Android Apk加壳技术实战详解
前言
前几天面试了一家信息加密相关的公司,经过两轮面试原以为坐等HR,结果还有一个实践测试ORZ…面试这么多家公司,真心觉得这家公司很特殊,尤其是那个逻辑测试…算了,不扯远了,走回正题。
面试官加我QQ后,扔来了链接:
Android的实践:APK加壳【1】初步方案实现详解
嗯…不会,没接触过!果然是信息加密的公司/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~ 此处省略∞个字。
结合文章内容,自己又百度了一些相关文章,其中以下面这篇文章源码的介绍是最详细,实现流程最为细致:
Android中的Apk的加固(加壳)原理解析和实现
然而实现起来又遇到诸多问题,上面两篇文章都是15年的,那个时候基本都使用的ADT环境开发,与现在的AS相比还是又很多区别的。比如:Apk加壳的关键dex文件,ADT编译后可以在工程的bin目录下轻松找到,然而翻遍AS的目录也没找到。而且百度到的文章都是的ADT环境实现的,而且90%都是一样的。
无奈又去看了一些类加载和dex文件相关的内容,如:Android动态加载Dex机制解析
然后摸石头过河,一步步尝试,终于完成目标。
由于时间原因,加之自身能力有限,所以对源码并没有十分的理解,只知道使用了动态加载+反射机制实现的。所以本文不对源码进行深入分析,主要讲解实践过程。
开发环境:Windows:Android Studio + IDEA
简介&原理
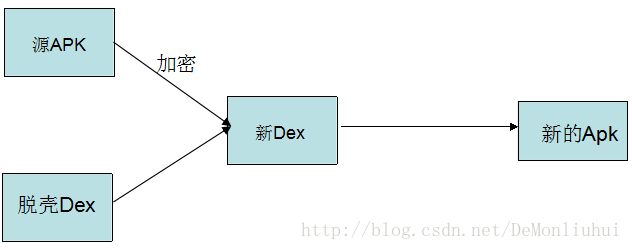
Apk加壳:就是通过给目标APK加一层保护程序,把需要保护的内容加密、隐藏起来,来防止反编译的一种方法。
所以我们在加壳过程中需要三个关键对象:
1、需要加密的Apk(源Apk,本文中的demo.apk)
2、壳程序Apk(负责解密Apk工作,本文中shell.apk)
3、加密工具(将源Apk进行加密和壳Dex合并成新的Dex,本文章的Java程序)
具体的原理及源码请参考上面提到的两篇文章。
实战步骤
1.源apk,demo程序
详细的代码请戳:https://github.com/DeMonLiu623/Shell/tree/master/Demo
为了让实例更有说服性,demo中的包含了:获取当前包名,广播监听网络状态变化,Glide框架显示网络图片(网络操作+图片显示)等功能。
网络图片链接如下:http://omuzv9mvf.bkt.clouddn.com/D.png
效果如下:
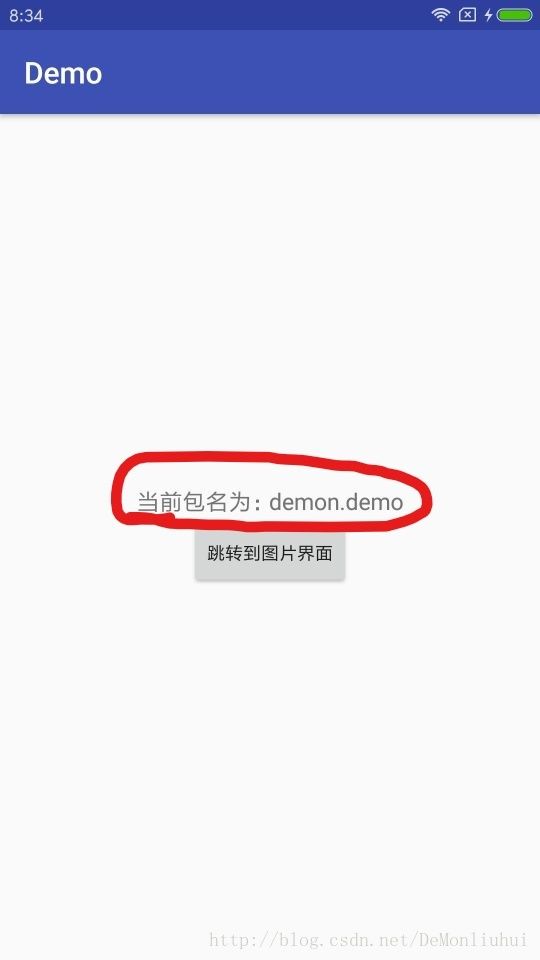

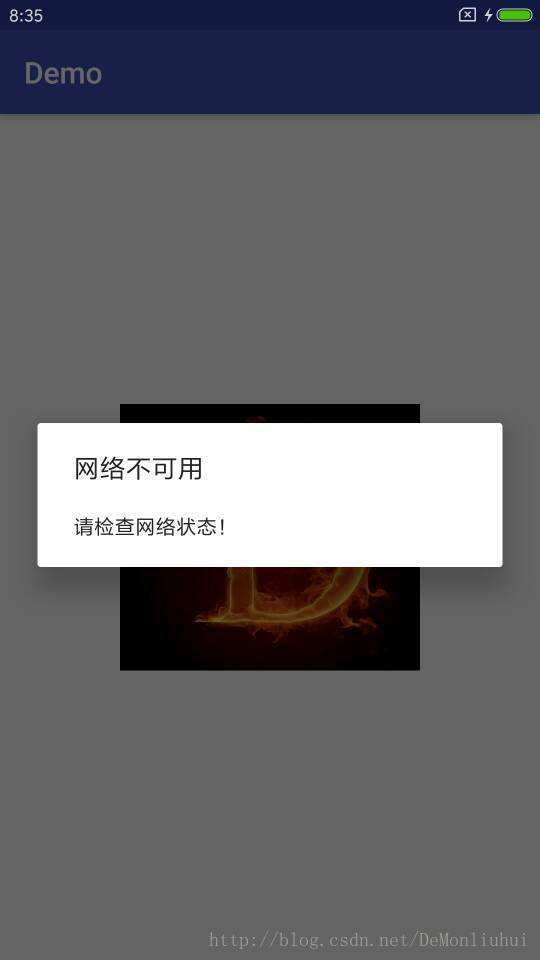
关键代码
demo代码比较简单,这里给出比较关键的Application和配置文件代码。
因为Application和配置文件代码对壳程序的配置有很关键的作用。
1.MyApplication
public class MyApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i("demo", "apk onCreate:" + this);
}
}2.AndroidManifest.xml
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="demon.demo">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<application
android:name=".MyApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
<activity android:name=".ImageActivity" />
application>
manifest>签名Apk
使用AS获取签名的Apk,注意此处的签名文件需要与下文保持完全的一致,否则可能会造成一些错误。
签名完毕后,复制apk到指定位置留用,并改名为demo.apk。
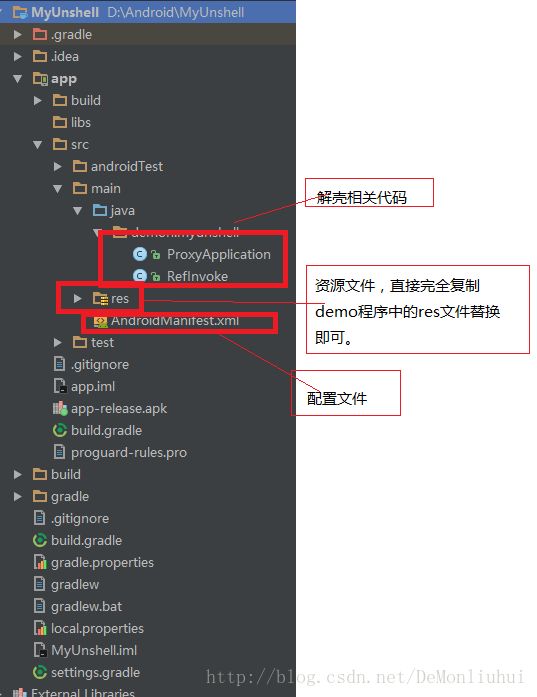
2.壳APk,解壳程序
详细的代码请戳:https://github.com/DeMonLiu623/Shell/tree/master/MyUnshell
工程目录结构如下:
关键代码
1.ProxyApplication.java
public class ProxyApplication extends Application{
private static final String appkey = "APPLICATION_CLASS_NAME";
private String apkFileName;
private String odexPath;
private String libPath;
//这是context 赋值
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
try {
//创建两个文件夹payload_odex,payload_lib 私有的,可写的文件目录
File odex = this.getDir("demo_odex", MODE_PRIVATE);
File libs = this.getDir("demo_lib", MODE_PRIVATE);
odexPath = odex.getAbsolutePath();
libPath = libs.getAbsolutePath();
apkFileName = odex.getAbsolutePath() + "/shelldemo.apk";
