用BlockBoundQueue和c++11实现多线程生产者消费者问题
最近在读到陈硕的《linux多线程服务端编程》这书时,发现了两个特别好用的模板类 : BlockQueue和BlockBoundQueue,用来实现多线程中的生产者消费者问题是特别方便的。但是其源码中用到boost库,所以在这里我稍微修改下,实现如下。
这里只写出BlockBoundQueue,读者可自行写出BlockQueue
// file : blockBoundQueue.h
#ifndef YANG_BLOCKBOUNDQUEUE
#define YANG_BLOCKBOUNDQUEUE
#include 分析上面代码,首先std::queue容器并没有提供full()这个成员函数,所以我们要自己维护一个size_t type 的变量count_,并初始化为0 。其次,我们要禁用掉拷贝构造和赋值函数,只保留构造函数即可。最重要的两个成员函数是push()和get(),在这里每次进入这两个函数之后,先加锁,这里我们用到了RAII的技法来保证我们的加锁操作是异常安全的,并且通过两个条件变量notEmpty 和 notFull 的配合,实现了线程安全的出队和入队操作。
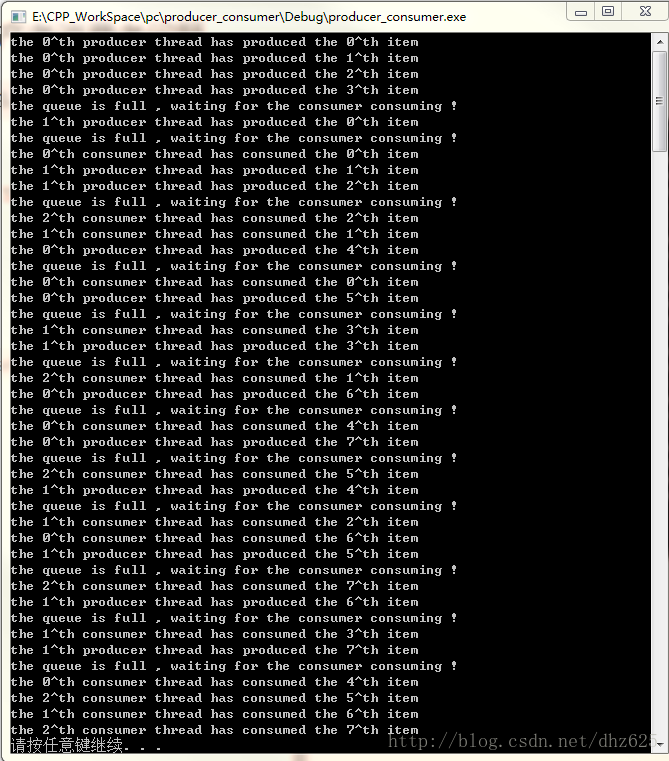
下面我们来实现下,篇幅的原因,直接上多生产者多消费者模式,因为其他的几种都是它的特列。
// file : main.cpp
#include 总结 : 利用BlockBoundQueue可以很方便的实现生产者消费者模式,并且其本身实现起来简洁优雅,我们应该学会使用。
参考资料:
Linux多线程服务端编程 陈硕著
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/
https://baptiste-wicht.com/posts/2012/04/c11-concurrency-tutorial-advanced-locking-and-condition-variables.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/haippy/p/3236136.html