheckpointRDD.iterator(),CheckpointRDD 负责读取文件系统上的文件,生成该 rdd 的 partition。这就解释了为什么那么 trickly 地为 checkpointed rdd 添加一个 parent CheckpointRDD。
总结:
- 下面来看一个关于checkpoint的例子:
object testCheckpoint { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val sc =new SparkContext(new SparkConf().setAppName("testCheckpoint").setMaster("local[*]")) //设置检查点目录 sc.setCheckpointDir("file:///f:/spark/checkpoint") val rdd=sc.textFile("file:///F:/spark/b.txt").flatMap{line=>line.split(" ")}.map(word=>(word,1)).reduceByKey(_+_) rdd.checkpoint() //rdd.count() rdd.groupBy(x=>x._2).collect().foreach(println) } }
-
checkpoint流程分析
checkpoint初始化
我们可以看到最先调用了
SparkContext的setCheckpointDir设置了一个checkpoint 目录
我们跟进这个方法看一下/** * Set the directory under which RDDs are going to be checkpointed. The directory must * be a HDFS path if running on a cluster. */ def setCheckpointDir(directory: String) { // If we are running on a cluster, log a warning if the directory is local. // Otherwise, the driver may attempt to reconstruct the checkpointed RDD from // its own local file system, which is incorrect because the checkpoint files // are actually on the executor machines. if (!isLocal && Utils.nonLocalPaths(directory).isEmpty) { logWarning("Spark is not running in local mode, therefore the checkpoint directory " + s"must not be on the local filesystem. Directory '$directory' " + "appears to be on the local filesystem.") } checkpointDir = Option(directory).map { dir => val path = new Path(dir, UUID.randomUUID().toString) val fs = path.getFileSystem(hadoopConfiguration) fs.mkdirs(path) fs.getFileStatus(path).getPath.toString } }
这个方法挺简单的,就创建了一个目录,接下来我们看RDD核心的
checkpoint方法,跟进去/** * Mark this RDD for checkpointing. It will be saved to a file inside the checkpoint * directory set with `SparkContext#setCheckpointDir` and all references to its parent * RDDs will be removed. This function must be called before any job has been * executed on this RDD. It is strongly recommended that this RDD is persisted in * memory, otherwise saving it on a file will require recomputation. */ def checkpoint(): Unit = RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { // NOTE: we use a global lock here due to complexities downstream with ensuring // children RDD partitions point to the correct parent partitions. In the future // we should revisit this consideration. if (context.checkpointDir.isEmpty) { throw new SparkException("Checkpoint directory has not been set in the SparkContext") } else if (checkpointData.isEmpty) { checkpointData = Some(new ReliableRDDCheckpointData(this)) } }
这个方法没有返回值,逻辑只有一个判断,
checkpointDir刚才设置过了,不为空,然后创建了一个ReliableRDDCheckpointData,我们来看ReliableRDDCheckpointData/** * An implementation of checkpointing that writes the RDD data to reliable storage. * This allows drivers to be restarted on failure with previously computed state. */ private[spark] class ReliableRDDCheckpointData[T: ClassTag](@transient rdd: RDD[T]) extends RDDCheckpointData[T](rdd) with Logging { 。。。。。 }
这个
ReliableRDDCheckpointData的父类RDDCheckpointData我们再继续看它的父类/** * RDD 需要经过 * [ Initialized --> CheckpointingInProgress--> Checkpointed ] * 这几个阶段才能被 checkpoint。 */ private[spark] object CheckpointState extends Enumeration { type CheckpointState = Value val Initialized, CheckpointingInProgress, Checkpointed = Value } private[spark] abstract class RDDCheckpointData[T: ClassTag](@transient rdd: RDD[T]) extends Serializable { import CheckpointState._ // The checkpoint state of the associated RDD. protected var cpState = Initialized 。。。。。。 }
RDD 需要经过
[ Initialized --> CheckpointingInProgress--> Checkpointed ]
这几个阶段才能被 checkpoint。
这类里面有一个枚举来标识CheckPoint的状态,第一次初始化时是Initialized。
checkpoint这个一步已经完成了,回到我们的RDD成员变量里checkpointData这个变量指向的RDDCheckpointData的实例。
checkpoint什么时候写入数据
- 我们知道一个spark job运行最终会调用
SparkContext的runJob方法将任务提交给Executor去执行,我们来看runJobdef runJob[T, U: ClassTag]( rdd: RDD[T], func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U, partitions: Seq[Int], resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit): Unit = { if (stopped.get()) { throw new IllegalStateException("SparkContext has been shutdown") } val callSite = getCallSite val cleanedFunc = clean(func) logInfo("Starting job: " + callSite.shortForm) if (conf.getBoolean("spark.logLineage", false)) { logInfo("RDD's recursive dependencies:\n" + rdd.toDebugString) } dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, localProperties.get) progressBar.foreach(_.finishAll()) rdd.doCheckpoint() }
最后一行代码调用了
doCheckpoint,在dagScheduler将任务提交给集群运行之后,我来看这个doCheckpoint方法/** * Performs the checkpointing of this RDD by saving this. It is called after a job using this RDD * has completed (therefore the RDD has been materialized and potentially stored in memory). * doCheckpoint() is called recursively on the parent RDDs. */ private[spark] def doCheckpoint(): Unit = { RDDOperationScope.withScope(sc, "checkpoint", allowNesting = false, ignoreParent = true) { if (!doCheckpointCalled) { doCheckpointCalled = true if (checkpointData.isDefined) { if (checkpointAllMarkedAncestors) { // TODO We can collect all the RDDs that needs to be checkpointed, and then checkpoint // them in parallel. // Checkpoint parents first because our lineage will be truncated after we // checkpoint ourselves dependencies.foreach(_.rdd.doCheckpoint()) } checkpointData.get.checkpoint() } else { dependencies.foreach(_.rdd.doCheckpoint()) } } } }