File dexFile = new File(apkFileName);
Log.i("demo", "apk size:"+dexFile.length());
if (!dexFile.exists())
{
dexFile.createNewFile(); //在payload_odex文件夹内,创建payload.apk
// 读取程序classes.dex文件
byte[] dexdata = this.readDexFileFromApk();
// 分离出解壳后的apk文件已用于动态加载
this.splitPayLoadFromDex(dexdata);
}
// 配置动态加载环境
Object currentActivityThread = RefInvoke.invokeStaticMethod(
"android.app.ActivityThread", "currentActivityThread",
new Class[] {}, new Object[] {});//获取主线程对象 http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/14223493
String packageName = this.getPackageName();//当前apk的包名
//下面两句不是太理解
ArrayMap mPackages = (ArrayMap) RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect(
"android.app.ActivityThread", currentActivityThread,
"mPackages");
WeakReference wr = (WeakReference) mPackages.get(packageName);
//创建被加壳apk的DexClassLoader对象 加载apk内的类和本地代码(c/c++代码)
DexClassLoader dLoader = new DexClassLoader(apkFileName, odexPath,
libPath, (ClassLoader) RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect(
"android.app.LoadedApk", wr.get(), "mClassLoader"));
//base.getClassLoader(); 是不是就等同于 (ClassLoader) RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect()? 有空验证下//?
//把当前进程的DexClassLoader 设置成了被加壳apk的DexClassLoader ----有点c++中进程环境的意思~~
RefInvoke.setFieldOjbect("android.app.LoadedApk", "mClassLoader",
wr.get(), dLoader);
Log.i("demo","classloader:"+dLoader);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.i("demo", "error:"+Log.getStackTraceString(e));
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
{
//loadResources(apkFileName);
Log.i("demo", "onCreate");
// 如果源应用配置有Appliction对象,则替换为源应用Applicaiton,以便不影响源程序逻辑。
String appClassName = null;
try {
ApplicationInfo ai = this.getPackageManager()
.getApplicationInfo(this.getPackageName(),
PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
Bundle bundle = ai.metaData;
if (bundle != null && bundle.containsKey("APPLICATION_CLASS_NAME")) {
appClassName = bundle.getString("APPLICATION_CLASS_NAME");//className 是配置在xml文件中的。
} else {
Log.i("demo", "have no application class name");
return;
}
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
Log.i("demo", "error:"+Log.getStackTraceString(e));
e.printStackTrace();
}
//有值的话调用该Applicaiton
Object currentActivityThread = RefInvoke.invokeStaticMethod(
"android.app.ActivityThread", "currentActivityThread",
new Class[] {}, new Object[] {});
Object mBoundApplication = RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect(
"android.app.ActivityThread", currentActivityThread,
"mBoundApplication");
Object loadedApkInfo = RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect(
"android.app.ActivityThread$AppBindData",
mBoundApplication, "info");
//把当前进程的mApplication 设置成了null
RefInvoke.setFieldOjbect("android.app.LoadedApk", "mApplication",
loadedApkInfo, null);
Object oldApplication = RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect(
"android.app.ActivityThread", currentActivityThread,
"mInitialApplication");
//http://www.codeceo.com/article/android-context.html
ArrayList mAllApplications = (ArrayList) RefInvoke
.getFieldOjbect("android.app.ActivityThread",
currentActivityThread, "mAllApplications");
mAllApplications.remove(oldApplication);//删除oldApplication
ApplicationInfo appinfo_In_LoadedApk = (ApplicationInfo) RefInvoke
.getFieldOjbect("android.app.LoadedApk", loadedApkInfo,
"mApplicationInfo");
ApplicationInfo appinfo_In_AppBindData = (ApplicationInfo) RefInvoke
.getFieldOjbect("android.app.ActivityThread$AppBindData",
mBoundApplication, "appInfo");
appinfo_In_LoadedApk.className = appClassName;
appinfo_In_AppBindData.className = appClassName;
Application app = (Application) RefInvoke.invokeMethod(
"android.app.LoadedApk", "makeApplication", loadedApkInfo,
new Class[] { boolean.class, Instrumentation.class },
new Object[] { false, null });//执行 makeApplication(false,null)
RefInvoke.setFieldOjbect("android.app.ActivityThread",
"mInitialApplication", currentActivityThread, app);
ArrayMap mProviderMap = (ArrayMap) RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect(
"android.app.ActivityThread", currentActivityThread,
"mProviderMap");
Iterator it = mProviderMap.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Object providerClientRecord = it.next();
Object localProvider = RefInvoke.getFieldOjbect(
"android.app.ActivityThread$ProviderClientRecord",
providerClientRecord, "mLocalProvider");
RefInvoke.setFieldOjbect("android.content.ContentProvider",
"mContext", localProvider, app);
}
Log.i("demo", "app:"+app);
app.onCreate();
}
}
/**
* 释放被加壳的apk文件,so文件
* @param
* @throws IOException
*/
private void splitPayLoadFromDex(byte[] apkdata) throws IOException {
int ablen = apkdata.length;
//取被加壳apk的长度 这里的长度取值,对应加壳时长度的赋值都可以做些简化
byte[] dexlen = new byte[4];
System.arraycopy(apkdata, ablen - 4, dexlen, 0, 4);
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(dexlen);