这个是一个递归,遍历RDD依赖链条,当rdd是checkpointData不为空时,调用checkpointData的checkpoint()方法。还记得checkpointData类型是什么吗?就是RDDCheckpointData,我们来看它的checkpoint方法,以下/** * Materialize this RDD and persist its content. * This is called immediately after the first action invoked on this RDD has completed. */ final def checkpoint(): Unit = { // Guard against multiple threads checkpointing the same RDD by // atomically flipping the state of this RDDCheckpointData RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { if (cpState == Initialized) {
//标记当前状态为 CheckpointingInProgress cpState = CheckpointingInProgress } else { return } } //这里调用的是子类的 doCheckPoint() val newRDD = doCheckpoint() // Update our state and truncate the RDD lineage RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { cpRDD = Some(newRDD) cpState = Checkpointed rdd.markCheckpointed() } }这个方法开始做checkpoint操作了。
checkpoint什么时候读取数据
- 我们知道Task是spark运行任务的最小单元,当Task执行失败的时候spark会重新计算,这里Task进行计算的地方就是读取checkpoint的入口。我们可以看一下
ShuffleMapTask里的计算方法runTask,如下override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = { // Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable. val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis() val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime } else 0L val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance() val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])]( ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) _executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime _executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime } else 0L var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null try { val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context) writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]]) writer.stop(success = true).get } catch { case e: Exception => try { if (writer != null) { writer.stop(success = false) } } catch { case e: Exception => log.debug("Could not stop writer", e) } throw e } }
这是spark真正调用计算方法的逻辑
runTask调用rdd.iterator()去计算该 rdd 的 partition 的,我们来看RDD的iterator()/** * Internal method to this RDD; will read from cache if applicable, or otherwise compute it. * This should ''not'' be called by users directly, but is available for implementors of custom * subclasses of RDD. */ final def iterator(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { if (storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) { getOrCompute(split, context) } else { computeOrReadCheckpoint(split, context) } }
- 我们知道Task是spark运行任务的最小单元,当Task执行失败的时候spark会重新计算,这里Task进行计算的地方就是读取checkpoint的入口。我们可以看一下
-
- 这里会继续调用
computeOrReadCheckpoint,我们看该方法/** * Compute an RDD partition or read it from a checkpoint if the RDD is checkpointing. */ private[spark] def computeOrReadCheckpoint(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { if (isCheckpointedAndMaterialized) { firstParent[T].iterator(split, context) } else { compute(split, context) } }
当调用rdd.iterator()去计算该 rdd 的 partition 的时候,会调用computeOrReadCheckpoint(split: Partition)去查看该 rdd 是否被 checkpoint 过了,如果是,就调用该 rdd 的 parent rdd 的 iterator() 也就是 CheckpointRDD.iterator(),否则直接调用该RDD的compute, 那么我们就跟进CheckpointRDD的compute/** * Read the content of the checkpoint file associated with the given partition. */ override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { val file = new Path(checkpointPath, ReliableCheckpointRDD.checkpointFileName(split.index)) ReliableCheckpointRDD.readCheckpointFile(file, broadcastedConf, context) }
这里就两行代码,意思是从Path上读取我们的CheckPoint数据,看一下
readCheckpointFile/** * Read the content of the specified checkpoint file. */ def readCheckpointFile[T]( path: Path, broadcastedConf: Broadcast[SerializableConfiguration], context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { val env = SparkEnv.get val fs = path.getFileSystem(broadcastedConf.value.value) val bufferSize = env.conf.getInt("spark.buffer.size", 65536) val fileInputStream = fs.open(path, bufferSize) val serializer = env.serializer.newInstance() val deserializeStream = serializer.deserializeStream(fileInputStream) // Register an on-task-completion callback to close the input stream. context.addTaskCompletionListener(context => deserializeStream.close()) deserializeStream.asIterator.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]] }
CheckpointRDD负责读取文件系统上的文件,生成该 rdd 的 partition。这就解释了为什么要为调用了checkpoint的RDD 添加一个parent CheckpointRDD的原因。
到此,整个checkpoint的流程就结束了。
- 这里会继续调用
参考:https://www.coderfei.com/2018/02/11/spark-6-spark-rdd-cache-checkpoint.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/653ebabc8f87