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(bais);
int readInt = in.readInt();
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(readInt));
byte[] newdex = new byte[readInt];
//把被加壳apk内容拷贝到newdex中
System.arraycopy(apkdata, ablen - 4 - readInt, newdex, 0, readInt);
//这里应该加上对于apk的解密操作,若加壳是加密处理的话
//?
//对源程序Apk进行解密
newdex = decrypt(newdex);
//写入apk文件
File file = new File(apkFileName);
try {
FileOutputStream localFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
localFileOutputStream.write(newdex);
localFileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException localIOException) {
throw new RuntimeException(localIOException);
}
//分析被加壳的apk文件
ZipInputStream localZipInputStream = new ZipInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)));
while (true) {
ZipEntry localZipEntry = localZipInputStream.getNextEntry();//不了解这个是否也遍历子目录,看样子应该是遍历的
if (localZipEntry == null) {
localZipInputStream.close();
break;
}
//取出被加壳apk用到的so文件,放到 libPath中(data/data/包名/payload_lib)
String name = localZipEntry.getName();
if (name.startsWith("lib/") && name.endsWith(".so")) {
File storeFile = new File(libPath + "/"
+ name.substring(name.lastIndexOf('/')));
storeFile.createNewFile();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(storeFile);
byte[] arrayOfByte = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
int i = localZipInputStream.read(arrayOfByte);
if (i == -1)
break;
fos.write(arrayOfByte, 0, i);
}
fos.flush();
fos.close();
}
localZipInputStream.closeEntry();
}
localZipInputStream.close();
}
/**
* 从apk包里面获取dex文件内容(byte)
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
private byte[] readDexFileFromApk() throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream dexByteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ZipInputStream localZipInputStream = new ZipInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(
this.getApplicationInfo().sourceDir)));
while (true) {
ZipEntry localZipEntry = localZipInputStream.getNextEntry();
if (localZipEntry == null) {
localZipInputStream.close();
break;
}
if (localZipEntry.getName().equals("classes.dex")) {
byte[] arrayOfByte = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
int i = localZipInputStream.read(arrayOfByte);
if (i == -1)
break;
dexByteArrayOutputStream.write(arrayOfByte, 0, i);
}
}
localZipInputStream.closeEntry();
}
localZipInputStream.close();
return dexByteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
}
// //直接返回数据,读者可以添加自己解密方法
private byte[] decrypt(byte[] srcdata) {
for(int i=0;ibyte)(0xFF ^ srcdata[i]);
}
return srcdata;
}
//以下是加载资源
protected AssetManager mAssetManager;//资源管理器
protected Resources mResources;//资源
protected Theme mTheme;//主题
protected void loadResources(String dexPath) {
try {
AssetManager assetManager = AssetManager.class.newInstance();
Method addAssetPath = assetManager.getClass().getMethod("addAssetPath", String.class);
addAssetPath.invoke(assetManager, dexPath);
mAssetManager = assetManager;
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.i("inject", "loadResource error:"+Log.getStackTraceString(e));
e.printStackTrace();
}
Resources superRes = super.getResources();
superRes.getDisplayMetrics();
superRes.getConfiguration();
mResources = new Resources(mAssetManager, superRes.getDisplayMetrics(),superRes.getConfiguration());
mTheme = mResources.newTheme();
mTheme.setTo(super.getTheme());
}
@Override
public AssetManager getAssets() {
return mAssetManager == null ? super.getAssets() : mAssetManager;
}
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
return mResources == null ? super.getResources() : mResources;
}
@Override
public Theme getTheme() {
return mTheme == null ? super.getTheme() : mTheme;
}
}
2.RefInvoke.java
public class RefInvoke {
/**
* 反射执行类的静态函数(public)
* @param class_name 类名
* @param method_name 函数名
* @param pareTyple 函数的参数类型
* @param pareVaules 调用函数时传入的参数
* @return
*/
public static Object invokeStaticMethod(String class_name, String method_name, Class[] pareTyple, Object[] pareVaules){
try {
Class obj_class = Class.forName(class_name);
Method method = obj_class.getMethod(method_name,pareTyple);
return method.invoke(null, pareVaules);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 反射执行类的函数(public)
* @param class_name
* @param method_name
* @param obj
* @param pareTyple
* @param pareVaules
* @return
*/
public static Object invokeMethod(String class_name, String method_name, Object obj ,Class[] pareTyple, Object[] pareVaules){
try {
Class obj_class = Class.forName(class_name);
Method method = obj_class.getMethod(method_name,pareTyple);
return method.invoke(obj, pareVaules);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 反射得到类的属性(包括私有和保护)
* @param class_name
* @param obj
* @param filedName
* @return
*/
public static Object getFieldOjbect(String class_name,Object obj, String filedName){
try {
Class obj_class = Class.forName(class_name);
Field field = obj_class.getDeclaredField(filedName);
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(obj);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 反射得到类的静态属性(包括私有和保护)
* @param class_name
* @param filedName
* @return
*/
public static Object getStaticFieldOjbect(String class_name, String filedName){
try {
Class obj_class = Class.forName(class_name);
Field field = obj_class.getDeclaredField(filedName);
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(null);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 设置类的属性(包括私有和保护)
* @param classname
* @param filedName
* @param obj
* @param filedVaule
*/
public static void setFieldOjbect(String classname, String filedName, Object obj, Object filedVaule){
try {
Class obj_class = Class.forName(classname);
Field field = obj_class.getDeclaredField(filedName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, filedVaule);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 设置类的静态属性(包括私有和保护)
* @param class_name
* @param filedName
* @param filedVaule
*/
public static void setStaticOjbect(String class_name, String filedName, Object filedVaule){
try {
Class obj_class = Class.forName(class_name);
Field field = obj_class.getDeclaredField(filedName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(null, filedVaule);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.AndroidManifest.xml
这里要注意添加源Apk的权限,组件,组件必须使用完整的包名。
使用meta-data配置源Apk中的MyApplication,也要使用完整包名。
注意对比两个配置文件的区别。
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="demon.myunshell">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<application
android:name=".ProxyApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<meta-data
android:name="APPLICATION_CLASS_NAME"
android:value="demon.demo.MyApplication" />
<activity android:name="demon.demo.MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
<activity android:name="demon.demo.ImageActivity" />
application>
manifest>签名Apk
使用AS获取签名的Apk,注意要使用相同的签名文件。
签名完毕后,复制apk到指定位置留用,并改名为shell.apk。
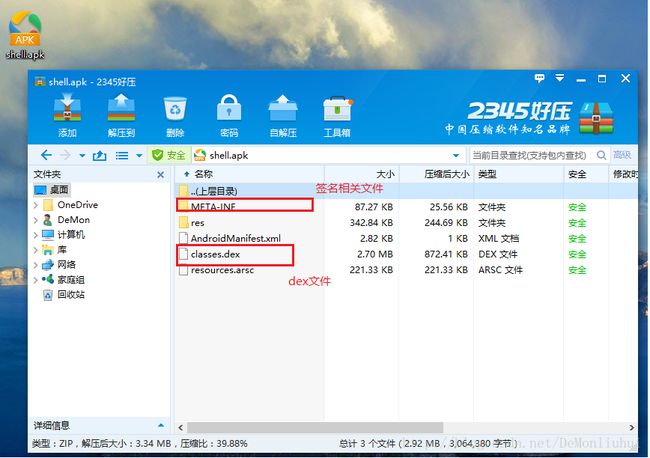
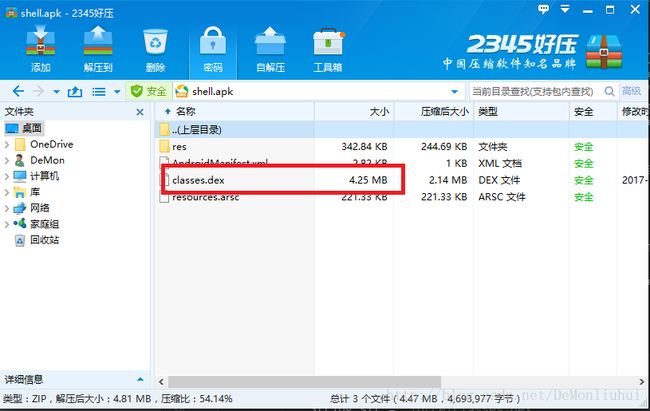
获取dex文件
这一步尤为关键。
经过了解,我们可以通过解压Apk的方式获取到dex文件。如下图:
复制其中的dex文件到指定位置留用,并更名为shell.dex(主要是为了区分加密后合成的新的dex文件)
3.加密工具,Java程序
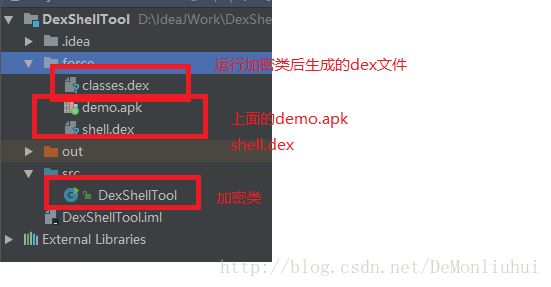
详细的代码请戳:https://github.com/DeMonLiu623/Shell/tree/master/DexShellTool
新建java程序,目录结构如下:
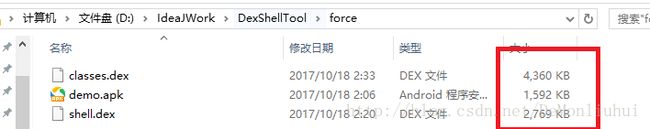
工程下新建force文件夹,将demo.apk,shell.dex复制到里面去,运行如下代码,生成新的dex文件,即classes.dex:
/**
* Created by DeMon on 2017/10/17.
*/
public class DexShellTool {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
File payloadSrcFile = new File("force/demo.apk"); //需要加壳的程序
System.out.println("apk size:"+payloadSrcFile.length());
File unShellDexFile = new File("force/shell.dex"); //解壳dex
byte[] payloadArray = encrpt(readFileBytes(payloadSrcFile));//以二进制形式读出apk,并进行加密处理//对源Apk进行加密操作
byte[] unShellDexArray = readFileBytes(unShellDexFile);//以二进制形式读出dex
int payloadLen = payloadArray.length;
int unShellDexLen = unShellDexArray.length;
int totalLen = payloadLen + unShellDexLen +4;//多出4字节是存放长度的。
byte[] newdex = new byte[totalLen]; // 申请了新的长度
//添加解壳代码
System.arraycopy(unShellDexArray, 0, newdex, 0, unShellDexLen);//先拷贝dex内容
//添加加密后的解壳数据
System.arraycopy(payloadArray, 0, newdex, unShellDexLen, payloadLen);//再在dex内容后面拷贝apk的内容
//添加解壳数据长度
System.arraycopy(intToByte(payloadLen), 0, newdex, totalLen-4, 4);//最后4为长度
//修改DEX file size文件头
fixFileSizeHeader(newdex);
//修改DEX SHA1 文件头
fixSHA1Header(newdex);
//修改DEX CheckSum文件头
fixCheckSumHeader(newdex);
String str = "force/classes.dex";
File file = new File(str);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileOutputStream localFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(str);
localFileOutputStream.write(newdex);
localFileOutputStream.flush();
localFileOutputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//直接返回数据,读者可以添加自己加密方法
private static byte[] encrpt(byte[] srcdata){
for(int i = 0;ibyte)(0xFF ^ srcdata[i]);
}
return srcdata;
}
/**
* 修改dex头,CheckSum 校验码
* @param dexBytes
*/
private static void fixCheckSumHeader(byte[] dexBytes) {
Adler32 adler = new Adler32();
adler.update(dexBytes, 12, dexBytes.length - 12);//从12到文件末尾计算校验码
long value = adler.getValue();
int va = (int) value;
byte[] newcs = intToByte(va);
//高位在前,低位在前掉个个
byte[] recs = new byte[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
recs[i] = newcs[newcs.length - 1 - i];
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(newcs[i]));
}
System.arraycopy(recs, 0, dexBytes, 8, 4);//效验码赋值(8-11)
System.out.println(Long.toHexString(value));
System.out.println();
}
/**
* int 转byte[]
* @param number
* @return
*/
public static byte[] intToByte(int number) {
byte[] b = new byte[4];
for (int i = 3; i >= 0; i--) {
b[i] = (byte) (number % 256);
number >>= 8;
}
return b;
}
/**
* 修改dex头 sha1值
* @param dexBytes
* @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException
*/
private static void fixSHA1Header(byte[] dexBytes)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
md.update(dexBytes, 32, dexBytes.length - 32);//从32为到结束计算sha--1
byte[] newdt = md.digest();
System.arraycopy(newdt, 0, dexBytes, 12, 20);//修改sha-1值(12-31)
//输出sha-1值,可有可无
String hexstr = "";
for (int i = 0; i < newdt.length; i++) {
hexstr += Integer.toString((newdt[i] & 0xff) + 0x100, 16)
.substring(1);
}
System.out.println(hexstr);
}
/**
* 修改dex头 file_size值
* @param dexBytes
*/
private static void fixFileSizeHeader(byte[] dexBytes) {
//新文件长度
byte[] newfs = intToByte(dexBytes.length);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(dexBytes.length));
byte[] refs = new byte[4];
//高位在前,低位在前掉个个
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
refs[i] = newfs[newfs.length - 1 - i];
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(newfs[i]));
}
System.arraycopy(refs, 0, dexBytes, 32, 4);//修改(32-35)
}
/**
* 以二进制读出文件内容
* @param file
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
private static byte[] readFileBytes(File file) throws IOException {
byte[] arrayOfByte = new byte[1024];
ByteArrayOutputStream localByteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
while (true) {
int i = fis.read(arrayOfByte);
if (i != -1) {
localByteArrayOutputStream.write(arrayOfByte, 0, i);
} else {
return localByteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
}
}
}
}
查看如上图的force文件夹,如果加密合并成功后classes.dex的大小几乎等于demo.apk+shell.dex。
4.重新签名Apk
解压软件打开前面的shell.apk,将上面得到的新classes.dex复制替换原来的classes.dex。
因为dex文件改变所以我们要重新签名,即要删除原来的签名文件,得到新的shell.apk。
完成后,如下图:
注意观察classes.dex的大小,判断是否复制成功。
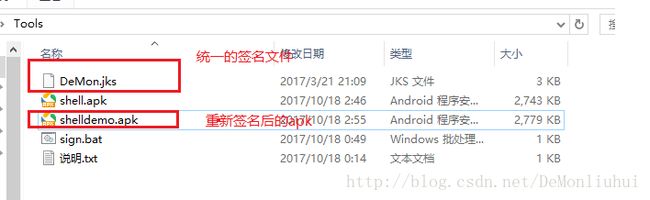
对于Apk的重新签名,为了方便我们新建一个Tools文件夹(https://github.com/DeMonLiu623/Shell/tree/master/Tools )。
将前面的签名文件,shell.apk复制进去。
签名命令太长不好记,我们新建sign.bat文件,添加如下内容,注意使用该命令系统必须配置Java环境变量,可根据自身情况进行修改,方便下次使用:
jarsigner -verbose -keystore DeMon.jks -storepass 123456 -keypass 123456 -sigfile CERT -digestalg SHA1 -sigalg MD5withRSA -signedjar shelldemo.apk shell.apk key上面命令说明:
jarsigner -verbose -keystore 签名文件 -storepass 密码 -keypass alias的密码 -sigfile CERT -digestalg SHA1 -sigalg MD5withRSA 签名后的文件 签名前的apk alias名称双击运行sign.bat文件,成功签名Tools文件会新增一个shelldemo.apk,会比shell.apk稍大,大概就是生成的签名文件的大小。
正确签名后的文件夹内容如下:
shelldemo.apk就是成功加壳后的apk,可以安装运行。
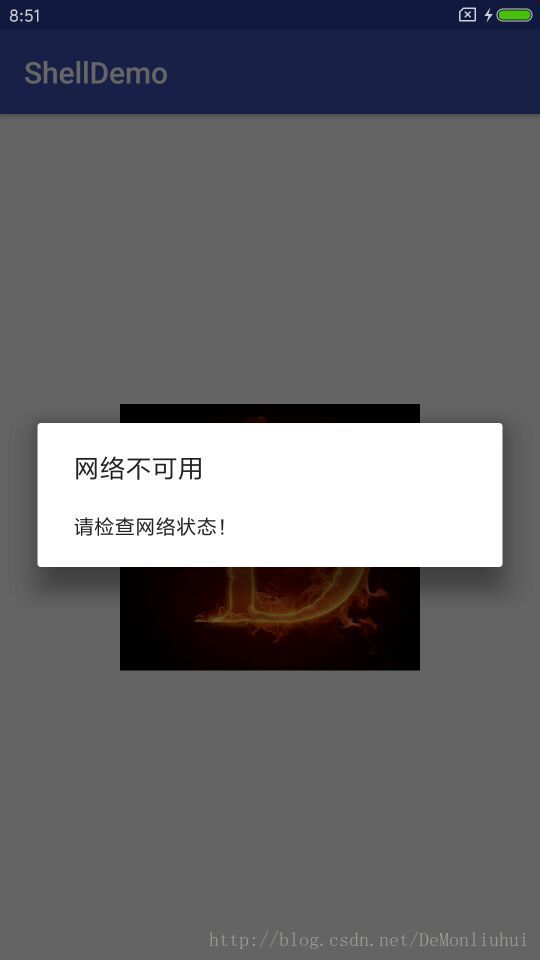
5.效果图
安装运行效果如下图:
注意对比demo.apk的效果图,除了标题和包名与不一致外,功能上完全相同,即符合预期。Apk加壳成功!
总结
1、加壳程序
任务:对源程序Apk进行加密,合并脱壳程序的Dex文件 ,然后输入一个加壳之后的Dex文件
语言:任何语言都可以,不限于Java语言
技术点:对Dex文件格式的解析
2、解壳程序
任务:获取源程序Apk,进行解密,然后动态加载进来,运行程序
语言:Android项目(Java)
技术点:如何从Apk中获取Dex文件,动态加载Apk,使用反射运行Application。
缺点:
1. 工作复杂的,涉及到的技术点多的。
2. Apk体积变大,尤其是res文件成倍增长。
3. 第一次安装启动需要等待加载时间较长,用户体验不好。
GitHub地址
https://github.com/DeMonLiu623/Shell